- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Root
The roots help in holding the plant firmly in the soil they are said to anchor the plant to the soil.
Types of Roots
(1) Tap roots (2) Fibrous Roots
1. Tap root system : When a dicot seed (seeds with two seed leaves) germinates, the radicle gives rise to a long deep - seated root. It is thick and large this is called the primary root or tap root.
• The primary root gets divided into branches which are known as secondary roots.
• The branches of secondary roots are called tertiary roots
• The primary root is longer than its branches and grows vertically downward into the soil.
• It is found in most of the dicot plants like castor, pea, mango, gram and beans.
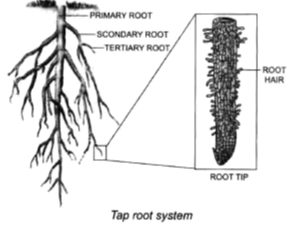
2. Fibrous Root system.
• In the fibrous root, the primary root is short - lived and is replaced by a cluster of thin fibre like roots. These are called fibrous roots.
• These roots spread from a common point and are about the same size.
• They spread out in the soil and give firm support to the plant.
• They are found in most of the monocot plants.(Plants that have seeds with single seed - leaf) Like wheat, maize, barley and grasses.
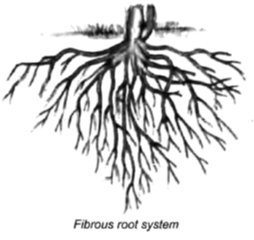
Do you know :
Leaf venation and the type of roots in a plant are related : Plants having leaves with reticulate venation have tap root while plants having leaves with parallel venation have fibrous roots.
Function of Roots
1. Fixation : It fixes the plant firmly in the soil.
2. Absorption : The root hairs help in the absorption of water and minerals from the soil.
3. Prevention of soil erosion : Roots bind the soil finely and prevent soil erosion
4. Storage : In plant like carrot, turnip, radish and sweet potato and tapioca, the roots are modified for the storage of food.
Supporting Roots
• In plants such as black pepper, money plant and betel the roots help the plant to climb up a support as the stems are too weak to stand on their own Hence they are known as climbing roots
• In plant such as banyan new roots grow downwards from the main stem or branches.These are aerial roots that grown towards the soil and act as pillar to support the plant. They are known as prop roots.
Fig. Modification of roots for support
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Stem

- It bears leaves, buds, flowers, fruits, etc.
- The stem conducts water from the roots to the leaves and to the other parts and food from leaves to the roots and other parts of the plant.
- Potatoes, yams, ginger, onion, etc. though present in the soil, are actually stem and store food within them.
There are two other kinds of plants which are:
Creepers: These are plants which have soft, weak and green stems and hence cannot stand straight and instead spread on the ground.
Some common examples are sweet potato, watermelon, pumpkin etc.

Climbers: These are also plants with soft and weak stems but instead of spreading on the ground they take support with a nearby object to climb up.
Some common examples of creepers are cucumber, bean, grapevine, money-plant etc.
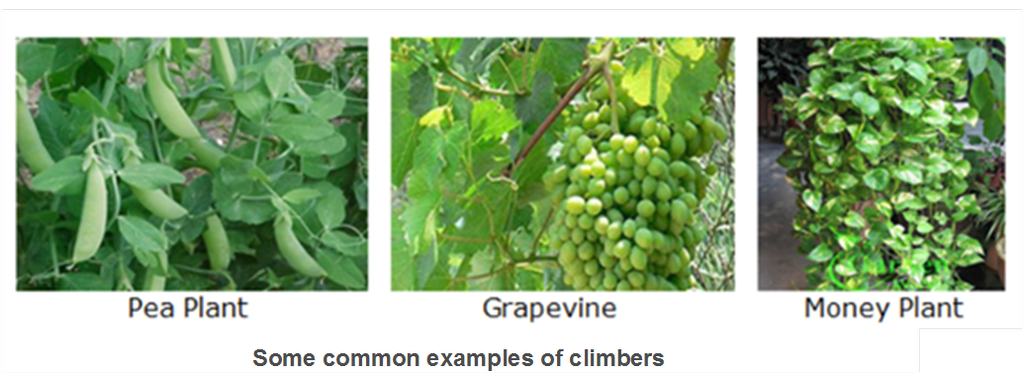
Let us observe and study each part of a plant step by step:
Stem
The Stem is the part of a plant which is responsible for supplying water to all parts of the plant. It is the stem which bears branches, flowers, leaves, fruits and buds. The root sucks the water and minerals from the soil and it is the stem’s function to push this water upward to other parts of the plant.
We can observe this by soaking the stem of a plant in a glass with water. On adding colored ink to the water, we observe that after a while the stem and leaves of the plant start to turn the color of the ink, which is proof that the stem carries the water to the different parts of the plant.
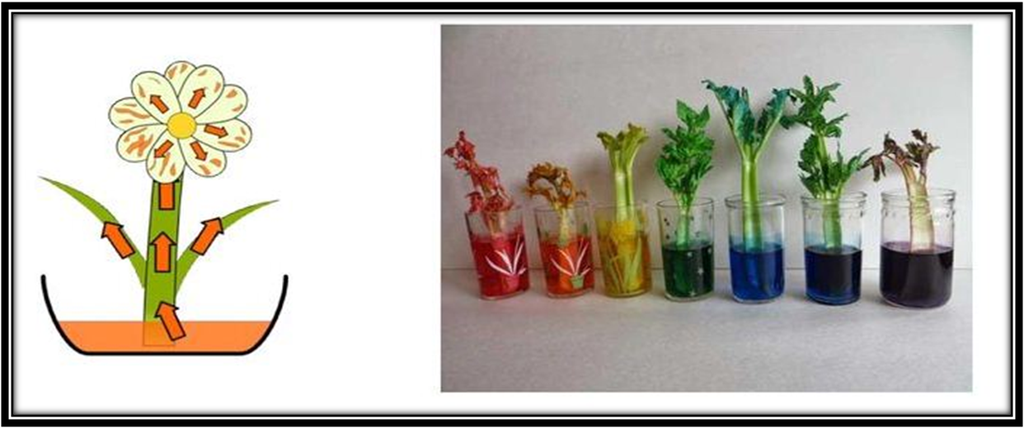

The experiment helps demonstrate how stems are responsible for carrying water to different plant parts

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
