Is air present everywhere around us?
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Is Air Present Everywhere Around Us?

Is Air Present Everywhere Around Us?

Air is present all around us. We cannot see the air around us but we can feel its presence when the leaves rustle or branches sway.
Importance of Air
- We need air for breathing.
- All living beings need air for breathing.
- We need air to burn something.
- Life is possible on earth because of air.
The invisible gaseous medium around us, mainly constituted by oxygen and nitrogen is known as air. It is through this air that we are able to carry out the process of respiration. Air is transparent and colourless. It occupies space and is present all around us.
Atmosphere: The thin blanket of air surrounding the surface of the Earth is called the atmosphere.
The atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers on the basis of variations in temperature that changes due to increasing altitude. Air gets scant as we move up in the atmosphere. These are as follows:
- Troposphere: This is the first layer to the atmosphere which is nearest to the surface and is responsible for weather conditions. The troposphere itself is said to contain about more than 75% of the atmosphere!
- Stratosphere: This is the layer just above the troposphere which contains the ozone layer and where the aeroplanes fly and is also home to most of the clouds!
- Mesosphere: This is the third and the coldest layer of our atmosphere and extends to a good 80 km above the surface of the Earth.
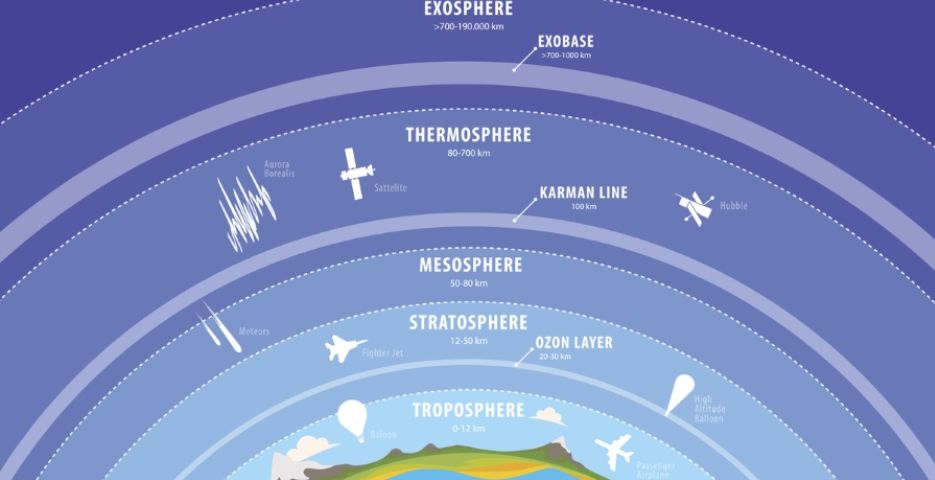
- Thermosphere: This is the fourth and one of the hottest layers of Earth where temperatures go to a 1500o This is where the space shuttles go to study Earth from space! The air in this layer is very thin and about 99.9% of the atmosphere is said to lie below this particular layer.
- Exosphere: This is the outermost layer of the atmosphere where molecules and atoms escape into space. Beginning at 480 km above the Earth, this layer then extends into the space.
What is air made up of?
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
What Is Air Made Up of?
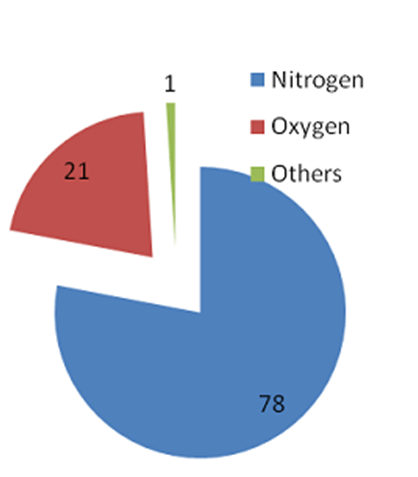
Air is a mixture of different gases and particles; oxygen, water vapour, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, dust and smoke.
- Air is not one substance but is a mixture.
- Air is a mixture of some gases, water vapour and dust particles.
- The gases in the air are mainly nitrogen, oxygen, a small amount of carbon dioxide and some other gases.
