1. Numbers: Comparing, Shifting Digits, Revisiting Place Value and Large Numbers
- Books Name
- Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
CHAPTER -1
KNOWING THE NUMBERS
Comparing Shifting Digits, Revisiting Place Value and Large Numbers
Numbers are compared to check which Number is Greater or smaller than the other number. There are different ways to know that a number is smaller or Greater.
These are:
If the numbers used in the question is different. The number having next number is smaller and the other number is Bigger.
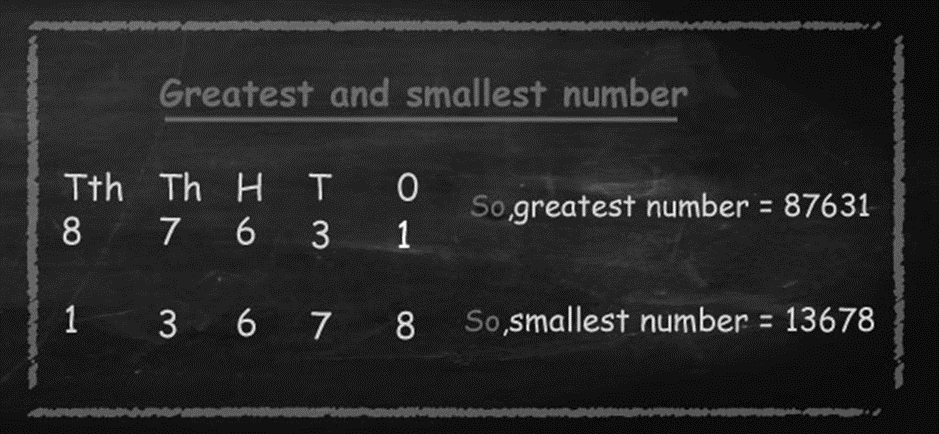
For Example: 1. Find out Greatest Number from 125 and 120.
Solution: 125 is bigger number and 120 is smaller Number. Hence the number 125 is greatest.
2. Find out greatest and smallest number from 320, 1340, 158, 228, 5446, and 4525
Solution: Here 5446 is the greatest and 158 is the smallest.
If the number of digits is equal than the number at the greatest place is compared.
If the integers at the greatest place are different, the greater value is larger number and the smaller value is the smaller number.
For Example: 1.Compare 285 and 685,
Solution: The numbers of integers are same, but number at greatest (then hundreds) place, is 2 and 6. Since 6 is greater number than 2, hence 685 is greater and 285 is smaller.
If the integers at the greatest place are equal, then another place is compared and so on.
For Example: 1. Compare 353 and 335.
Solution: The number of integers and number at greatest place are same then we will check the second greatest number place and compare both the numbers. Since 5 is advanced than 3. Therefore 353 is greater number and 335 is smaller number
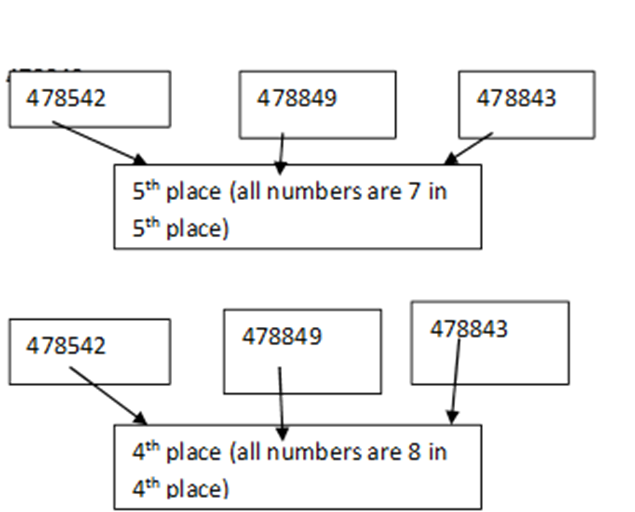
2. Compare among 478542, 478849 and 478843.
Solution: There are same number of integers and number at the greatest integers places are same for last three positions (4th place numbers are same for all the numbers), (5th place numbers are same for all the numbers) and (6th place numbers are same for all the numbers) and 2nd place is also same for all the numbers).3rd place number is same for
Second and third digit. So now we will compare first digit 3rd place number with another two numbers third place. Since 8 is bigger than 5.
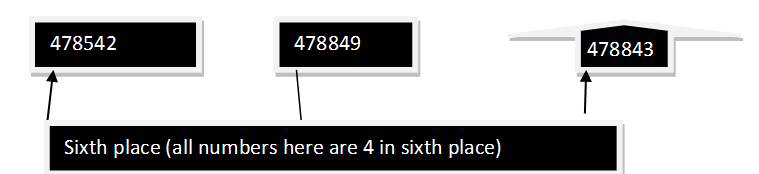

