1. Numbers: Comparing, Shifting Digits, Revisiting Place Value and Large Numbers
- Books Name
- MD AFZAL AHMAD Mathematics Book
- Publication
- MD AFZAL AHMAD
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics

Introduction:-
Counting Numbers: -The numbers which we can count. Like 1, 2, 3, 9, 37 etc.
Natural Numbers: -The numbers which we can count and it starts from 1 and goes on. Like 1, 2, 3, 4, …….100, …….2000, …………... etc.
Whole Numbers: -The counting numbers which starts from Zero are called whole numbers and goes on. Like 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …….100, …….2000, …………... etc.
Integers: -Integers are the collection of whole numbers and negative numbers. Integers can be positive numbers, Zero and negative numbers but it cannot be a fraction. Like -229, -85, -16, -5, -1, 0, 1, 5, 29, 219, 5000 etc.
Even Numbers: -The numbers which are completely divisible by 2. It means those numbers which we divide by 2, remainder becomes Zero (0). Like 2, 4, 6, 22, 100, 294, 604 etc
Smallest Even number is 2.
Odd Numbers: - The numbers which are not completely divisible by 2. It means those numbers which we divide by 2, remainder becomes One (1). Like 1,3, 5, 7, 21, 101, 299, 1001 etc
Smallest Odd number is 1.
Composite Number: -A composite number is a natural number or positive integers which has more than two factors.
It means the given number is completely divisible by more than two numbers. Like 6, which is completely divisible by 1, 2, 3 and 6. It means 6 has four factors.
Example: - 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 256 etc.
Smallest composite number is 4.It has three factors, these are 1,2, 4.
Prime Number: -A prime number is a natural number that is completely divisible by 1 and the number itself. Prime number has only two factors these are 1 and the number itself.
Like 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47 etc.
Smallest prime number is 2.
Twin Prime Number: -Two prime numbers are called twin prime, if there is present only one composite number between them.Like {3,5}, {5,7}, {11,13}, {17,19}, {29,31}, {41,43} etc. Two consecutive prime number can be twin primes.
{2,3} is not a twin prime number, because there is no composite number in between them.
Co-prime Number: -Two numbers are co-prime, if they have no common factor other than 1 or we can say that the HCF (Highest Common Factor) of these numbers is 1.Like {1,3}, {4,5}, {13,31}, {18, 35}, {15,17}, {29,30}.
It is not necessary that these numbers should be prime.
2. Large Numbers in Practice
- Books Name
- MD AFZAL AHMAD Mathematics Book
- Publication
- MD AFZAL AHMAD
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Roman Numbers
Roman Numbers are one of the earlier system of writing numbers. Like I, II, III, IV, V etc.
The Roman Numerals:
I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X These Roman numbers denote 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 respectively.
Some more Roman Numbers

Rules for the Roman Number System:
1) If a symbol is repeated, its value is added as many times as it occurs.
Like, II is equal to 2, III is 3, XX is 20, XXX is 30, CC is 200, MM is 2000, MMM is 3000 etc.
2) A symbol is not repeated more than three times. But the symbol V, L, D are never repeated.
3) If a symbol of smaller value is written to the right side of a symbol of greater value, its value gets added to the value of greater symbol. Like,
VI = 5+1 =6 VII= 5+2= 7 XIII= 10+3= 13 LXV= 50+10+5= 65CLX= 100+50+10=160
4) If a symbol of smaller value is written to the left of the symbol of greater value, its value is subtracted from the value of greater symbol.
IV = 5-1= 4 IX= 10-1= 5 XL= 50-10= 40 XC= 100-10= 90 CD= 500-100= 400
5) The symbols V, L and D are never written to the left of a symbol of greater value, i.e. V, L and D are never subtracted.
The Symbol I can be subtracted from V and X only.
The symbol X can be subtracted from L, M and C only.
Roman Numbers using these rules
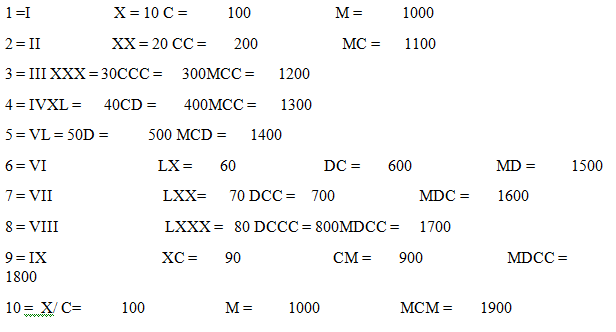
Some Solved Examples.
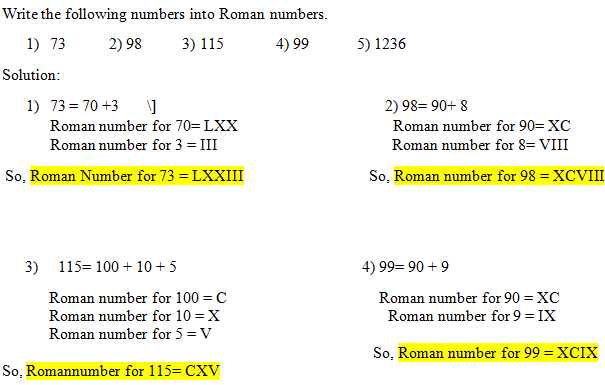
5) 1236 = 1000 + 200 + 30 + 6
Roman number for 1000 = M
Roman number for 200 = CC
Roman number for 30 = XXX
Roman number for 6 = VI
So, Roman number for 1236= MCCXXXVI
Comparing Numbers
- Books Name
- MD AFZAL AHMAD Mathematics Book
- Publication
- MD AFZAL AHMAD
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Comparing Numbers
How to compare numbers:
We do compare numbers by seeing which number is larger or which one is smaller.
Let we have numbers like 7,1, 3, 9, 5.
By seeing we can say, here 1 is the smallest number and 9 is the largest number.
Examples:
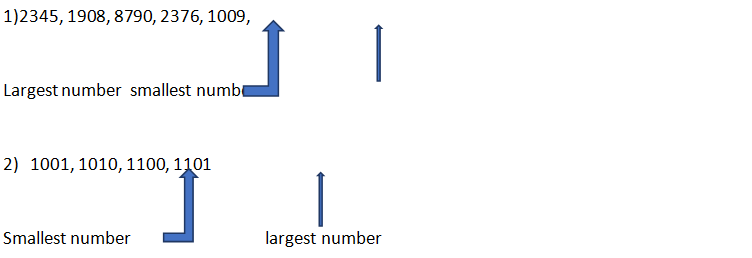
Rules to compare numbers
1. Count the number of digits. Number with more digits is greater.

How many numbers can we make from given number of digitswithout repeatation of digits.
Let we have four digits, like 5, 3, 4, 6. We want to make four different numbers using these digits without any repeatation.
These four numbers are 3,456, 4,356, 5,346 , 6,543
Here, Smallest number is 3,456 and largest number is 6,543.
Arranging Numbers.
Ascending Order:-Arrangement of numbers from smallest to greatest
Example:- 17<19<35<102
Descending Order:-Arrangement of numbers from greatest to smallest
Example:- 102> 35>19>17

 Success Academy
Success Academy
 Carrier Point
Carrier Point
 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
