Introduction
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
INTRODUCTION
You all know that food, clothing and shelter are the three basic needs of life. Yue eat food survive and protect yourself from diseases, you need a house to live in. We wear clothes for protection against climate, for modesty and beauty, and also to show status. The material that you use for clothing is called fabric.
If we go to a shop to buy fabric for our dress, we would see a variety of fabries there. Those fabrics are made up of many types of fibres. Some materials are warm, some are soft, some fabrics materials go bad after washing while others remain the same.
Variety in Fabrics
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
HISTORY OF CLOTHING MATERIAL
In ancient times people used the bark and big leaves of trees or animal skins and furs to cover themselves.
After people began to settle in agricultural communities, they learnt to weave twigs and grass into mats and baskets. Vines, animal fleece or hair were twisted together into long strands. These were woven into fabrics. The early Indians wore fabrics made out of cotton that grew in the regions near the river Ganga. Flax is also a plant that gives natural fibres. In ancient Egypt, cotton as well as flax were cultivated near the river Nile and were used for making fabrics.
In those days, stitching was not known. People simply draped the fabrics around different parts of their body. Many different ways of draping fabrics were used. With the invention of the sewing needle, people started stitching fabrics to make clothes. Stitched clothes have gone through many variations since this invention. But, it is also amazing that even today saree, dhoti, lungi or turban is used as an un-stitched piece of fabric.
Just as there is a large variety in the food eaten all over our country, a large variety exists also in fabrics and clothing items.
Variety in Fabrics
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
VARIETY IN FABRICS
Clothes are made of different materials. We get these materials from both plants and animals.
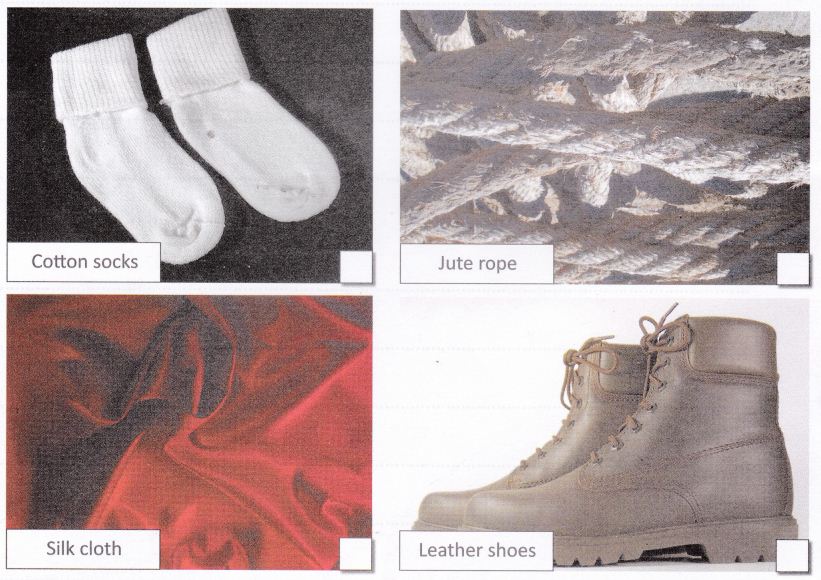
Fiber And Fabric:
Clothes are made mostly from fibres. Fibres are thin strands of thread, that are woven to make fabric, for example, cotton fabric, silk fabric, etc. The fabric is stitched to make clothes. For example, cotton fabric can be stitched into a cotton frock or a cotton kurta.
Yarn: Yarn is defined as a long, twisted and continuous strand composed of interlocked fibers or filaments which are used in knitting and weaving to form cloth.
Fibre
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Yarn to fabric
There are many ways by which fabrics are made from yarns. The two main processes are weaving and knitting.
(a) Weaving : The process of arranging two sets of yarns together to make a fabric is called weaving.
Two sets of yarn are woven to make a fabric. The yarns are much thinner. Weaving of fabric is done on looms. The looms are either hand operated or power operated.
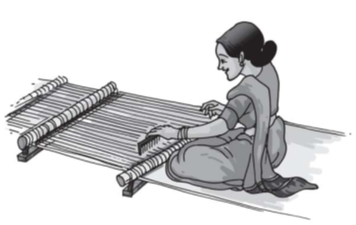
Handloom
Activity–2
Aim : Weaving of paper strips.
Materials required : Sheets of paper of differnt colours.
Method : Cut square pieces of length and width equal to 30 cm from each sheet. Now, fold both the sheets into half. On one sheet draw lines as shown in
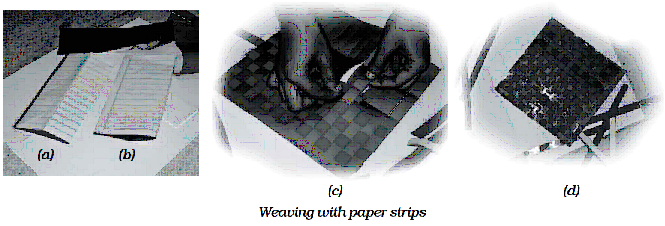
(a) and on the other as shown in (b). Cut both the sheets along the dotted lines and then unfold. Weave the strips one by one through the cuts in the sheet of paper as shown in (c). Fig. (d) shows the pattern after weaving all the strips.
(b) Knitting : In knitting, a single yarn is used to make a piece of fabric A single yarn gets pulled out continuously as the fabric gets unravelled. Socks and many other clothing items are made of knitted fabrics. Knitting is done by hand and also on machines.
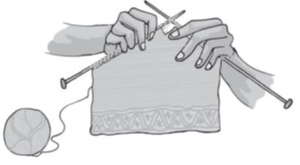
Knitting
Fibre
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Fibers
All Cloth materials are made up of long, narrow, thin structures called fibers.
The thin threads or filaments which form a yarn are called Fibres.
Fibers are obtained from natural as well as man-made sources.
Fibres:

