Introduction
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Introduction
A substance which gives energy and keeps the body in good health is called food. Several types of nutrients constitute food. Food is one of the basic requirements of all living organisms. In fact, no organisms need food for their growth and development. Food also provides energy for various life processes in the body. Food is necessary for both plants and animals.
What do Animals Eat?
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Food : A necessity for human life
* Food is essential for all living organisms because of the following reasons :
(i) For energy requirement to perform various functions of body to sustain life.
(ii) For growth : You have seen yourself growing. Without proper food, your growth would not be possible.
(iii) For repair of damaged or injured body parts ; when you get hurt,your skin is damaged and the blood is lost. Repair of such damaged parts takes place by the addition of new cells.
(iv) For protection from diseases and infection.
Food Variety
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Foods eaten by living organisms
On the basis of their food habit, animals are of three types :
(i) Herbivores : Animals which eat plants and plant products – these are called herbivores. e.g. Cow, sheep, deer elephant etc.
(ii) Carnivores : Animals which eat flesh of other animals are called carnivores. e.g. Lion, Tiger, Fox, Wolf etc.
(iii) Omnivores : Animals eating both plants and animals are called omnivores.e.g. Humans, crow, squirrels and cockroaches.
Food Materials and Sources
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Source of food
There are two main sources of food in the world for all human beings – namely plants and animals.
* Plants as Source of Food : Foods obtained from plants are of different types — cereals, pulses, vegetables, fruits, oils, sugar, tea, coffee and spices.
(i) Cereals are the most important sources of food for man and animals. They are rich sources of carbohydrates. Three most important cereals are wheat, rice and maize. These cereals are obtained from grains (biologically, grains are fruits of a plant).
(ii) Pulses or Legumes (commonly called 'dals') are rich in proteins and are obtained from plants.
(iii) Vegetables are rich sources of vitamins, minerals and roughage.Water content in vegetables is high (70 to 90 per cent) and their food value is low.
(iv) Fruits have high water content, low food value, but are rich in minerals and vitamins. In common usage, the term 'fruit' is used for those which are usually eaten without cooking.
Common fruits are banana, mango apple, grapes, pineapple, guava, orange, litchi, and so on.
(v) Sugars are produced by the green plants through photosynthesis. Chief sugar producing plants are sugarcane and sugarbeet.
In case of sugarcane, the plant part used is the stem, while in sugarbeet, it is the root.
(vi) Tea and coffee are common beverages, Tea is obtained from leaves, while coffee is obtained from seeds.
(vii) Spices have no food value and are used for adding flavour to food. Before the advent of refrigeration, spices were also used for preserving foods.
The important spices are pepper (kali mirch), cardamon (ilaichi), ginger (adrak), turmeric (haldi) and chillies (mirch), cloves (loung), saffron (kesar), fennel (saunf), cumin (jeera), coriander (dhania), asafoetida (heeng), fenugreek (methi), nutmeg (jaiphal) and thyme (ajwain).
(viii) Oils : Oils are rich in fat and provide energy. Cotton, groundnut, mustard, coconut, soyabean and sunflower seeds give us oil.
(ix) Medicines : Some plants have medicinal value and are used for curing certain diseases especially in Ayurveda. Mint, Basil (tulsi), ginger, fenugreek (methi), etc. are used in medicines.
Plant Parts and Animal Products as Food
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Plants Parts as Sources of Food :
Table : Edible Parts of Some Plants
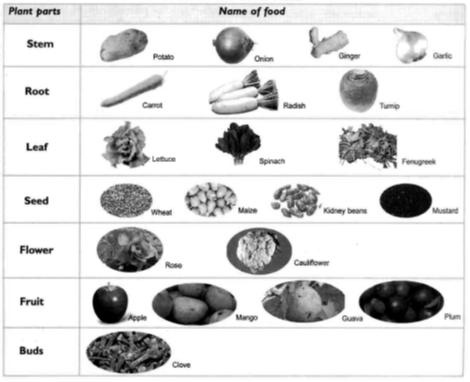
Animals as Sources of Food : Animals provide us food in the form of milk, meat, fish , eggs and honey.
(i) Milk - yielding animals : Cow and buffalo.
(ii) Meat - yielding animals : Sheep, goat and pig. Meat of pig is called pork.
(iii) Poultry animals : Birds like hen, duck and turkey.
Poultry products are rich sources of proteins and have right kind of fat for good health .
Animals which provide meat and egg are called poulty animals.
(iv) Fish : Fish is a major source of food rich in animal proteins. Fish proteins have high digestibility and growth-promoting value. Also, cod and shark liver oils are rich in vitamin - D. In India , fish are found both in fresh water (ponds, lakes and rivers) and sea water.
* Fresh Water Fishes : Catla, Labeo, Pirrhina, Barbus, Mystus, Clarius.
* Sea Water Fishes : Hilsa, cat fish, sardines, ribbon fish, red mullet, pomfret, bombay duck.Rearing and management of fish on a large scale is known as pisciculture.
(v) Honey bees : The insects which provide us honey are known as honey bees. The honey bees collect necter (sweet juice) from flowers, convert it into honey and store it in their nest, which is known as the beehive.
The rearing of honey bees on a large scale is known as apiculture. The place used for the rearing of honey bees is called an "apiary". Honey is produced by honey bees from the necter of flowers. It consists of water, sugar minerals and enzymes. It is an antiseptic (which destroys the growth of micro organisms) and is easily digestible. For this reason, honey is used in medicines.
Plant parts as food
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Food habits of people : In our country, people of different states have different food habits. Food habits are affected by food production and supply. Let us know the food habits of people in different Indian states.
(i) Andhra Pradesh : Rice, dry vegetable preparation, arhar dal , upma, dosa, rasam, curd, pickle etc.
(ii) Bihar : Rice chapati, sattu (flour of roasted gram), dal, baingan ka bharta (brinjal preparation), bachka (thin slices of vegetales coated with besan), bhujya (of potato and oninon), pappad, chutni etc.
(iii) Gujarat : Chapati, rice dal, vegetable preparaton, lassi (buttermilk), thepla (fried chapatis made of wheat flour), dhokla, khandvi etc.
(iv) Punjab : Roti, parantha, missi roti, butter, lassi (buttermilk), pulses, curd, sarson ka saag, chole, gajar ka halwa, dahi bhalla etc.
(v) Rajasthan : Bajra, dalia, roti, dal, kachori, sev (a besan preparation), vadi (moong dal preparation), dal-bati.
(vi) Tamil Nadu : Idli, dosa, rice sambhar, banana chips, etc.
What do Animals Eat?
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
* Functions of food :
• Food provides energy.
• Food helps in growth and development.
• Food helps in the replacement of worn out tissues, repair of damaged cells and healing of wounds.
• Food protects the body against diseases.
* Basal metabolic rate (BMR) : The smallest amount of energy that body needs to keep alive is called basal metabolic rate (BMR).

 TOPPERS ACADEMY FOR ACHIEVERS
TOPPERS ACADEMY FOR ACHIEVERS
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