Water vapours

Air contains water vapours.
- When air comes in contact with a cool surface, it gets cooled and fog appears.
- The presence of water vapour in the air is important for the water cycle in nature.
Dust particles
Air contains dust particles.
- The presence of dust particles in air varies from place to place and time to time.
Oxygen
- The component of air that supports burning is called oxygen.
- Oxygen is necessary for the survival of all living beings. It is required in respiration.
- Percentage of oxygen in the air is around 20.95%.
Nitrogen
- The major part of the air is nitrogen. It takes up four-fifth of the space (be around 78.11%) that air fills.
- Nitrogen does not support burning.
Carbon dioxide
- Carbon dioxide makes up a small component (0.03%) of air around us.
- It causes a feeling of suffocation.
- All materials, when they burn, consume oxygen and produce carbon dioxide.
- It is also produced along with water vapour during respiration.
- Plants need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and to live.
Atmosphere
- Our earth is surrounded by air in the form of a thin layer. This thin layer is called the atmosphere.
- The atmosphere extends up to several kilometres.
- The air becomes thinner and thinner as we go high up from the surface of the earth.
- The atmosphere is quite active due to the movement of air, concerning the earth.
- The processes like cloud formation, thundering, rain etc., occur in the atmosphere.
Constituents of Air
Air is a mixture of a number of gases and some other particles such as:
- Water Vapour: Air contains water vapour which helps maintain the water cycle. When air comes in contact with cold surfaces, it is these vapours that turn into or condense into droplets of water. The amount of water vapor in the air from place to place and time to time. At a normal 30°C for instance can contain say up to 4% of water vapour.
- Oxygen: It is the oxygen in the air that helps humans and animals carry out the respiration process. Oxygen is also required for fire to keep burning. If we were to keep an inverted tumbler covering a burning candle, the candle will go off in a few seconds because of the lack of oxygen-containing air due to the tumbler. Dry air is said contain about 21% of oxygen.
- Nitrogen: Dry air is said to contain about 78% of nitrogen. This component of air helps plants in their growth process.
- Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide is a very small (only 0.04%) component of air and is a byproduct of respiration by humans and animals. Fire also uses up oxygen to burn and then produces carbon dioxide and a few other gases upon burning. This is why we feel suffocated if there is something burning inside a room. This happens due to an excess of carbon dioxide as the fire continues to burn in the room, choking out oxygen in the air.
- Dust and Smoke: Smoke is another component given out when fire burns. It is very harmful and adds fine dust particles and a few other gases to the air. This is why industries use long chimneys in order to release this smoke in the air. But as we know this act is what contributes to air pollution in the environment.
Air also contains very fine dust particles which can be seen when a beam of light enters a dark room. The tiny particles flying around in the beam are actually these dust particles. It is hence advised by our elders to breathe only through our nose and not our mouths so that the fine hair and mucus in the nose is able to filter out these dust particles so that we don’t inhale them and harm ourselves.
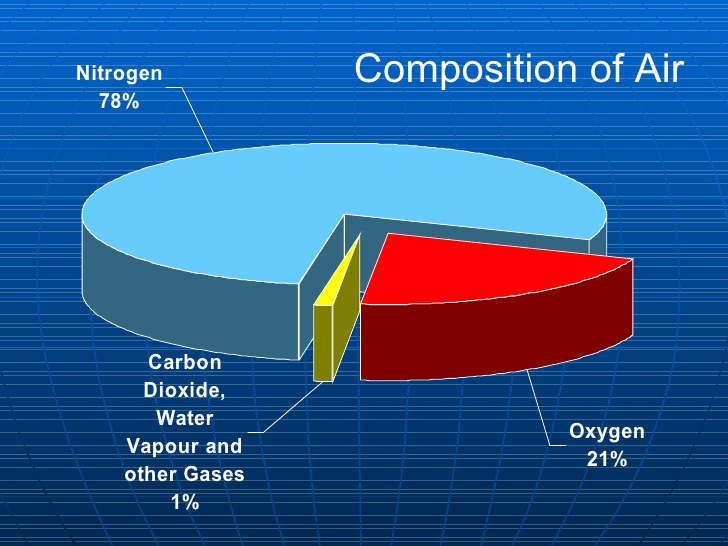
The composition of the components of air
As we can see from the Figure above, Oxygen and nitrogen together make up 99% of air while the other components come up to a mere 1% of all air in our environment.