Where do Fibres come from?
Fibres can be broadly classified into two broad categories:
Natural Fibres: Fibres that come from plants and animals i.e. are found in nature are called Natural Fibres. Examples:
We get jute and cotton from plants.
Wool is acquired from the fleece of a goat and sheep. It can also be acquired from the hair of yak, rabbits and camels.
The process involved in making Animal Fibre into wool follows a series of steps — Shearing, Scouring, Sorting, Cleaning, Dyeing, Straightening, Rolling and Combing.
Silk Fibre can be procured from the cocoon of silkworms. The process of obtaining Silk from Silkworm is called Sericulture.
Synthetic Fibres: Fibres that are made of chemical substances i.e. substances not found directly in nature are classified as synthetic fibres. Examples include nylon, acrylic and polyester.

Spinning Cotton Yarn
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
YARN
Fibres are thin and small cannot be made into a fabric directly. So they are first converted into yarns which are longer, thicker and stronger.
A yarns is a continuous strand made up of a number of fibres which are twisted together.
(i) Yarn making
The process of making yarns from fibres is called spinning. Here the fibres are not only twisted but also pulle out or drawn.
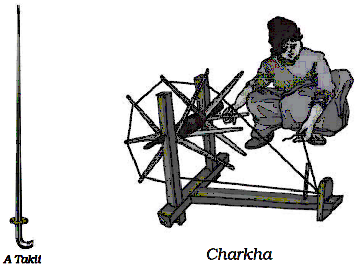
The spinning process helps to hold the fibres together and makes the yarns strong, smooth and fine. Spinning can be done by using a takli(spindle), a charkha or a spinning machine.
AIM : To show no. of strands in yarn.
Material required : A yarn of cotton fabric.
Method : Place this piece of yarn on the table. Now, press one end of the yarn with your thumb. Scratch the other end of the yarn along its length with your nail as shown. This yarn splits up into no. of strands.

FABRIC
Fabric are made using yarns. Fabric is the material that is used to make clothing or household articles.
Spinning Cotton Yarn
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Spinning Cotton Yarn
- Spinning: Spinning is the process of constructing yarn from fibres in which fibres from a huge heap of cotton wool are taken out and twisted which brings them together to form a yarn.
- There are two major devices called Takli which is a hand spindle and Charkha which is also a hand-operated device, are used for spinning.
- Charkha: Charkha is a machine on which yarn was spun directly from ginned cotton in olden days.
- The spinning of yarn on a bigger scale is done using spinning machines following which these yarns are used to weave fabric.
- Khadi was the term used to denote clothes which were made from homespun yarn.

