1. Introduction to The Decimals
- Books Name
- Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Introduction to The Decimals
What is decimal?
The Numbers used to represent Numbers lower than unit 1 are called decimal numbers. The decimal point or the period plays a significant part in a Decimal Number. This period separates the fractional part and whole number part in a decimal number. Place value of a number can be defined as the value of a number as per the place of that number in a number. Decimals Exemplifications Let us consider a decimal number0.5694 to see the different place values of each number.
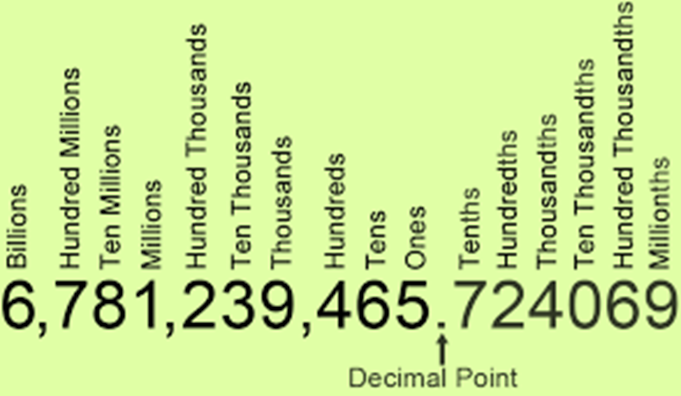
The value of the number at the first place after the decimal point is tenths place value. Tenths can be calculated as 1 unit divided in 10 equal corridor i.e. 0.1. Thus, considering this there are 5 tenths in the number0.5694.
The value of the number at the alternate place after the decimal point is hundredths place value. The number in that place tells you how numerous hundredths are there. Hundredths can be calculated as 1 unit divided in100 equal parts.i.e0.01. thus, considering this there are 6 hundredths in the number0.5694
The value of the number at the third place after the decimal point is thousandths place value. The number in that place tells you how numerous thousandths are present. Thousandths can be calculated as 1 unit divided in1000 equal corridor i.e. 0.001. Thus, considering this there are 9 thousandths in the number0.5694
Ten- thousandths
The value of the number at the fourth place after the decimal point is ten- thousandths place value. The number in that place tells you how numerous ten- thousandths are present. Ten- thousandths can be calculated as 1 unit divided into 10000 equal corridori.e0.0001. Thus, Considering this there are 4 thousandths in the number0.5694
For Example:
23/10 can be written in decimal as 2.3
23/100 can be written in decimal as 0.23
Knowing about Tenths
As we know that 1 cm = 10 mm, so if we have to find the contrary also
1 mm = 1/10 cm or one-tenth cm or0.1 cm.
Hence, the first number after the numeric represents the tenth part of the whole.
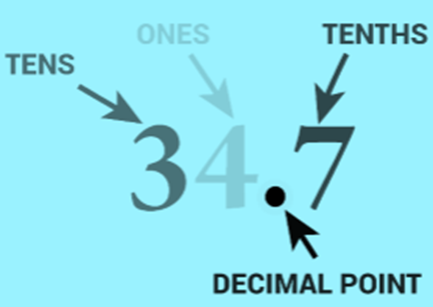
Tenths
This reads as “thirty-four point seven ”.
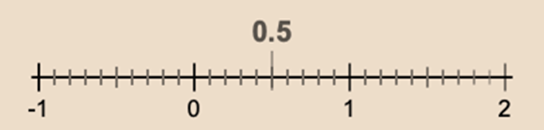
Representation of decimals on the number line,
Let us suppose we have to represent0.5 on the number line.
