1. Introduction to The Decimals
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Decimals
Decimals are an extension of our number system For an example 5.75. Here the dot represents a decimal point. Decimals are fractions whose denominators are 10, 100, 1000 etc. A decimal has two parts, namely, the whole number part and decimal part.
Decimal Places : The number of digits contained in the decimal part of a decimal number is known as the number of decimal places.
For example :
3.75 has two decimal places and 85.325 has three decimal places.
Division of a unit in ten equal parts
If an object is divided into 10 equal parts then its each part is one tenth of the whole. It is written as ![]()
![]() is also written as 0.1 and is read as 'one tenth' or point one'.ss
is also written as 0.1 and is read as 'one tenth' or point one'.ss
Ex. 0.5 is read as 5 tenth. or point five.
It can be written as 2.3 and read as two point three.
Let us take an example, there is two tower each consist two blocks and each block is equal to one unit than tower represents 10 units. So, the number shown here is :
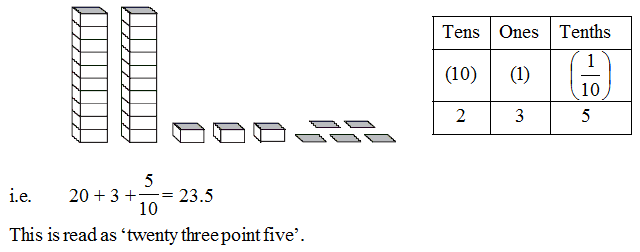
Representing Decimals on number line
We represented fractions on a number line. Let us now represent decimals too on a number line. Let us represent 0.6 on a number line. We know that 0.6 is more than zero but less than one. There are 6 tenths in it. Divide the unit length between 0 and 1 into 10 equal parts and take 6 parts as shown below :

Ex.1 Write the following numbers in the place value table : (a) 20.5 (b) 4.2
Sol.: Let us make a common place value table, assigning appropriate place value to the digits in the given numbers. We have,
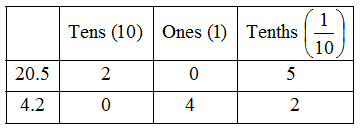
Ex.2 Write each of the following as decimals : (a) Two ones and five-tenths (b) Thirty and one-tenth

2. Decimals in Measurement
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Division of a unit in hundred equal parts
If an object is divided into 100 equal parts then its each part is one hundredth of the whole. It is written 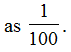

Let us look at some more place value tables.
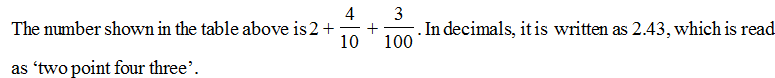
Ex.1 Given the place value table, write the number in decimal form.
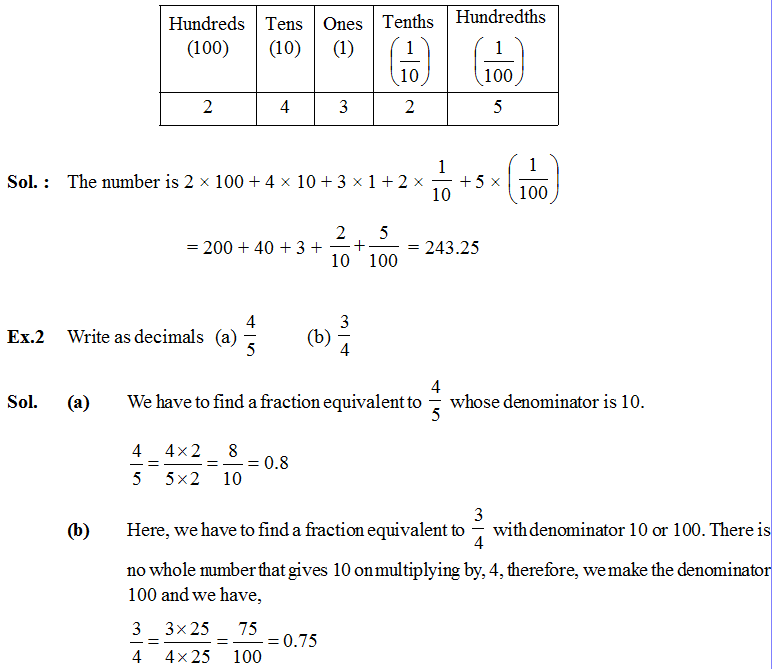
Ex.3 Write as fractions in lowest terms (a) 2.34 (b) 0.342
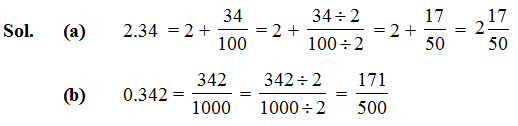
3. Addition and Subtraction of Decimals
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Comparing decimals
Decimal numbers may be compared by using the following steps :
Step I Obtain the decimal numbers.
