1. Prime and Composite Numbers
- Books Name
- Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
CHAPTER - 03
PLAYING WITH NUMBERS
Prime and Composite Numbers
A Prime number is a number which has exactly two factors i.e. ‘1’ and the number itself. A composite number has more than two factors, which means piecemeal from getting divided by 1 and the number itself, it can also be divided by at least one positive integer. 1 isn't a prime or composite number. Except these two numbers, there's also same order of numbers which are co prime numbers.

Detailed explanations of these numbers are given below.
Prime Numbers

Illustration of Prime Number
3 is a prime number because 3 can be divided by only two numbers
i.e. 1 and 3 itself.
3/1 = 3
3/3 = 1
in the same way, 2, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17 are prime numbers.
Composite Numbers
A composite number has more than two factors, which means aside from getting divided by the number 1 and itself, it can also be divided by at least one integer or number. We don't consider ‘1’ as a composite number.

Illustration of Composite Number
12 is a composite number because it can be divided by 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 12. So, the number ‘12’ has 6 factors.
•12/1 = 12
•12/2 = 6
•12/3 = 4
•12/4 = 3
•12/6 = 2
•12/12 = 1
Types of composite Numbers
There are two types of composite Numbers
1. Even composite Numbers
2. Odd composite Numbers
Odd Composite Numbers
The odd positive integers or the odd Numbers that aren't prime Numbers are called odd composite Numbers. For illustration, 9, 21, 33, 45, etc., are odd composite Numbers.
Even Composite Numbers
The even Numbers that aren't prime Numbers are called even composite Numbers. For illustration, 4, 10, 16, 28, 56, etc., are even composite Numbers.

Sieve of Eratosthenes is a system to find the prime Numbers and composite Numbers from the group of Numbers. A Greek Mathematician Eratosthenes, in the third century B.C introduced this.
The Sieve of Eratosthenes system is easy to find the prime Numbers from a set of Numbers.
The way to find the prime Numbers
from 1 to 100 are as follows
Step 1 First write all the natural Numbers from 1 to 100,row-wise and column-wise as shown in the below figure.
Step 2 put a cross over 1, as it's neither a prime number nor a composite.
Step 3 Now, encircle the number 2(which is a prime number) and cross all the multiples of 2, similar as, and so on. Since all the multiples of 2 are composite.
Step 4 next, encircle the number 3, and put a cross over all the multiples of 3, similar as, etc. Since piecemeal from 3 all its multiples are composite.
Step 5 makes circle the number 5 and put a cross over all the multiples of 5.
Step 6 Now encircle 7 and cross all the multiples of 7
Step 7 Encircle 11 and cross all the multiples of 11
Step 8 Continue the process unless all the Numbers are moreover encircled or crossed.
Composite number is a number with any set of Numbers that don't have any other common factor other than 1. It's also known as fairly prime Numbers.
Properties of co-prime Numbers
• All prime Numbers are co-prime to each other.
• Any successive whole Numbers are always co-primed.
• Sum of any two co-prime Numbers is always co-primed.
•Co-prime Numbers need not be prime Numbers.

Twin prime are a match of prime numbers that differ by 2.
3.1 Factors and Multiples
The numbers that can be divided completely by another number is known as factor.
When a number is multiplied by a natural number then the number we get in result is called Multiple of that Number.
E.g. 18 is a multiple of 1,2,3,6,9,18 and
∴ 2,5 and 10 are the factors of 10.

2. Divisibility Rule
- Books Name
- Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Tests for divisibility of Numbers
Divisibility rule of 2 and 4?
We can tell if 2 divides into this number without a remainder by just looking at the last number-the last number is a 4.
This means that the number is Even and 2 will divide into it without a remainder is divided by 2.
The Rule for 2 any whole number that ends in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8 will be divided by 2.
A number is divided by 3 if the sum of the integers of the number is divided by 3.
The Rule for 4 if the last two integers of a whole number are divided by 4, also the entire number is divided by 4.
Tests for divisibility of numbers 5- 8,
The Rule for 5 Number that are divided by 5 must end in 5 or 0.
A number is divided by 6 if the number is divided by both 2 and 3.
A number is divided by 7 if the given number is divided by 7
The Rule for 8 if the last three integers of a whole number are divided by 8, also the entire number is divided by 8
Tests for divisibility of numbers 9- 11
A number is divided by 9 if the sum of the integers is divided by 9.
The Rule for 10 numbers that are divided by 10 need to be even and divided by 5, because the prime factors of 10 are 5 and 2. Primarily, this means that for a number to be divided by 10, the last number must be a 0.
A number is divided by 11 if the sum of the integers is divided by 11.
Some results on divisibility rule

