Dealing with Garbage
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Garbage in Garbage Out


Dealing with Garbage

Garbage is defined as the items or materials that are to be discarded because they no longer serve any purpose for us or are of no use to us.
Landfill:

Waste material, faeces of animals, kitchen waste, garden waste, etc., are collected in dustbins from where it is thrown out into the low lying areas for filling a purpose.
Dustbins:
The utensil or space where the waste material is collected is called a dustbin.


Green dustbins:
We use green dustbins for collecting biodegradable waste.
Blue dustbins:
The non-biodegradable wastes which do not decompose naturally are kept in blue dustbins.
Waste:
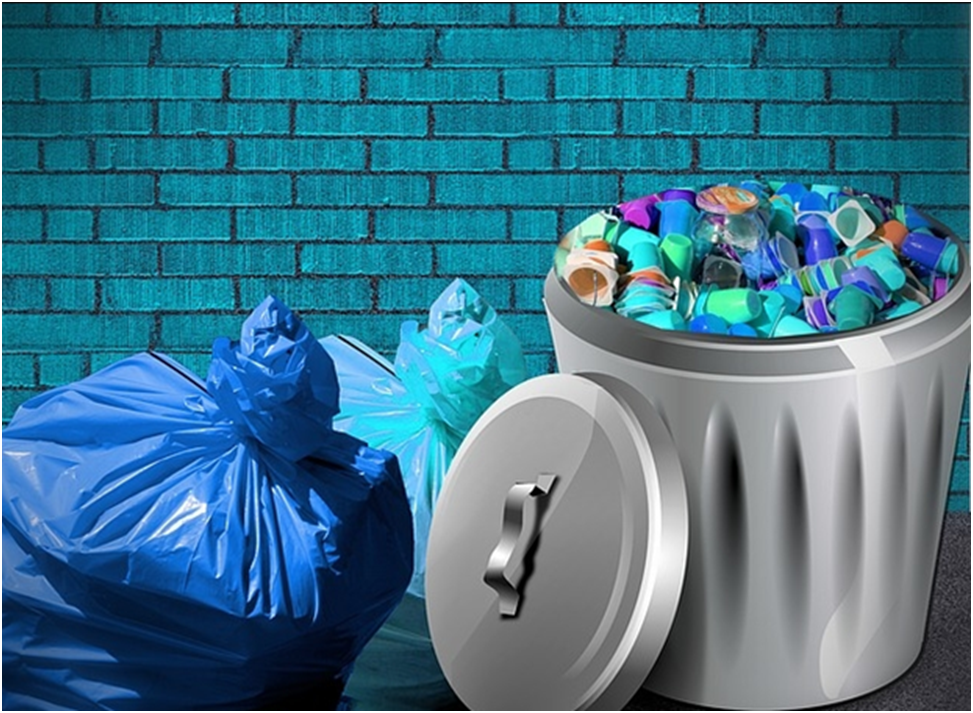

Waste is any substance, which is discarded after primary use, or it is worthless, defective and of no use.
Biodegradable wastes:
Biodegradable wastes are items such as eggshells, vegetable and fruit skin, tea leaves, waste food etc. which can be mixed with soil and roots over time by the action of certain microorganisms. This is usually not accompanied by a pungent smell. Now this mixture of soil and rotten organic materials can be used as manure to provide nutrients to the plants. This process of conversion of biodegradable waste into manure for plants is known as composting.
Non-biodegradable waste:
The non-biodegradable waste consists of items that do not rot over time by the action of microorganisms. Examples of such items are metal scraps, plastics, glass etc.
Garbage is defined as the items or materials that need to be discarded because they no longer serve any purpose for us or are of no use to us.
Tonnes of garbage and is generated by us on a daily basis. Garbage is often associated with a pungent smell and a large amount of garbage may release fumes which are not healthy. Hence, we put such items in dustbins to be taken to faraway places so that our surroundings are clean and healthy.
Waste is generated by all of us and has four main sources:
Domestic: These constitute the kind of wastes that are generated by households, offices schools etc. and include food remains, fruit and vegetable skins, clothing items, used plastic items etc.
Industrial: These constitute the kind of wastes generated by power plants, chemical plants, cement factories, food processing industries, textile industries, each producing waste specific to the kind of industry they are a part of.
Agricultural: This constitutes the kind of waste that is produced by undertaking agricultural activities husks, expired medicines, fertiliser and pesticide containers etc.
Commercial: This constitutes the kind of waste generated by commercial enterprises including disposable plastic cutlery, food items, food packets, textiles etc.
Not all garbage can be classified as useless as there very well are products which can be reused or recycled. When garbage is taken away by the municipality, it is taken to a low lying and open area known as a landfill. Here, garbage is separated into two categories: the items that can be used again for some other purpose and items that cannot be used. The latter is then spread over the landfill and covered with a blanket of soil. Once full, it is converted into a playground or a park.

