- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Rectilinear propagation of light :
Light travels in a straight line. In vacuum or air, light travels with the velocity of 3 × 108 m/s.
Examples of rectilinear propagation of light in everyday life :
(i) When the sunlight enters through a small hole in a dark room, it appears to travel in straight lines.
(ii) The light emitted by the head light of a scooter at night appears to travel in straight lines.
(iii) If we almost close our eyes and try to look towards a lighted bulb, it appears to give light in the form of straight lines, which travel in various direction.
Shadow
A shadow is a dark outline or image cast by an opaque object that blocks light coming from a source of light.

(a) The cause of formation of shadows is
Rectilinear propogation of light (light travels on straight lines)
(b) Essentials of a shadow:
(i) Source of light
(ii) Presence of opaque object in the path of light
(iii) Screen on which shadow is formed
(c) Location of a shadow:
Shadow fills the space between the opaque object and the screen. It is the volume and not area on the screen.
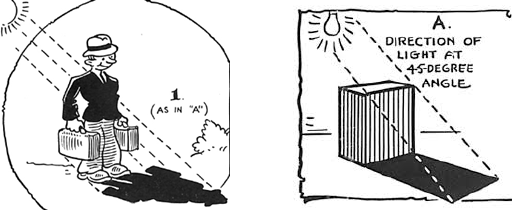
(d) Formation of shadow :
It is formed when light hits the opaque object which does not let the light pass through. Everywhere else around the opaque object, the light continues in a straight path until it bounces off the ground or wall behind the object. The wall or ground behind the opaque object is the screen. On this screen is a dark patch, or shadow, with the same outline as the object surrounded by light. The colour of the opaque object does not affect the colour of the shadow that is formed.
Shadow sticks :
A shadow stick is a vertical pole placed in the ground. Sunlight casts its shadow on to a level surface below.(e.g. a sheet of card or just level ground)

As the Sun moves from A to C, the shadow shortens and then lengthen accordingly
The length and position of the shadow then depends on both the time of year and the time of day. Local noon can be found from the time when the shadow is shortest. At this time the Sun is highest in the sky and crossing the meridian.
However, shadow sticks are not good clocks - the azimuth of the Sun’s shadow at a given time changes throughout the year with the Sun’s declination.
The shape, size and other characteristics of a shadow depend upon :
(i) Position and distance of the source of light with respect to the object.
(ii) The distance between the object and the surface on which the shadow falls.
(iii) The size of the source of light.
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Transparent, Opaque and Translucent objects
WHAT IS LIGHT?
- The devices such as mobile phones, microwave ovens, remote control and scanning machine use electromagnetic radiations (radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves and X-rays) to work.
- Light is a form of energy as well as an electromagnetic wave that can be detected.
- In a vacuum, light travels in a straight-line path at the speed of 3 x 108m. The sunlight takes 8 minutes and 32 seconds to reach the earth.
Importance of Light
- Light is the main source of energy for animals and plants.
- The sunlight provides natural warmth that creates suitable conditions for the growth and development of life.
- The green plants required sunlight to make their food by the process of photosynthesis.
- The natural colour of light is white, but this white light has seven different colours: violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red.
- The objects absorb specific colours of light and reflect the other colours. This reflected colour declare the colour of the object. For example, grass cannot absorb the green colour. So, the green colour is reflected that comes to our eyes.
Sources of Light
The objects that emit light are called sources of light. There are two sources of light: natural and man-made. For example, the sun, stars and fireflies are natural sources(Figure 1 a), while an electric bulb, a burning lamp and tube light are man-made sources of light(Figure 1 b).
The objects that become hot when they emit light are called hot sources of light. For example,
- Objects that produce their own light are called Luminous Objects. Example, Sun, Fire
- the sun, a burning candle or lamp and an electric bulb, etc. (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Hot source of light: the sun

Figure 1: Sources of light: a) Cold source of light: Firefly(natural source; b) Candle(man-made source)
Bioluminescence: A natural phenomenon of emitting light by the objects. In bioluminescence, the objects covert chemical energy into light energy. Some of the examples are phytoplankton, fireflies, jellyfish and algae, etc.
Luminous objects: The objects that have their own light. For example, the sun, stars and torch, etc.
Non-luminous objects: The objects that do not produce their own light. For example tables, chairs and books, etc.
Objects that do not produce their own light but are visible when reflect light falling on them are called Non-Luminous Objects. Example - Table, planets. Non-luminous objects can be classified as:


Propagation Of Light
Usually light travels in a straight line. When we want to represent the propagation of light with a diagram, we represent it with the help of rays and beams. Ray A ray is a line with an arrow that shows the direction of propagation of light, and such a diagram is called a ray diagram.
Beam A group of light rays moving in an organized manner is called a beam of light.
The property of light to travel in straight lines explains many interesting phenomena related to light, like formation of shadows by opaque objects and formation of images in a pin-hole camera.


 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
