- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Flower
• The Flower is the site of sexual reproduction in plants .
• A flower may be defined as a modified shoot in which nodes and internodes are highly condensed.
• It develops from the floral bud.
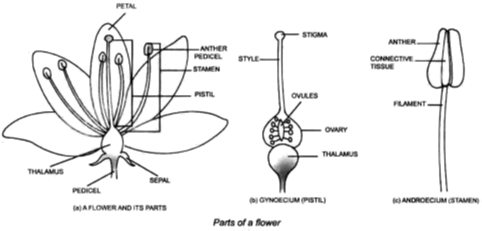
• Parts of a Flower : Flowers vary in size, shape and colour but all flowers have the same basic parts. A Flower consists of following parts :
• Pedicel and Thalamus
• Calyx or Sepals
• Corolla or Petiols
• Androecium / stamen / Male Reproductive organ
• Gynoecium / Pistils/ Female Reproductive organ.
(i) Pedicel and Thalamus :
• The Flower is borne on a stalk called pedicel.
• The upper most end of the pedicel is some what swollen. This swollen part of the pedicel is known as the Thalamus.
• It bears all the four whorls of a flower.
(ii) Calyx : It is the First outermost whorl of a Flower.
• It consist of leaf like structures called sepals.
• Sepals are generally green in colour and manufacture food.
• They also protect the new delicate inner parts of the flower during the bud stage.
(iii) Corolla : It is the second whorl of a flower.
• Each segment of the corolla is known as a petals.
• Petals are usually brightly coloured due to the presence of pigments.
• The bright colour, sweet smell and nectar attract the insect which in turn, help in pollination.
(iv) Androecium / stamen / male Reproductive organ :
• It is the third floral whorl which is composed of one or more male reproductive organs called stamen A typical stamen is differentiated into three parts they are filament, connective and anther.
(A) Filament : It is form the stalk that bears more or less cylindrical or ovoid anther
(B) Connective : It connects anther to filament.
(C) Anther : It is present on the top of filament. Each anther consist of two lobes that is why it is called as bilobed.
• Each anther lobe has two pollen sac which contain millions of tiny microscopic pollen grain, called as microspores.
• The pollen grains are like yellow dusty powder in appearance.
(v) Gynoecium / pistil / Female Reproductive organ :
• It is located in the centre of flower.
• The gynoecium is the fourth whorl which is composed of one or more carpels.
• The freely occuring units of the carpels in a flower are called pistils .
• Each pistil usually consist of three distinct parts :
(A) ovary (B) Style (C) Stigma
(A) Ovary : It is a basal swollen part of the pistil. The ovary bears the ovules on a raised tissue called the placenta. Each ovule contains the female reproductive cell.
(B) Style : From the top of the ovary arise a long elongated structure which connects the stigma with ovary. It is meant for raising the level of the stigma.
(C) Stigma : The terminal end of style is called as stigma.
• The stigma is normally rough, hairy and sticky.
• It is meant for receiving pollen grains during pollination.
Note : Structure of the flower is not always the same. The number of sepals, petals, stamens and pistils may also be different in different flowers. Sometimes, some of these parts may even be absent. When choosing flowers to study, avoid using Marigold, chrysanthemum and sun flower. These are not single flowers but group of flowers.
Function of a flower
Reproduction :
• Flower is a reproductive unit of a plant and it grows into the fruit which bears seeds.
• A typical flower possesses male and female reproductive organs.
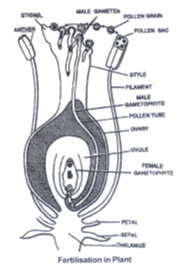
• The male sex cells are contained in the pollen grains found in the anther.
• The Female sex cells are contained in the ovules found in the ovaries.
• Pollination : Pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma by a process called pollination.
• Fertilization : After pollination, a male cell and a female cell fuse together and this process is called fertilization.
• Under favourable conditions seed germinate and give rise to seedling which develop into new plants. This process is called sexual Reproduction.
• Usefulness of flowers For Human Beings :-
(i) Aesthetic : Flowering plants are grown in houses gardens , parks and roadside for their brilliant colour, beautiful shapes and sweet smell.
(ii) Cut Flowers : Flowers yield perfumes or scents. The common ones are rose, Jasmine and also for decoration.
(iii) Spices : cloves, so often used as a spice and in medicine, are the dried Flower buds of the clove plant.
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Herbs, Shrubs and Trees
As we all know, Earth is the only planet in our solar system that has the viable conditions for life to exist. While the presence of water and oxygen is the main reason, we must also recognize that life would not have been possible if it weren’t for the oxygen-emitting plants, life would not have been able to take shape on Earth. These plants are not only our source of oxygen but also the major source of the food that we eat.
Plants are living things that grow on land or in water. From snowy mountain slopes to dry, hot deserts, plants can survive almost anywhere on Earth.
Plants can be divided into two groups :
(i). Flowering Plants
Ex : sunflowers, orchids
(ii). Non-flowering Plants
Ex : mosses and ferns
All plants make their own food, taking energy from sunlight. Unlike animals, plants cannot move from place to place, and most are rooted in the ground.
Herbs, Shrubs and Trees
Herbs, shrubs and trees: Plants are usually grouped into herbs, shrubs and trees on the basis of their heights, stem and branches:
- Herbs: Plants with green and tender stems are called herbs. They are usually short and sometimes do not have branches.
- Shrubs: Some plants have branches arising from the base of the stem. The stem is hard but not very thick. They are called shrubs.
- Trees: Some plants are very tall and have hard and thick stems. They have branches arising from the upper part of the stem. They are called trees.
Creepers and climbers:
The stem of some plants are very thin and weak. They either lie on the ground or need support to stand up. They are called creepers and climbers respectively.
- Climbers are much more advanced than creepers. Climbers have a very thin, long and weak stem which cannot stand upright, but they can use external support to grow vertically and carry their weight. These types of plants use special structures called tendrils to climb. Few climber’s plants names include pea plant, grapevine, sweet gourd, money plant, jasmine, runner beans, green peas, etc.
- Creepers, as the name suggests, are plants that creep on the ground. They have very fragile, long, thin stems that can neither stand erect nor support all its weight. Examples include watermelon, strawberry, pumpkin and sweet potatoes.
We can classify plants on the basis of the thickness of their stems and the place of origin of their branches, into three broad categories:
Herb: These are plants that have green and frail stems. Usually, these are small plants with not many branches.
Some common examples of herbs are Basil, Coriander, Mint, Oregano, Thyme, Parsley, Rosemary etc.

Herbs: Small plants with tender stems

Shrubs: These are plants with hard but not exactly thick stems. Their branches generally originate from the base of their stems. These are much taller than herbs but usually shorter than trees.
Some common examples of shrubs are Aloe Vera, Rose plant, Jasmine plant, Blackberry plant etc.

Trees:
These are plants which are very tall and have a thick and hard stem. The branches originate from the upper part of the tree and are very high above the ground.
Some common examples of trees are neem, peepal, coconut tree, mango tree etc.


 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