Image 1: A landfill
The useful components of the garbage can usually be classified into two categories: biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes.
Biodegradable wastes are items such as egg shells, vegetable and fruit skin, tea leaves, waste food etc. which can be mixed with soil and roots over time by the action of certain microorganisms. This is usually not accompanied by a pungent smell. Now this mixture of soil and rotten organic materials can be used as manure to provide nutrients to the plants. This process of conversion of biodegradable waste into manure for plants is known as composting.
Non-biodegradable waste comprises of items that do not rot over time by the action of microorganisms. Examples of such items are metal scraps, plastics, glass etc.
Apart from these, there is another category of non-biodegradable waste also known as electronic waste or e-waste that is composed of electrical appliances or components that no longer serve their specified function and are hence needed to be reused, re-sold, recycle or disposed off. These are non-biodegradable as no action by any microorganism is effective in breaking them down.

Image 2: Biodegradable v/s non-biodegradable items

Image 3: The correct way to dispose biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste
Garbage should be allowed to be processed by the authorities and not burnt because the burning of garbage releases toxic fumes which are harmful to the health of everybody.
Vermicomposting
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Vermicomposting

Compost is an organic matter that has been decomposed and recycled as a fertilizer and soil nutrient.
Vermicomposting is the process of conversion of biodegradable waste into manure with the help of a special type of earthworm called red worms.
- Vermicomposting is the process of conversion of biodegradable waste into manure with the help of a special type of earthworms called red worms.
- A layer of sand or chicken mesh is used as the base to which all types of biodegradable waste including dried leaves, husk, vegetable peels and remnants of fruit, dried animal excreta newspaper, cardboard etc. A little water is sprinkled on this layer. On preparing this mixture, add the red worms to it and covered with a layer of grass or a sheet of cloth.
- The work, however, is not done yet. Red worms need to be fed. They do not have teeth. They have what is called a gizzard. This helps the worms grind their food.
- Fruit and vegetable remains, tea leaves, grass etc. act as food for the red worms and should be buried 2-3 cm deep in the soil. In a day, a worm can eat up as much food as it weighs.
- However, pickles, milk, vinegar and salty materials might help in the growth of disease-causing microorganisms and hence should not be added to the pit.
- They should not be kept in a very hot or a very cold environment. Red worms need care and water. They have the potential to double up in a month’s time, given proper nourishment and care.

Image 4: Red worms

Image 5: Vermicomposting pit
The compost gets ready in three to four weeks’ time.
Think and Throw
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Think and Throw