Availability of Oxygen in Water and Soil
It is often asked how animals under the soil and in water are able to breathe. The answer is that both soil and water have air dissolved in them.
- When we heat or boil water, we often notice that bubbles start to form. These bubbles are in fact, an indication that air molecules are present in the water. When water is heated, the air dissolved in it escapes first followed by water itself getting converted into vapour. This is how animals living underwater are able to respire.
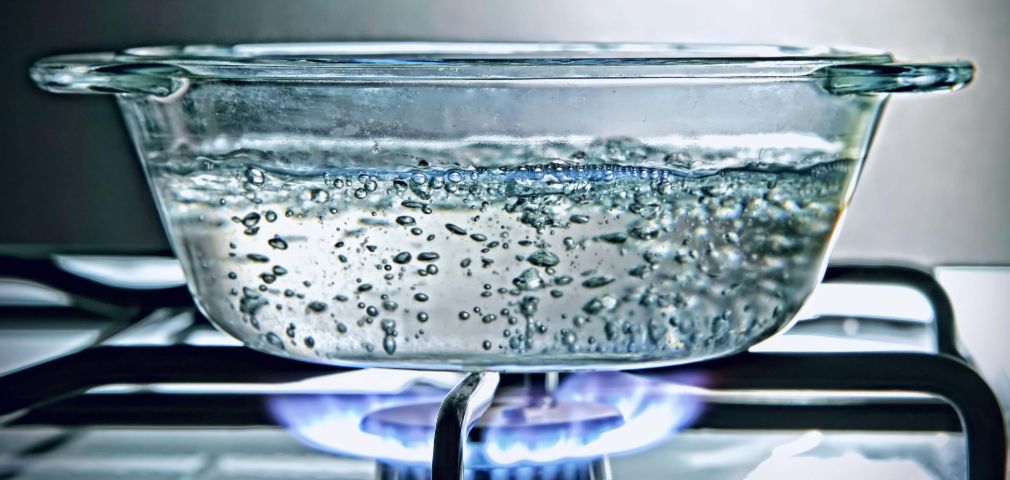

Figure 3 Air bubbles can be seen when water is heated
- To see the presence of water in the soil, we take a small lump of it in a beaker and add water to it. We see bubbles coming out of it which as we discussed, is proof of the existence of air molecules in the soil. As water is added, it displaces the water molecules in the soil which we see in the form of bubbles. Animals make use of this air to breathe under the soil. Some animals make holes and burrows in the soil to help make pathways for air to enter the soil. When it rains heavily, earthworms and other animals come out of the soil because these pathways get blocked by the water and they need to come outside to find the air to breathe.
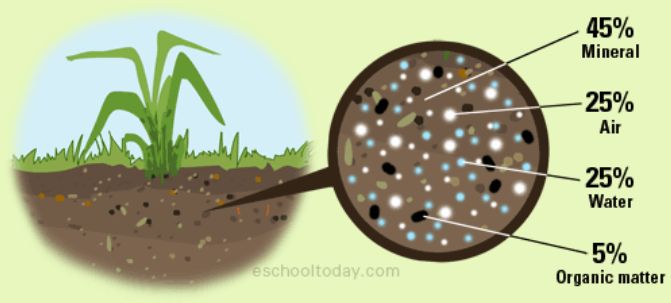
Figure 4 Air particles present in soil
How does oxygen become available to animals and plants living in water and soil?
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
How Does Oxygen Become Available to Animals and Plants Living in Water and Soil?
In Plants:
Plants have tiny pores called stomata, found on the underside of a leaf.
