- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Fibres
A hair like strand from which all fabrics are made, are know as fibres.
CLASSIFICATION OF FIBRES
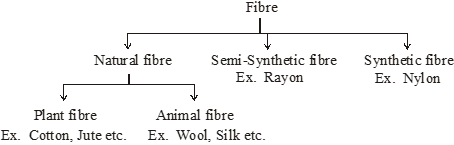
(a) Natural Fibres :
Fibres obtained from plants and animals are called natural fibres. For example cotton, jute, wool and silk.
(i) Plant fibres : The fibres obtained from plants are known as plant fibres
Example : cotton, jute
(ii) Animal fibres : The fibres obtained from animal are known as animal fibres.
Example : wool and silk
(b) Semi-synthetic fibres :
These are obtained from naturally occurring fibres by chemical modifications. For example, cellulose on reaction with acetic anhydride in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid gives cellulose diacetate, which is used for making threads of acetate and other materials like films and glasses.
(c) Synthetic (artificial) fibres :
Synthetic fibres are manufactured by man in the laboratories. For example: nylon, acrylic and polyester.
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Yarn to Fabric
There are many ways by which fabrics are made from yarns. The two main processes are weaving and knitting. The process of arranging two sets of yarns together to make a fabric is called weaving.
Weaving and knitting are used for making different kinds of fabric. These fabrics are used for a variety of clothing items.
Weaving: The process of entwining two sets of yarn simultaneously to make fabric is called Weaving. The process is done using a loom (which can either be operated by hand or by a machine) which interlaces two sets of yarn at right angles to each other.
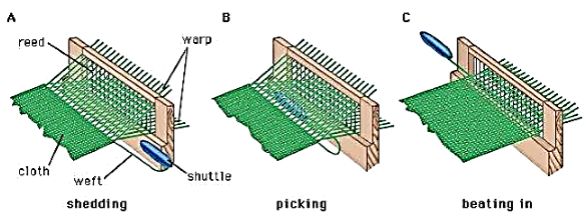
The above figure represents the process of weaving.
- Knitting: Knitting is the process by which a single strand of yarn is used to make a piece of fabric. Socks, sweaters, mufflers and a lot of other winter clothes are made of knitted fabrics. Knitting can be done by hand as well as by machines.
- Knitting involves making fabric by forming a series of connected loops of yarn by using knitting needles or machines. Sweaters are made from wool strands by knitting.



 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