Questions to think upon while throwing garbage?
- How much of garbage do you think, is thrown out by each house every day? You can make an estimate by using a bucket as a measure.
- Use a 5-10 litre bucket to collect the garbage from your home for a few days. In how many days does the bucket become full?
- You know the number of members in your family. If you find out the population of your city or town.
- Can you now estimate the number of buckets of garbage that may be generated in a day in your city or town? We are generating mountains of garbage every day.
Recycling of Paper
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Recycling of Paper
- Recycling is reusing waste materials that are discarded.
- Recycling reduces the wastage of products and pollution.
STEPS TO RECYCLE PAPER
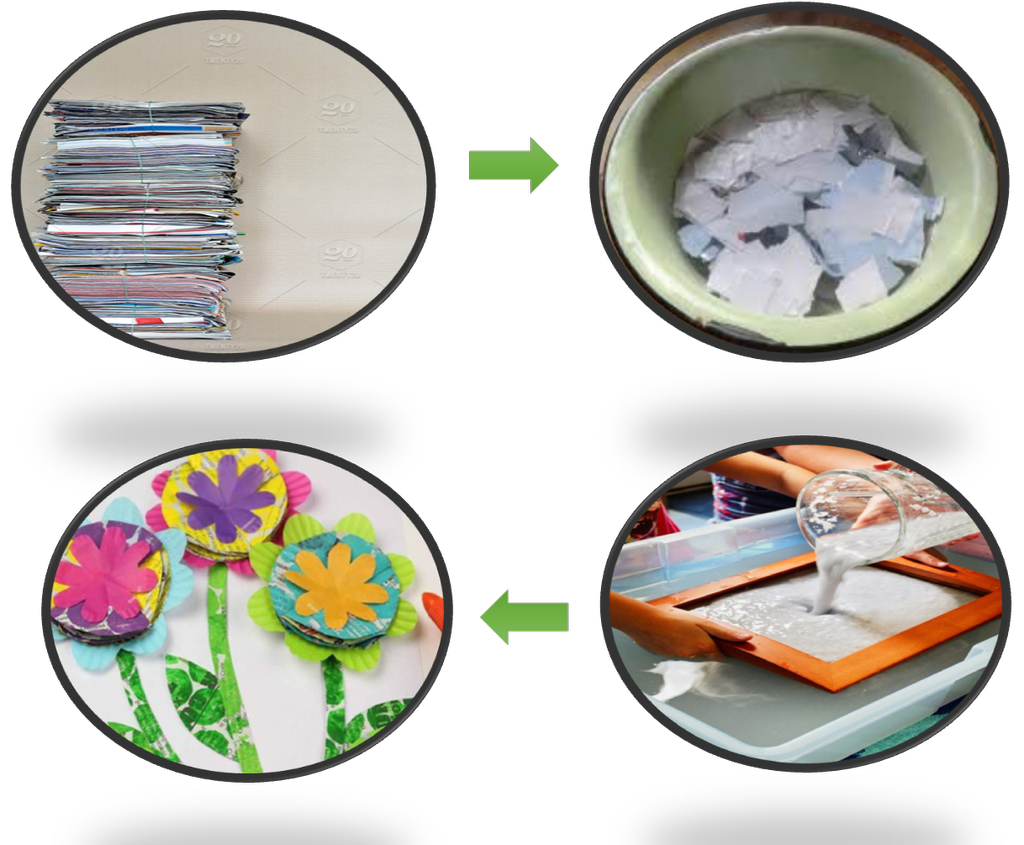