is lesser than 0 and lower than 1 also it can be represented on number line by dividing unit length between 0 and 1 into ten equal corridor and the fifth part will represent 0.5
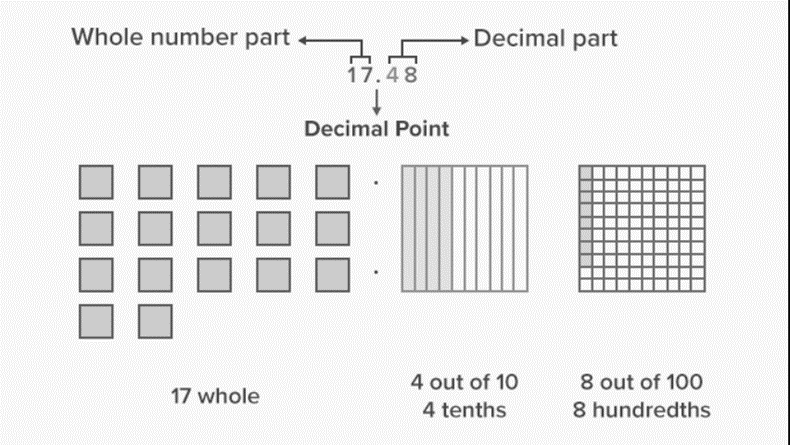
Knowing about Hundredths,
In Hundredth, one block is divided into 100 equal regions and each part comprises1/100 of the entire block.
If a square is divided into 100 small squares the area of each small square will be1/100 or one hundredth of the entire square.
The area of the lower square shaded red is one hundredth of the entire square.
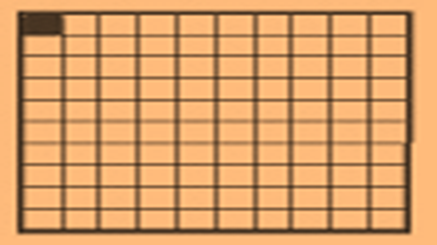
The decimal note is1/100 = 0.01.
Comparing decimals
While comparing two decimal numbers, we consider the following rules
We compare the place values of integers from left to the right.
Extra zeroes to the right of the last number of a decimal value do not change the value of the number.
Redundant depths between decimal point and a decimal number do not change its value.

Relationship between fractions and decimals
Numbers are values of fragments. Therefore, fragments can be converted into numbers and numbers can be converted into fragments.
Numbers as fragments
Conversion is done by seeing the place value of numbers.
In conversion to bit, the numeric can be written simply as a number with denominator having as numerous depths as the number of integers after the decimal point.
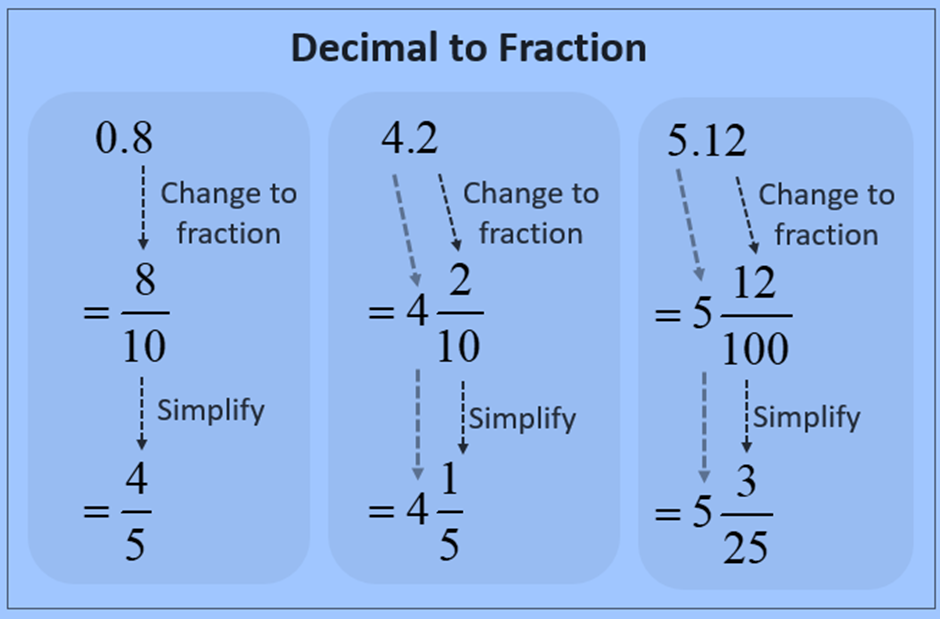
Problem Write the following as fragments in smallest forms.0.05
Result
Then 0 is at Ones place, 0 is at tenths place and 5 is at hundredths place.