3. LCM and HCF
- Books Name
- Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Common factors and common multiples
What are Multiples?
Multiple is a result attained by multiplying a number by an integer (it should not be a bit). By taking out the product of the counting numbers and that of whole numbers the multiples of the whole number are attained. For illustration, if we
multiply number 6 by 1,number 6 by 2, number 6 by 3, and so on then we can find the multiples of number 6,
The multiples are the product of this addition. Every multiple of a number is lower than or equal to that number.
The number of multiples of given number is infinite
Common Multiple: common multiples of numbers are the
Multiple of numbers that are common to two numbers .
Common Factors: Factors that are common to two or more numbers are known as their common factors.
Factors of 30 and 45 are –
30 = {1, 2, 3, 5, 10, 15, and 30}
45 = {1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 45}
1, 3, 5 and 15 are the Common factors of 30 and 45.
For illustration, the factors of 20 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, and 20.
For illustration, the multiples of 20 are 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, etc.
- Some more divisibility rules
If the number of integers of a number is even, also add the first number and subtract the last number from the rest of the number.
Example 3784
Number of integers = 4
Now, 78 3 – 4 = 77 = 7 × 11
Therefore, 3784 is subtract by 11
If the number of integers of a number is odd, also subtract the first and the last integers from the rest of the number.
Illustration 82907
Number of integers = 5
Now, 275 × 11 = 290 – 8 – 7
Therefore, 82907 are subtracting by 11.
Form the groups of two integers from the right end number to the left end of the number and add the even groups. However, also the number is subtracting by 11, if the sum is a multiple of 11.
Example 3774 = 37 74 = 111 = 1 11 = 12
3774 isn't subtracted by 11.
253 = 2 53 = 55 = 5 × 11
253 is subtracting by 11.
Subtract the last number of the number from the rest of the number. However, also the original number will be subtracting by 11, if the attendant value is a multiple of 11.
Example 9647
964 – 7 = 957 = 9647
95 – 7 = 88 = 8 × 11 =957 =
Therefore, 9647 is subtracted by 11.
Divisibility Rule of 12
Still, also the number is subtracting by 12 exactly, If the number is subtract by both 3 and 4.
Illustration 5864
Sum of the integers = 5 8 6 4 = 23 (not a multiple of 3)
Last two integers = 64(subtract by 4)
The given number 5846 is subtracting by 4 but not by 3; hence, it isn't subtract by 12.
Divisibility Rules for 13
For any given number, to check if it's subtract by 13, we've to add four times of the last number of the number to the remaining number and repeat the process until you get a two-number number. Now check if that two-number number is subtracting by 13 or not. However, also the given number is subtracting by 13, if it's subtract.
For illustration 2795 → 279(5 x 4)
→ 279(20)
→ 299
→ 29(9 x 4)
→ 29 36
→ 65
Number 65 is subtracting by 13, 13 x 5 = 65.
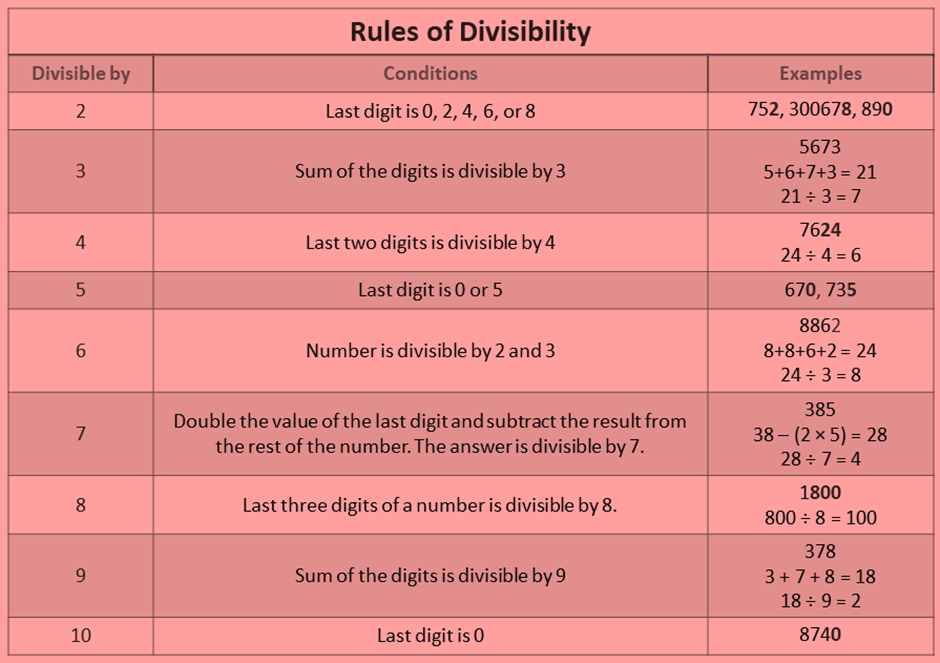
Prime Factorisation
Prime factorization is to write a composite whole number as the product of prime numbers only.
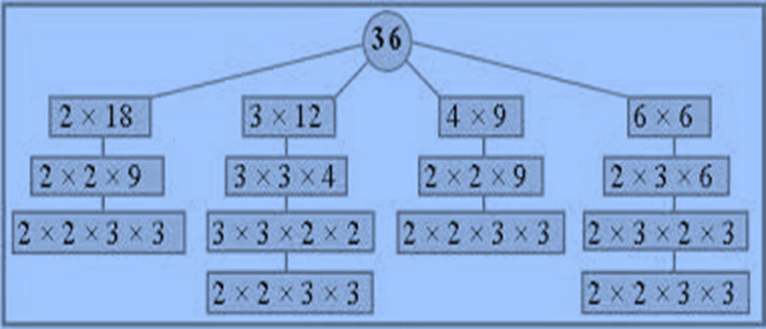
Highest common factor
HCF) of two or more given Numbers is the Highest (or topmost) of their common factors. It's also known as Greatest Common Divisor (GCD).
The topmost common factor of given numbers is called H.C.F.
To find the HCF of two or more Numbers, we can use any of the given system.
1. Common factor system
2. Prime factorization system
Lowest Common Multiple
The smallest common multiple of given numbers is called L.C.M.
L.C.M. of two or more high numbers is equal to their addition.
L.C.M. of two or more high numbers is equal to 1.
Every numbers have the smallest common factor number is always 1.

Problems on HCF and LCM


 Param Publication
Param Publication
 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