You will require pieces of old newspapers, magazines, used envelopes, notebooks, or any other paper.
- Do not use shiny, plastic coated paper. You will also need a frame fitted with a wire mesh or a net.
- You can also use a large sized sieve in place of a frame. Tear the paper into small pieces.
- Put them in a tub or a bucket and pour water in it. Let the pieces of paper remain submerged in water for a day.
- Make a thick paste of paper by pounding it. Now, spread the wet paste on the wire mesh fixed to the frame.
- Pat it gently to make the thickness of layer of the paste as uniform as possible. Wait till water drains off.
- If required spread an old cloth or a sheet of newspaper on the paste to let it soak up the extra water.
- Now, carefully remove the layer of paste from the frame, spread it on a sheet of newspaper in the sun.
- Keep the corners of the newspaper sheet pressed by putting some weights so that these do not curl up.
- You can add food colour, pieces of dry leaves or flower petals or pieces of colored paper in the paste before spreading it.
It would help you to get a recycled paper with beautiful patterns on it.
- Recycling paper on a small scale is a relatively easy process.
- We should always write on both sides of paper sheets.
- Unused pages from old notebooks can be torn off and made into a new notebook for doing rough work and other miscellaneous work.
- We can also reuse envelopes and covers by using stickers to write new addresses.
- We can also make fresh paper from old newspapers.
Plastics boon or a curse?
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Plastics – Boon or A Curse?
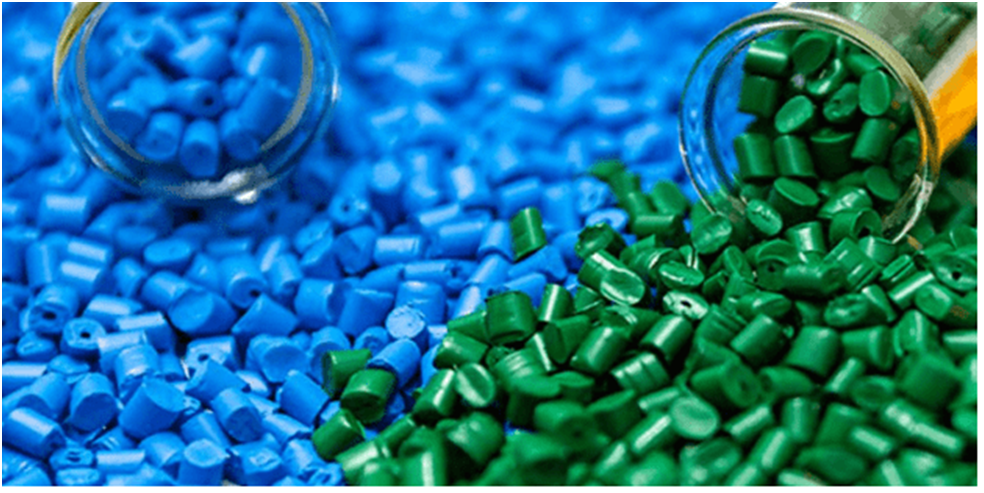

The plastic problem is mounting day by day. A huge amount of plastic is thrown away carelessly on the street and in water bodies and such irresponsible disposal of plastic can cause a number of problems:
- Animals and birds alike, in search of food, end up consuming some amounts of plastic due to which many of them end up choking on these.
- Although plastic bags seem convenient to store food items, consuming these are very harmful to our health.
- It gets worse when dirty and thrown away plastic bags are re-used upon mere dusting and washing them which is also very harmful.
- Upon burning or heating, plastics give rise to toxic and dangerous fumes and gases, which can potentially cause cancer in humans.
- Careless disposal of plastic on the roads also ends up choking the sewer and drainage systems.
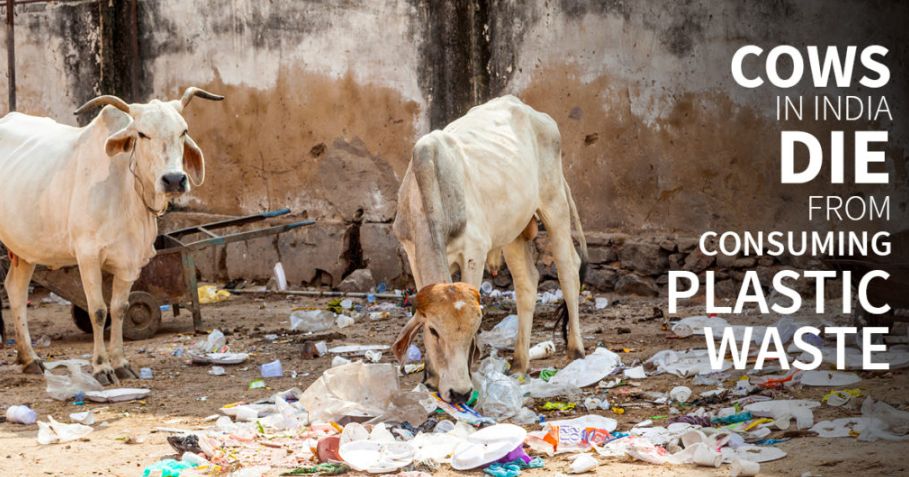