= 0 * 1 0 *1/10 5 *1/100
= 0 05/100
= 5/100
= 1/20
There are two integers after the decimal point.
= 1/20
2. Decimals in Measurement
- Books Name
- Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Decimals in Measurement
Usage of decimals in money
Dealing with decimal numbers is certain, when dealing with money. In numerous situations, similar as when we have to convert paisa into rupee. Suppose we go to an original shop to buy 500 gm of turmeric, where, one kg of turmeric costs Rs. 51. So, how important Money should we hand over to the shopkeeper? We divide Rs. 51 by 2, which is equal to25.5. In order to hand over the exact quantum, we must understand what25.5 means in terms of rupees. Let us learn this with the help of a simple illustration.
1 Rs. = 100 paise
1 paise = 1/100 paise
1 paise = Rs. 0.01
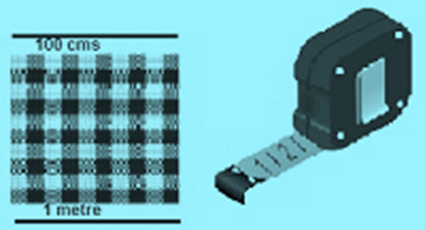
Usage of decimals in length
While measuring the length of an item, it is not necessary that the length of an object is a multiple of the given scale. For illustration, while measuring the length of a table with a metre scale, the length may not be a whole number; it may lie between two ladders on the metre scale. In similar situations, the decimal numbers are used.
1metre = 100 cms
1 cm = 1/100 m
1cm = 0.01 m
Usage of decimals in weight
We use decimal numbers while dealing with weight. For illustration, when we are buying a watermelon, it can not always weigh in whole numbers; it can be lower than 2 kg but further than 1 kg. In similar situations, the shopkeeper has to calculate how important to charge for a watermelon, grounded on its weight
1kg = 1000 grams
gram = 1/1000 kgs
1 gram = 0.001 kgs

3. Addition and Subtraction of Decimals
- Books Name
- Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Addition and Subtraction of Decimals
Addition of decimals,
Addition of numbers numbers is same as addition of whole numbers. The only difference is that we insure that all decimal points will be in same column before addition. We use the following way to add the numbers.
Write the integers of the given decimal numbers one below the other similar that all the decimal points are in the same perpendicular Line.
Add as you add whole numbers.

Subtraction of decimals
Deduction of numbers numbers is same as deduction of whole numbers. The only difference is to insure that all decimal points will be in same column before deduction.
We use the following way for deduction of numbers.
Write the two numbers numbers, writing the bigger number first in columns similar that the decimal points are in the same column and the integers having the same place values are in the same column.
Decrease the numbers (ignoring the decimal points) as in the case of whole numbers.
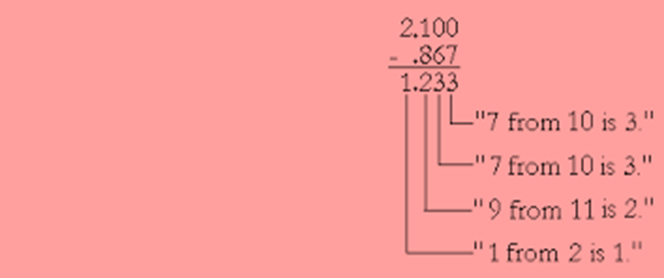
Put the decimal point in the result directly under the decimal points of the two given numbers.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