Step II Compare the whole number parts of the numbers. The number with greater whole number part will be greater. If the whole number parts are equal, go to next step.
Step III Compare the extreme left digits of the decimal parts of two numbers. The number with greater extreme left digit will be greater. If the extreme left digits of decimal parts are equal, then compare the next digits and so on.
Ex.1 Which is greater of 48.23 and 39.35 ?
Sol. The given decimals have distinct whole number parts, so we compare whole number parts only.
In 48.23, the whole number part is 48.
In 39.35, the whole number part is 39.
∵48 > 39
∴ 48.23 > 39.35
Ex.2 Write the following decimals in ascending order :
5.64, 2.54, 3.05, 0.259 and 8.32
Sol Converting the given decimals into like decimals, we get :
5.640, 2.540, 3.050, 0.259 and 8.320
Clearly, 0.259 < 2.540 < 3.050 < 5.640 < 8.320
Hence, the given decimals in the ascending order are
0.259, 2.54, 3.05, 5.64 and 8.32
Using Decimals
Decimal properties can be used in variuos day to day examples
(1) Money
We know that 100 paise = M1
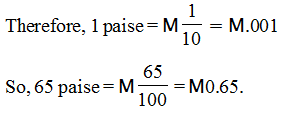
(2) Length : If we want to measure the length of the table in metres. We had a 50 cm scale.
We found that the length of the table top was 156 cm.
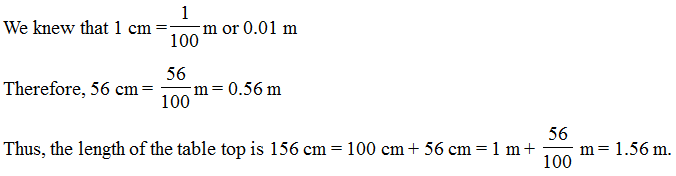
(3) Weight : We bought 500g potatoes, 250g capsicum, 700g onions, 500g tomatoes, 100g ginger and 300g radish. Then the total weight of the vegetables in the bag is given by
= 500 g + 250 g + 700 g + 500 g + 100 g + 300 g = 2350 g
Subtracting of Decimals
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Subtraction of Decimals
Addition and Subtraction of Decimals : Decimals can be added or subtracted by using the following steps:
Step I Convert the given decimals to like decimals (same decimal places).
Step II Write the decimals in columns with their decimal points directly below each other so that tenths come under tenths, hundredths come under hundredths and so on.
Step III Add or subtract as we add or subtract whole numbers.
Step IV Place the decimal point, in the answer, directly below the other decimal points.
Ex.1 Lata spent M9.50 for buying a pen and M2.50 for one pencil. How much money did she spend?
Sol.: Money spent for pen = M9.50
Money spent for pencil = M 2.50
Total money spent = M9.50 + M2.50
Total money spent = M12.00
Ex.2 Rahul bought 4 kg 90 g of apples, 2 kg 60 g of grapes and 5 kg 300 g of mangoes. Find the total weight of all the fruits he bought.
