- Books Name
- MD AFZAL AHMAD Mathematics Book
- Publication
- MD AFZAL AHMAD
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
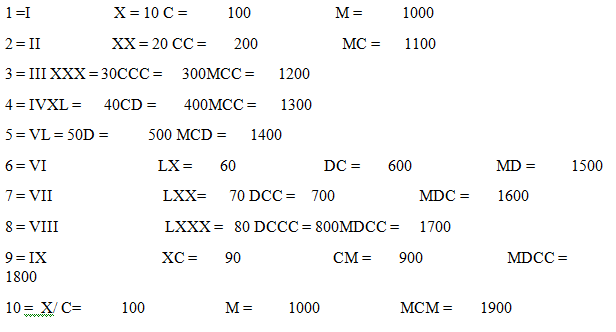
Roman Numbers
Roman Numbers are one of the earlier system of writing numbers. Like I, II, III, IV, V etc.
The Roman Numerals:
I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X These Roman numbers denote 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 respectively.
Some more Roman Numbers

Rules for the Roman Number System:
1) If a symbol is repeated, its value is added as many times as it occurs.
Like, II is equal to 2, III is 3, XX is 20, XXX is 30, CC is 200, MM is 2000, MMM is 3000 etc.
2) A symbol is not repeated more than three times. But the symbol V, L, D are never repeated.
3) If a symbol of smaller value is written to the right side of a symbol of greater value, its value gets added to the value of greater symbol. Like,
VI = 5+1 =6 VII= 5+2= 7 XIII= 10+3= 13 LXV= 50+10+5= 65CLX= 100+50+10=160
4) If a symbol of smaller value is written to the left of the symbol of greater value, its value is subtracted from the value of greater symbol.
IV = 5-1= 4 IX= 10-1= 5 XL= 50-10= 40 XC= 100-10= 90 CD= 500-100= 400
5) The symbols V, L and D are never written to the left of a symbol of greater value, i.e. V, L and D are never subtracted.
The Symbol I can be subtracted from V and X only.
The symbol X can be subtracted from L, M and C only.
Roman Numbers using these rules
Some Solved Examples.
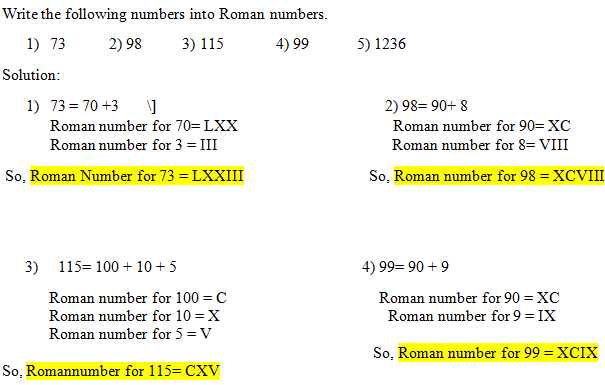
5) 1236 = 1000 + 200 + 30 + 6
Roman number for 1000 = M
Roman number for 200 = CC
Roman number for 30 = XXX
Roman number for 6 = VI
So, Roman number for 1236= MCCXXXVI

 Carrier Point
Carrier Point
 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