- On the left we can see a charkha and on the right we can see a simple takli.
Some Plant Fibres
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Some Plant Fibres
(i) Cotton : Cotton plants are usually grown at places having black soil and warm climate. The fruits of the cotton plant (cotton bolls) are about the size of a lemon. After maturing, the bolls burst open and the seeds covered with cotton fibres can be seen.It looks like a field covered with snow.
From these bolls, cotton is usually picked by hand. Fibres are then separated from the seeds by combing. This process is called ginning of cotton. Ginning was traditionally done by hand. These days, machines are also used for ginning.

Cotton is cultivated where warm and sunny weather stays for at least half of the year. Cotton plants require warm temperature ranging between 21º C to 27ºC with sunny and dry weather. By the time of harvesting rainfall between 50 cm to 80 cm is another conducive condition for its growth. Black soil, which has the ability to retain moisture is best suited for cotton cultivation. When cotton crop grows to maturity, the seeds with their fibres are harvested. Fibres are separated from the seeds and raw cotton is then shipped to textile factories.
Cotton is used in the manufacture of fish nets, coffee filters, tents and in book binding.
In India, main cotton producing states are Maharashtra, Haryana, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab and Gujarat. Sourthern United states, China and India are the largest producer of cotton.
Some Plant Fibres
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Some Plant Fibres
Cotton (Fig. 4.3), jute, coir, silk cotton, hemp, and flax are examples of plant fibres. Denim, used to make jeans, is made from cotton.

Cotton:
The cotton plant is a shrub. It grows well in black soil and warm climate. It needs moderate rainfall. Cotton is a soft fibre that grows around the seeds of the cotton plant. A variety of textile products are made from cotton. In India, ‘lchadi’, a coarse hand-woven cloth, is made from cotton.


- Cotton plants are grown in fields usually at places having a warm climate and black soil.
- Some cotton producing Indian states are Punjab, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra etc.
- Cotton plants bear fruits the size of a lemon called Cotton Balls which burst open upon maturing and the seeds wrapped up in cotton fibre become visible. Cotton is generally picked by hand from these balls.
Ginning: Ginning of cotton can be defined as the process of separating cotton fibres from cotton seeds. Traditionally, ginning used to be done by hand but these days machines called double roller cotton ginning machines are widely in use.

In the above figure, we see a boy ginning by hand.
2. Jute

A jute plant
Jute:
Jute is a fibre obtained from the bark of the jute plant (Fig. 4.6).
- It can be grown in different soil types, ranging from clayey to sandy soil.
- It grows best in loamy soil (mixture of sand, silt, and clay), sandy soil, and clayey soil.
- It grows well in regions where it rains a lot.
- Almost 80% of the world’s high-quality jute comes from Bangladesh. Bangladesh, India, China, Nepal, and Thailand are the main producers of jute.

- Jute fibre is obtained from the stem of the plant.
- Unlike cotton, jute is cultivated in the rainy season.
- Some jute producing Indian states are Bihar, Assam and West Bengal.
- The plant is harvested during its flowering stage.
- The stems of these harvested plants are then soaked in water for four to five days
- The stems are left to rot and then the fibres are picked out by hand.
- Yarn: Yarn is the spun thread that is made from fibres in order to produce a fabric.
- Other Useful Plant Fibres:
There are other important plant fibres as well. - Coir: Coir is the fibre obtained from the outer covering or the husk of the coconut. Usually coconuts are left in water for a few months. The husk is then separated from the nut and beaten with wooden mallets to get the fibre. The fibre thus obtained is spun and dyed and is ready for weaving. Coir is used to make several household products like rope and floor covering and also as a stuffing in mattresses and pillows.