Sol.: Weight of apples = 4 kg 90 g = 4.090 kg
Weight of grapes = 2 kg 60 g = 2.060 kg
Weight of mangoes = 5 kg 300 g = 5.300 kg
Therefore, the total weight of the fruits bought is
4.090 kg
2.060 kg
+ 5.300 kg
11.450 kg
Total weight of the fruits bought = 11.450 kg.
Ex.3 Amit bought a Maths book for Rs. 45.60 and a geometry box for Rs. 62.55. What is the total amount spent by Amit ?
Sol. Money spent on Maths book = Rs. 45.60
Money spent on Geometry box = Rs. 62.55
∴ Total amount spent = Rs. 45.60 + Rs. 62.55 = Rs. 108.15
Ex.4 An empty box weighs 1 kg 240 g. When filled with oranges it weighs 19 kg 70 g. What is the weight of the oranges ?
Sol. Weight of empty box = 1 kg 240 g = 1.240 kg
Weight of box with oranges = 19 kg 70 g = 19.070 kg
∴ Weight of oranges = 19.070 kg – 1.240 kg = 17.830 kg.
Ex.5 A can can hold 12.5 litres of mixed fruit juice. 4.035 litres of apple juice and 6 litres 15 ml of orange juice have been poured in the can. What would be the amount of grape juice that can still be added in the can?
Sol. Amount of apple juice = 4.035 L
Amount of orange juice = 6 litres 15 mL = 6.015 L
Capacity of can = 12.5 L
∴ Reqd. amount of grape juice = 12.5 L – (4.035 + 6.015) L = 12.5 L – 10.050 L = 2.45 L
Multiplication & Dividing a decimal by a whole number
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Multiplication of a decimal by another decimal:
To multiply a decimal by another decimal, we follow following steps :
Step I Multiply the two decimals without decimal point just like whole numbers.
Step II Insert the decimal point in the product by counting as many places from the right to left as the sum of the number of decimal places of the given decimals.
Ex.1 Find the product of 9.2 and 6.07.
Sol. We have,
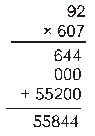
∴ 92 × 607 = 55844
Since the sum of the decimal places in the given decimals is 1 + 2 = 3.
So, the product must contain 3 places of decimals. Hence 9.2 × 6.07 = 55.844
Ex.2 Multiply 0.0345 by 0.0237
Sol. We have,
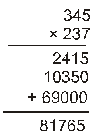
∴ 345 × 237 = 81765
We observe that the sum of the decimals in the given decimals is 4 + 4 = 8
So, the product must contain 8 places of decimals.
Hence, 0.0345 × 0.0237 = 0.00081765
Dividing a decimal by a whole number
A decimal can be divided by a whole number by using the following steps :
Step I Check the whole number part of the dividend.
Step II If the whole number part of the dividend is less than the divisor, then place a ‘0’ in the ones place in the quotient, other wise, go to step iii.
Step III Divide the whole number part of the dividend.
Step IV Place the decimal point to the right of ones place in the quotient obtained in step I.
Step V Divide the decimal part of the dividend by the divisor. If the digits of the dividend are exhausted, then place zeros to the right of dividend and remainder each time and continue the process.
Ex.1 Divide 93.45 by 15.
Sol. We have,
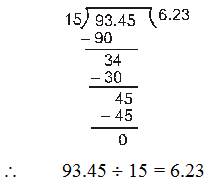
Ex.2 Divide 42.8 by 0.02
Sol. We have,
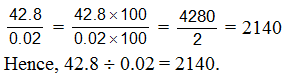
Ex.3 Divide 0.0024 by 0.04
Sol. We have,
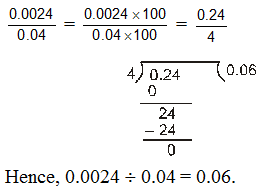
Ex4 The product of two decimals is 1.5008 . If one of them is 0.56, find the other.
Sol. Product of given decimals = 1.5008.
One decimal = 0.56.
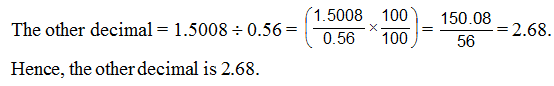

 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
 Param Publication
Param Publication
