- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Joints
Joints are the place of articulation between two or more bones or between a bone and a cartilage. Due to the presence of a number of joints, the movement of the different body parts and the whole body is possible.
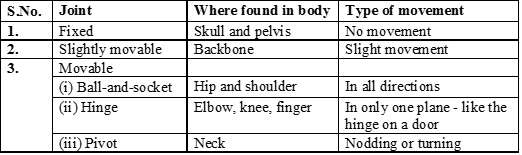
(a) Types of Joints :
(i) Fixed or immovable or fibrous joint : There is no space between the bones. The attached bones are tightly held with the help of white fibrous connective tissue. e.g. Joints of skull bones.
(ii) Slightly movable or cartilaginous joint : It is an articulation between the bones that allows very little movement. e.g. Between bones of vertebrae and pelvic girdle.
(iii) Movable joint or synovial joint : It is a joint which allows the movement of articulating bones such that they can move extensively upon each other.The space between bones is called synovial cavity. This cavity remains filled with a viscous and slippery synovial fluid. These are of following types :
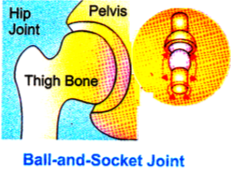
(A) Ball & socket joint : One bone forms a ball like head that fits into a socket formed in the other bone. The bone with head can move nearly in all the directions. e.g. Shoulder joint, hip joint.
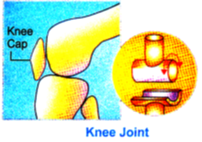
(B) Hinge joint : This joint allows movements in one plane only. e.g. Elbow joint & knee joint.
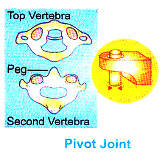
(C) Pivot joint : This joint allows only a rotatory movement of one bone on the other stationary bone. e.g. Atlas and axis vertebrae.
(D) Angular joint / Ellipsoid / Condyloid joint - This allows movement in two directions - side to side and back & forth. e.g. Wrist joint.
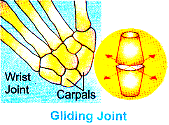
(E) Gliding joint : This joint permits sliding movement of two bones over each other, e.g. Carpal in wrist and tarsals in ankle.
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Gait of Animals
Some animals do not have bones. They have muscles which help to extend and shorten the body. During movement, animal first extends the front part of the body, keeping the rear position fixed to the ground. After that animal fixes the front end and releases the rear end. Now animal shortens the body and pulls the rear end forward. During this practice, animal moves forward by a small distance.
Rib cage: Ribs join with the chest bone and the backbone together to form a box. This is called rib cage.
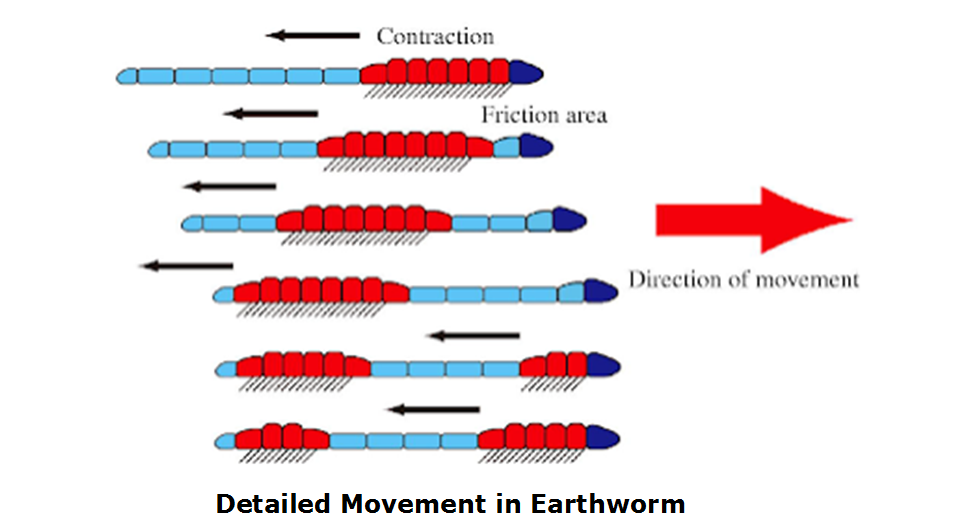
1. Earthworm:
- Does not have bones
- Earthworm body is made up of rings
- A slimy substances secreted by its body aids movement (NSO)
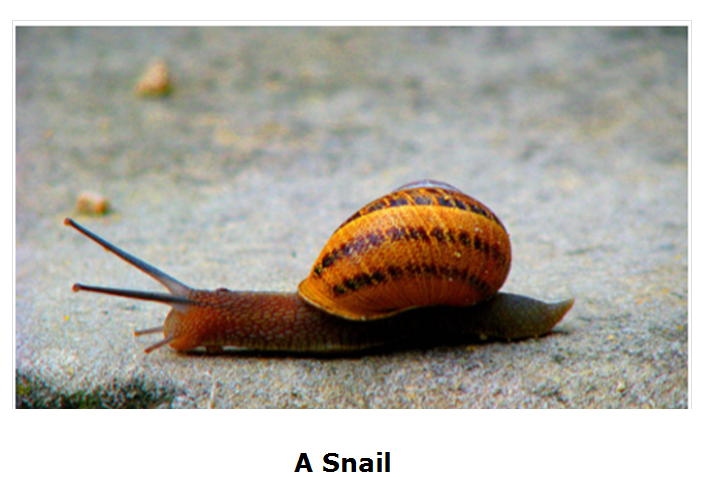
2. Snail:
- It has a slimy body, which does not have bones.
- The shell of the snail does not help in movement. It has to be carried along.
- The foot of the snail is a thick structure and is made up of strong muscles.
- A muscular organ called ‘Foot’ helps in locomotion.


SUMMARY
Backbone: Backbone or vertebral column is composed of 33 small ring like bones called vertebrae. It is a hollow bony tube.
Ball and socket joint: A joint in which rounded end of one bone fits into the cavity of the other bones.
Bristles: Hair like structures projecting out of the body of earthworms. With the help of these, it fixes itself with the ground.
Cartilage: It is the additional part of the skeleton that is not as hard as the bones and which can be bent also.
Cavity: The bowl like part (hollow space) in the shoulder bone allows the rounded end of the arm bone to fit into it to form ball and socket joint.
Fixed joints: Some of the joints allow no movement. These are called fixed joints, e.g., joints in skull and upper jaw.
Hinge joint: Hinge joint is found in the fingers, elbow and knee. It allows movement only in one direction.
Muscle: Muscles are involved in the movement of bones.
Outer Skeleton: Skeleton found outside the body is called outer skeleton, e.g., hair and nails in human.
Pelvic bones: Bones in the hip region are called pelvic bones.
Pivotal joint: The joint where our neck joins the head is a pivotal joint.
Rib cage: Ribs join the chest bone and the backbone together to form a box. This is called rib cage.
Shoulder bones: The two bones of the shoulders are called shoulder bones.
Skeleton: The framework of the body which is made up of bones and cartilage is called skeleton.
Streamlined: The body shape where body tapers at both ends is called streamlined body, e.g., body of birds and fish.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