- Silk cotton: Silk cotton is another plant fibre that is commonly used as a stuffing in pillow, sleeping bag, and life jacket. This fibre is obtained from the silk cotton tree, also called kapok.
The fruits of the kapok tree contain fibres that are light and fluffy (like cotton). When the fruit ripens, it bursts open, releasing the fibres. - Hemp: Hemp fibres are obtained from the stem of the hemp plant. Hemp fibres are used in the production of ropes, carpets, nets, clothes, and paper.
Flax Fibres obtained from the stem of the flax plant are woven to make a fabric called linen. Flax fibres are also used in the production of rope and high-quality paper.
Yarn to Fabric
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Fibres
A hair like strand from which all fabrics are made, are know as fibres.
CLASSIFICATION OF FIBRES
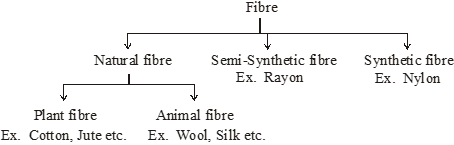
(a) Natural Fibres :
Fibres obtained from plants and animals are called natural fibres. For example cotton, jute, wool and silk.
(i) Plant fibres : The fibres obtained from plants are known as plant fibres
Example : cotton, jute
(ii) Animal fibres : The fibres obtained from animal are known as animal fibres.
Example : wool and silk
(b) Semi-synthetic fibres :
These are obtained from naturally occurring fibres by chemical modifications. For example, cellulose on reaction with acetic anhydride in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid gives cellulose diacetate, which is used for making threads of acetate and other materials like films and glasses.
(c) Synthetic (artificial) fibres :
Synthetic fibres are manufactured by man in the laboratories. For example: nylon, acrylic and polyester.
Yarn to Fabric
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Yarn to Fabric
There are many ways by which fabrics are made from yarns. The two main processes are weaving and knitting. The process of arranging two sets of yarns together to make a fabric is called weaving.
Weaving and knitting are used for making different kinds of fabric. These fabrics are used for a variety of clothing items.
Weaving: The process of entwining two sets of yarn simultaneously to make fabric is called Weaving. The process is done using a loom (which can either be operated by hand or by a machine) which interlaces two sets of yarn at right angles to each other.
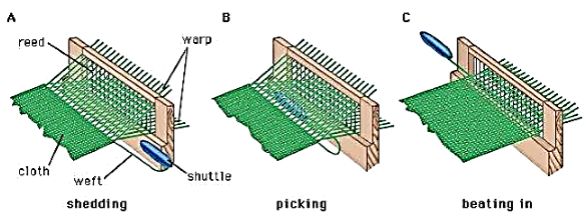
The above figure represents the process of weaving.
- Knitting: Knitting is the process by which a single strand of yarn is used to make a piece of fabric. Socks, sweaters, mufflers and a lot of other winter clothes are made of knitted fabrics. Knitting can be done by hand as well as by machines.
- Knitting involves making fabric by forming a series of connected loops of yarn by using knitting needles or machines. Sweaters are made from wool strands by knitting.


History of clothing material
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
(ii) Jute :
Jute fibre is obtained from the stem of the jute plant. It is cultivated during the rainy season. In India, jute is mainly grown in West Bengal, Bihar and Assam. The jute plant is normally harvested when it is at flowering stage. The stems of the harvested plants are immersed in water for a few days. The stems rot and fibres are separated by hand.