Image 6: The plastic problem is very harmful for all beings alike
Plastic, while very harmful for the environment has become a very indispensable part of our daily lives and hence it becomes all the more difficult to replace or in some cases, even cut-back on our plastic consumption. Plastics have a lot of characteristic features which give it an edge over its metal counterparts.
Bioplastics have hence emerged as the most environment-friendly version of plastics which are made of biodegradable items such as corn starch, vegetable fats and oils and other kinds of food waste. Bioplastics take about three to six months to be decomposed fully as opposed to several hundred years taken by their synthetic counterparts.
After learning so much, it should be everyone’s top priority to do their bit in saving the environment:
- 3Rs- Reduce, Re-use and Recycle. Reducing the use of plastic and re-using harmless plastic to help reduce its over-production. Recycling paper and such articles whenever possible.
- Carrying jute and cloth bags when carrying out errands to avoid the use of polythene bags.
- Properly disposing plastic and polythene bags
- Not using plastic products and bags to store eatables.
- Never burning plastic or dry leaves etc. and disposing them properly.
- Using registers and notebooks made of recycled paper as much as possible.
- Avoid putting waste materials in polythene bags and throwing them on the street.
- Adopting practices like recycling paper and vermicomposting to make the best use of biodegradable waste. This not only helps to reduce the waste that we produce but also becomes a valuable addition to the soil and helps in the nourishment of crops and plants.
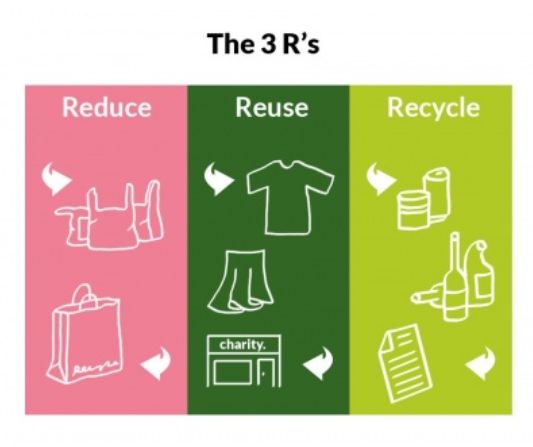
Image 7: Adopting environment-friendly practices benefits us all

Reducing the use of plastic and re-using harmless plastic to help reduce its over-production. Recycling paper and such articles whenever possible.
- Carrying jute and cloth bags when carrying out errands to avoid the use of polythene bags.
- Properly disposing of plastic and polythene bags
- Not using plastic products and bags to store edibles.
- Never burning plastic or dry leaves etc. and disposing of them properly.
- Using registers and notebooks made of recycled paper as much as possible.
- Avoid putting waste materials in polythene bags and throwing them on the street.
- Adopting practices like recycling paper and vermicomposting to make the best use of biodegradable waste.
This not only helps to reduce the waste that we produce but also becomes a valuable addition to the soil and helps in the nourishment of crops and plants.
Summary
- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Summary
Conclusion :
- Landfills: Landfill is an area where the garbage collected from a city or town is dumped. The area is later converted into a park.
- Large areas used for waste disposal are called landfills.
- There are mainly two types of wastes based on their ability to rot over some time:
- Biodegradable
- Non-Biodegradable wastes.
- Biodegradable wastes: Wastes that rot by the action of decomposers are called biodegradable wastes.
- Non-biodegradable wastes: Wastes that do not rot by the action of decomposers are called non-biodegradable wastes.
- Composting: Converting plant and animal waste including that from kitchen, into manure, is called composting.
- Recycling organic wastes like vegetable peels, waste food, leaves, etc., by burying them in compost pits is called composting.
- Vermicomposting: Composting with the help from kitchen garbage and a type of earthworm, called red worms, is called vermicomposting.
- Vermicomposting and landfills are two ways of managing solid wastes.
- Paper can be recycled to get useful products. Plastics cannot be converted into less harmful substances by the process of composting.
- We need to generate less waste and find ways of dealing with the increasing amount of garbage in our surroundings.
- Recycling: The process by which waste materials are used to make new products.
- Dead plants and animals and their products decay while objects like plastic and glass do not.
- By practicing the concept of 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle), we can manage our wastes well.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