Numerals
One of the early systems of writing numbers is the system of Roman Numerals. This system is still used in different places. For Example, we can see the use of Roman Numerals in Clock. It's also used in classes for the School time table.
Roman Numerals are expressed by seven letters of the Alphabets.
Rules of the System
The Roman Numerals I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X denote number 1 to 10 . Then
XI for 11,
XII for 12 … till XX for 20.
VI = 5 +1 = 6,
XII = 10 +2 = 12 and
LXV = 50 +10 + 5 = 65
2. Large Numbers in Practice
- Books Name
- Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Large Numbers in Practice
Large Numbers can be shown using the place value. It goes in the thrusting order as shown below
8 integers 7 integers 6 integers 5 integers 4 integers 3 integers
centimeter( cm) in used as a unit of dimension of length. We can use this unit for measuring the length of a pen, the range of a book or note booket. but this unit is too big to measure the consistence of a pen. So, we use another unit named as millimeter( mm). Also, centimeter and millimeter are veritably small units to measure the length of the wall or a room. We use another unit named as meter for the same. Indeed meter is too small unit when we state the distances between two municipalities or metropolises. For this we need kilometers( km).
The relations between units are
1 kilometer = 1000 meters( m)
1 meter = 100 centimeters( cm)
1 centimeter = 10 millimeters( mm)
Also, we have
100 cm = 1 m = 10mm × 100 = 1000 mm
1000 m = 1Km = 1000 × 100 cm = 100000 cm
100000 cm =1 km = 100000 × 10 mm = 1000000 mm
10 Million = 1 crore
1 million = 10 lakhs
(100,000) Hundred Thousands = 1 lakh
(10,000)Ten Thousands = Thousands Hundreds (1000,000)
We borrow the following rules to compare two large figures
Rule- 1 The number with further integers is lesser than the number with lower integers.
Rule- 2 When two figures have the same number of integers, compare the integers at the leftmost places. The number with the lesser number is lesser. If the integers at the leftmost places are the same also compare the coming integers and so on.
3. Estimation of Numbers
- Books Name
- Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Estimation
The estimation of a number is a reasonable approximation of the real value. Estimation means approaching an amount to the closeness needed. This is done by rounding off the figures involved and getting a quick and rough answer.

Rounding off a number to the nearest tens numbers
The numbers 1, 2, 3, 4 are nearest to 0. So, these numbers are rounded off to smaller ten. The numbers 6, 7, 8, 9 are nearest to 10. So, these numbers are rounded off to the bigger tens. The number 5 is nearest from both 0 and 10, so it's rounded off to the advanced ten.
e.g.
(i) We round off 41 to the nearest ten as 40
(ii) We round off 67 to the nearest ten as 70
(iii) We round off 55 to the nearest ten as 60
Rounding off a number to the nearest hundreds number
The numbers 201 to 249 are closer to 200. So, these numbers are rounded off to the nearest hundred i.e. 200. The numbers 251 to 299 are closer to 300. So, these numbers are rounded off to the advanced hundred i.e. 300. The number 250 is rounded off to the advanced hundred.
(i) We round off 678 to the nearest 100 as 700.
(ii) We round off 510 to the nearest 100 as 500.
Rounding off a number to the nearest thousands number
Also, 1001 to 1499 are rounded off to the lower thousand i.e. 1000, and 1501 to 1999 to the advanced thousand i.e. 2000. The number 1500 is equidistant from both 0 and 1000, and so it's rounded off to the advanced thousand i.e. 2000.
(i) We round off 3574 to the nearest thousand as 4000.
(ii) We round off 8105 to the nearest thousand as 8000.
Estimation of sum or difference
When we estimate sum or difference, we should have an idea of the place to which the rounding is demanded.
e.g.
(i) Estimate 5798 + 29834
We can say that 29834 > 5798
We shall round off the figures to the nearest thousands.
29416 is rounded off to 30000
5679 is rounded off to 6000
Estimated sum
49000 + 3000 = 52000
(ii) Estimate 2476 – 946
We shall round off these figures to the nearest hundreds.
2476 is rounded off to 2000
946 is rounded off to 1000
Estimated difference
2000 – 1000 = 1000
Estimation of the product
To estimate the product, round off each factor to its topmost place, also multiply the rounded off factors.
Estimate 82 x 578
The first number, 82, can be rounded off to the nearest ten as 80.
The alternate number, 678, can be rounded off to the nearest hundred as 700.
Hence, the estimated product = 80 x 700 = 56000.
Using Brackets
Brackets help in simplifying an expression that has multiple operations. If any statement that includes the brackets is there, then perform the operation inside the bracket first and simplify each number in to a single number. Then carry out the operation that is outside the bracket.
e.g.
1. (6 8) x 10 = 14 x 10 = 140
2. (8 3) (9-4) = 11 x 5 = 55
Expanding Brackets
The use of classes allows us to follow a certain procedure to expand the classes totally.
E.g.
8 x 109 = 8 x (100 9) = 8 x 100 8 x 9 = 800 72 = 872
105 x 108 = (100 +5) x (100 + 8)
= (100+ 5) x 100 (100 + 5) x 8
= (100 x 100) (5 x 100) (100 x 8) (5 x 8)
= 10000 500 800 40
= 11340.
Brackets are used to reduce the confusion while solving the questions like add, subs tract, multiply and divide. For solving a bracket statement, first estimate and make a single number in the bracket and also estimate the outside part.
Problem:
(3+ 4) x 5 = (7) x 5 = 7 x 5 = 35
This shouldn't be calculated as (3 4) x 5 = (3) 4x5.
Classes are expanded to estimate individual integers inside the classes with the integers outdoors.
(3+ 4) x 5 = 3 x 5 4 x 5 = 15 20 = 35
Problem: Write the expressions for each of the following using classes.
Expression using words
Expression using Figures and classes
The number six is multiplied by the sum of seven and three
6 x (7 +3) OR (7 +3) x 6
Divide the subtraction of eighteen and six by four
(18-6)/ 4
Divide eighty five by four times the sum of five and four
85/ ((4 +5) x 4)


 Success Academy
Success Academy
 Carrier Point
Carrier Point
 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