It is a long, soft , shiny plant and is one of the cheapest natural fibres. Jute fibres are composed of cellulose and lignin.
• Jute is a rainy season crop, grown best in warm, humid climate.Jute plant requires temperature ranging from 17ºC to 40ºC and rain fall from 120 mm to 150 mm
• Almost 85% of the world’s jute cultivation is concentrated in deltas of Ganga.
• Harvesting of jute plant is done at flowering state. The stalks are cut close to the ground. They are then tied into bundles and soaked in water for 20 days. It softens the tissues and permits the fibres to be separated. The fibres are then stripped from the stalks in long strands and washed in clear, running water. Then they are spread on a that ched roof to dry.
• Jute is said to have more than a thousand uses. It is the second most important vegetable fibre after cotton, not only for its wider cultivation, but also for its uses.
• Jute is used to make cloth for wrapping bales of raw cotton, and to make sacks and coarse cloth. Jute fibres are also woven into curtains, chair coverings, bags, carpets, hessian cloth, etc
KEY WORDS
1. Cotton wool : Cotton wool is obtained from cotton plant. It is made up of thin cotton fibres.
2. Fabric : Woven material (cloth) is called fabric.
3. Fibre : Thread like animal or plant tissue is called a fibre.
4. Knitting : Knitting is a process of making a piece of fabric from a single yarn.
5. Spinning : The process of making yarn from fibres is called spinning.
6. Weaving : The process of arranging two sets of yarn together to make a fabric is called weaving.
7. Yarn : Spun fibres are called yarns.
History of clothing material
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
History of Clothing Material
- History Of Clothing:
About 30,000 years ago, people started using animal skins for clothing. - It is believed that wool was used as early as 6000 years ago.
Domestication of silkworms to produce silk occurred around 3000 BC in China. In India, cotton came into widespread use around 3000 BC. These fabrics were not stitched. - They were just wrapped around the body. Even today, sari, dhoti, and turban are unstitched pieces of cloth.
- During ancient times, people were not civilized and they used to live in the forest without any clothes.
- As time passed, humans to protect themselves from the harsh climatic condition, they started to cover their body using bark and big leaves of trees or animal skins and furs.
- Gradually, humans learnt to make large pieces from grass and plant fibres to cover their waist, nowadays it is known as a skirt. Further, they started to make robes like outfits using animal hairs.
- Revolution started once the needle was invented, people started to make the clothes from all sorts of fabrics available.
- Today fabrics are used extensively to decorate windows and curtains with beautiful windows. And also table clothes and bedsheets which makes the interior more attractive.
- Clothes of different designs, colours, and shapes are available today for clothing. Textile industries are one of the largest industries in today’s world.

- In earlier times, when people did not have access or the knowledge to process fibre, big leaves and the bark of trees were used by people to cover themselves.
- After settlement began in agricultural communities, they learnt how to weave. They used grass and twigs to make mats and baskets. Animal hair or fleece and vines were warped together into stretched out strands which were then woven into fabrics.
- There was an abundant growth of cotton in areas near Ganga, which the early Indians readily used to make fabrics for themselves.
- There is another plant named flax which yields natural fibres.
- The early Egyptians cultivated both cotton and flax and used them for creating fabrics. These plants grew near the river Nile.
- But in those days, people were not aware of the process of stitching. They simply used to wrap around the fabric around different parts of their bodies. Even today unstitched clothes like sarees, dhotis, lungis or turbans are widely in use.
- It was with the advent of the sewing needle that people learnt how to stitch fibres to make fabric.
Summary
Natural Sources: Cotton, jute, silk, wool, etc., are obtained from natural sources- plants or animals.
Man-made Sources: Polyester, nylon, rayon etc., are man-made materials used for making clothes.
Plant fibres: All the plants have fibres in their body structure, e.g., cotton and mango have fibres on their seed, coconut on its fruit, jute in its stem and banana tree in its leaf.
Animal fibres: Important animal fibres are wool (hair of sheep) and silk (from silkworm).
Yarn: Yarn is defined as a long, twisted and continuous strand composed of interlocked fibers
Fibre The thin threads or filaments which form a yarn are called Fibres.
Fabric The material made by weaving the threads from fibres is called fabric.
Weaving- Weaving involves the making of fabric from yarn.
Cotton bolls: Fruits of cotton plant are spherical-shaped structures of the size of wall nut which are called cotton bolls.
Production: Cotton is grown in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu and Madhya Pradesh.
Climate required: Cotton plants need warm climate.
Cotton is planted early in the spring.
Black soil is excellent for cotton’s cultivation.
Ginning- The process of separating the cotton fibres from its seeds is called ginning.
Spinning- The process of making yarn from fibres is called spinning.
Retting- The process of rotting the stems of the plants in water to remove the sticky substance and separate fibers is called retting.
- Clothing materials are obtained from both plants and animals.
- Fibres are woven to make fabrics and fabrics are stitched to make clothes.
- Fibres may be natural or synthetic.
- Cotton, jute, coir, silk cotton, hemp, and flax are some plant fibres.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