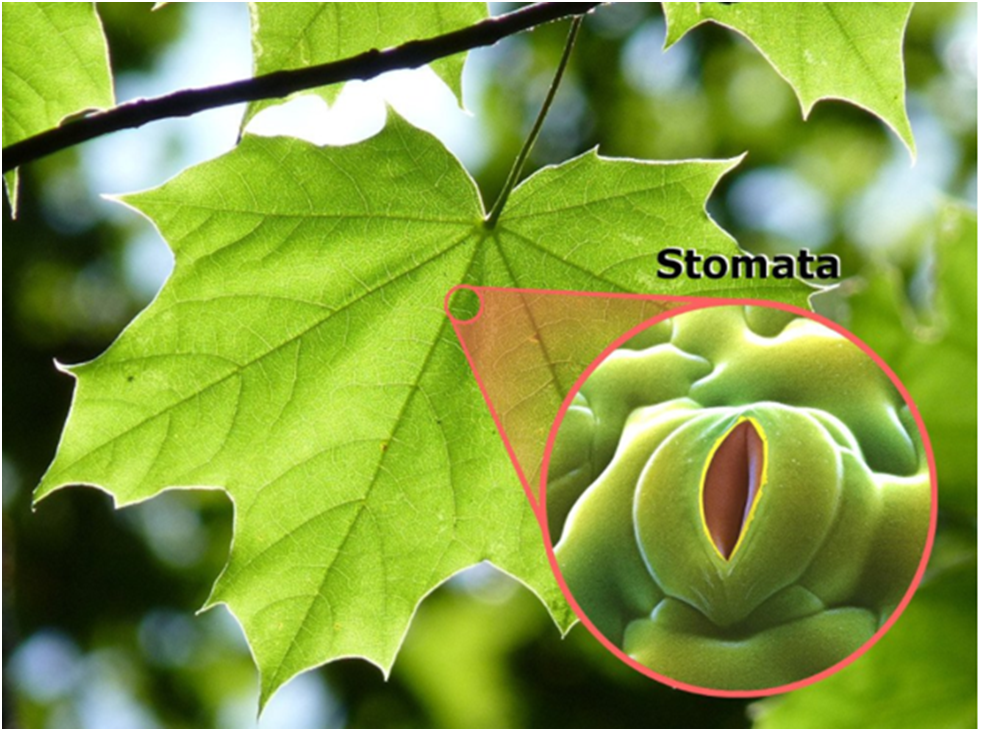
Air containing carbon dioxide and oxygen enters the plant through these openings where it gets used in photosynthesis and respiration.
In Animals:
All animals need to respire, be it a cockroach, a fish, or an elephant. It is just that they use different organs and mechanisms for respiration.
In Aquatic Animals and Plants:
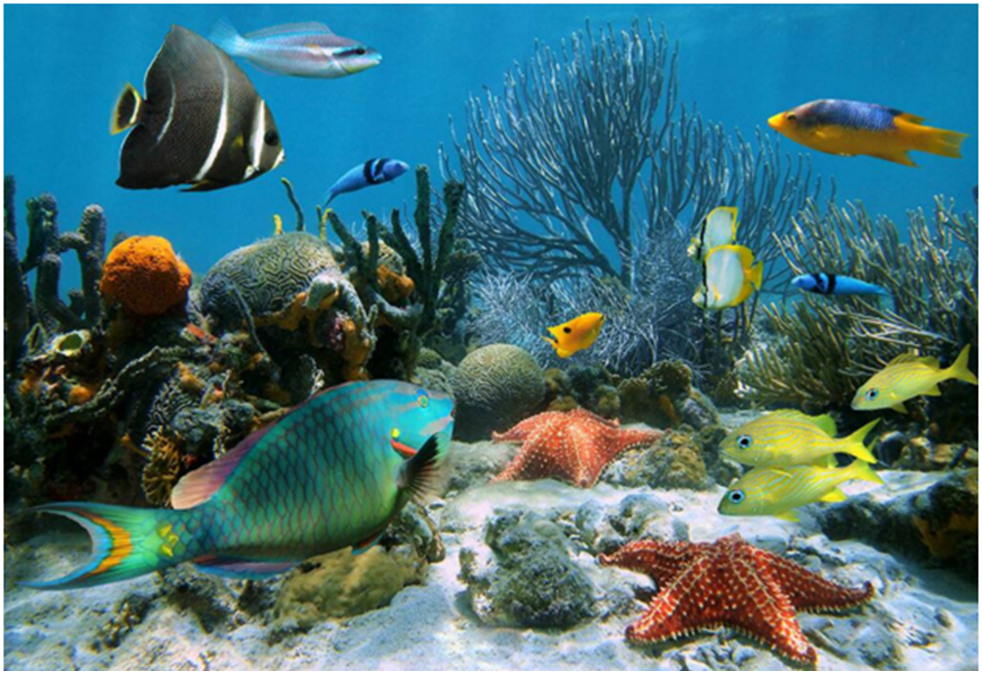

Most aquatic animals like fish, tadpoles, crabs, and shrimp have special organs for respiration called gills. Gills help to take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide. Some aquatic animals like dolphins and whales come to the surface of the water regularly to take in air, since they breathe with the help of the lungs. Aquatic plants like Hydrilla also breathe in oxygen dissolved in water through their stomata.
In Amphibians:
Amphibians like frogs, newts, and salamanders need breathing systems for both air and water. Crocodiles and alligators swim through the water with part of their snout above the water surface to breathe easily through nostrils.
In Birds:
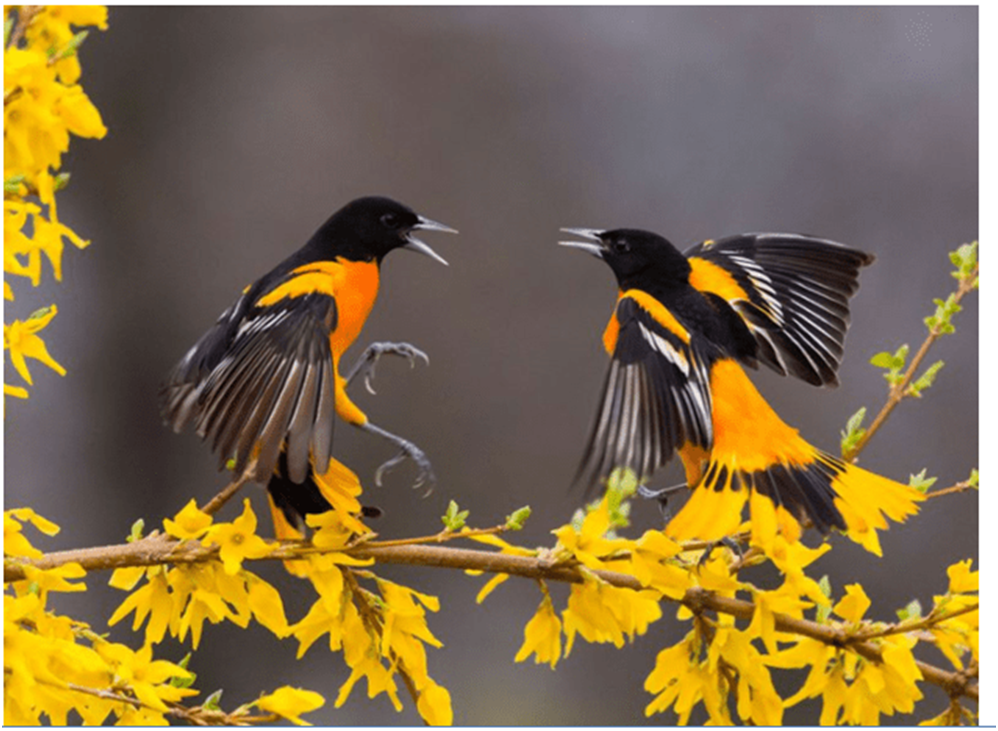

Birds have an efficient respiratory system as they need high levels of oxygen during flight. Birds have a pair of lungs with air sacs that remain open all the time so that air can easily pass through them.
In Mammals:
Most mammals breathe with the help of lungs. They take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide.
Balance of Oxygen in the Atmosphere
It is common knowledge that humans and animals can’t survive without plants because they produce oxygen via photosynthesis. The balance of oxygen in the environment is thus maintained through the respiratory processes of plants and animals.
The importance of Air
Air has a number of uses:
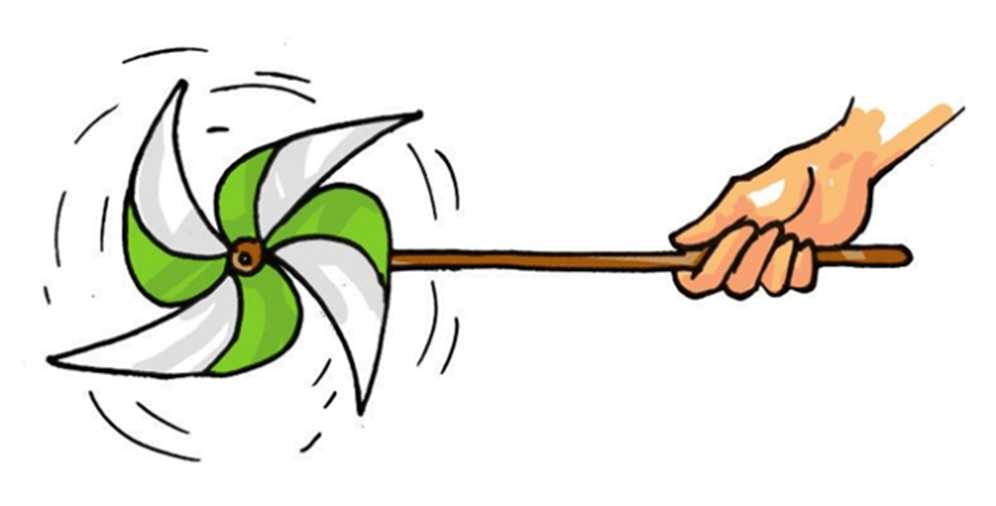
- The air which is in motion is known as wind. The wind is important for the rotation of windmills which help in drawing water from tube wells.
- They also help in running flour mills.
- Windmills are also used to produce electricity.
- Insects and birds are only able to fly because of the presence of air
- Boats, yachts, aeroplanes and parachutes also need air to sail and glide
- Air has a very important role to play in the water cycle as well.
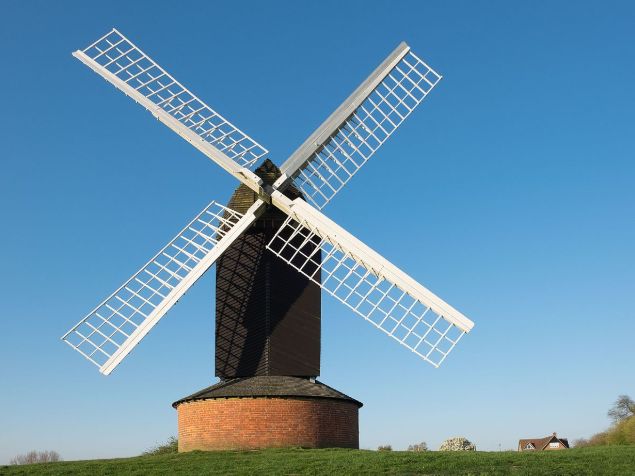

Figure 5 A windmill in action
- It also helps in distributing the pollen and seeds from flowers of various plants.

Figure 6 Air helps birds and insects fly
How is the oxygen in the atmosphere replaced?
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
How Is the Oxygen in the Atmosphere Replaced?
- Organisms usually come together where each benefits from the other.
- We get oxygen and other products from plants and they get not only carbon dioxide but other advantages from us.
- This is in the form of a cycle. Respiration and photosynthesis lead to the recycling of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the environment.
Summary
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Summary
Conclusion:
- All living organisms need air to survive. Air cannot be seen but can be felt when it moves.
- Air is a mixture of several gases.
- Oxygen is needed for respiration. Carbon dioxide is given out as a by-product after respiration.
- Insects take in air with the help of tiny holes in their bodies called spiracles; earthworms breathe through their skin, which is kept moist with the help of a substance called mucus.
- Some aquatic animals like whales and dolphins as well as mammals breathe with the help of lungs.
- Amphibians like frogs breathe with the help of lungs, when on land. In water, these animals breathe with the help of their moist skin.
- Birds breathe through lungs and air sacs that are open all the time.
- There are several causes of air pollution: excessive burning of fuels like wood, coal, and petroleum, machines releasing gases, vehicles releasing smoke, and several types of harmful gases released by industries.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
