Adolescence and Puberty
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Adolescence and Puberty
- Animals, as well as human beings, can reproduce only after a certain age or period in their lives after growing up into an adult.
- This is because of changes in hormones in their bodies that make them capable of reproduction.
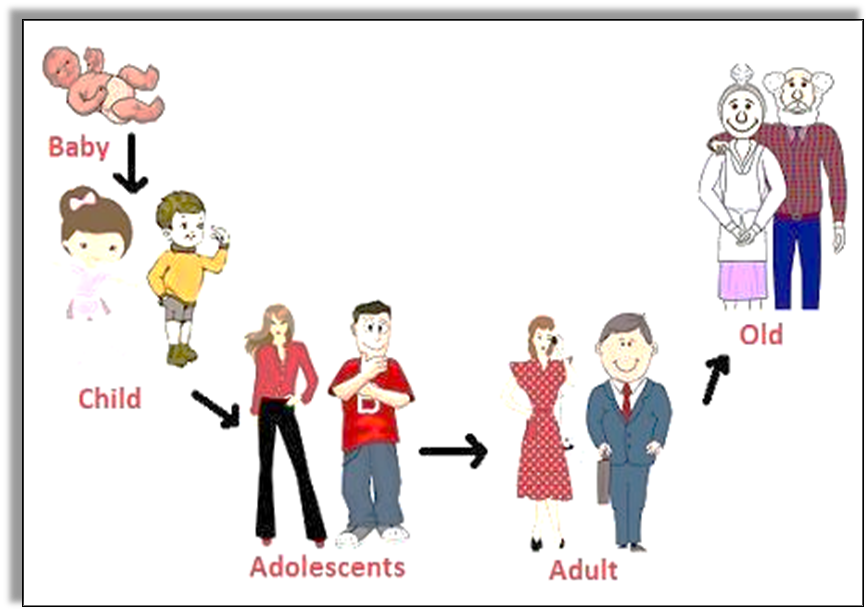
Puberty and Adolescence:
Puberty is the time in which sexual and physical characteristics mature. The exact age of puberty depends on several different things such as genes, nutrition and gender.
Puberty: The period of adolescence during which an adolescent reaches sexual maturity and becomes capable of reproduction.
Adolescence is the period between puberty and adulthood (generally between 11 and 19 or teenage). Puberty ends when an adolescent reaches reproductive maturity.
What is Adolescence?
- It is a period in life when the body leads to reproductive maturity and experiences some changes.
- This period may vary in different individuals.
- The adolescence period includes the teenage and therefore adolescents are often called Teenagers as well.
- Adolescence: It is the period of life, when the body changes, leading to reproductive maturity.
- It begins around the age of 11 and lasts up to 18 or 19 years of age. Adolescents are also called teenagers.
- In girls, adolescence begins a year or two earlier than boys, the period of adolescence varies from person to person.

What is Puberty?
- Puberty is the period in life when animals and human beings become capable of reproduction.
- The changes that occur in the body during the adolescent age are an indication that an individual is reaching puberty.
Changes at Puberty
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Changes at Puberty
What changes occur in humans at puberty?
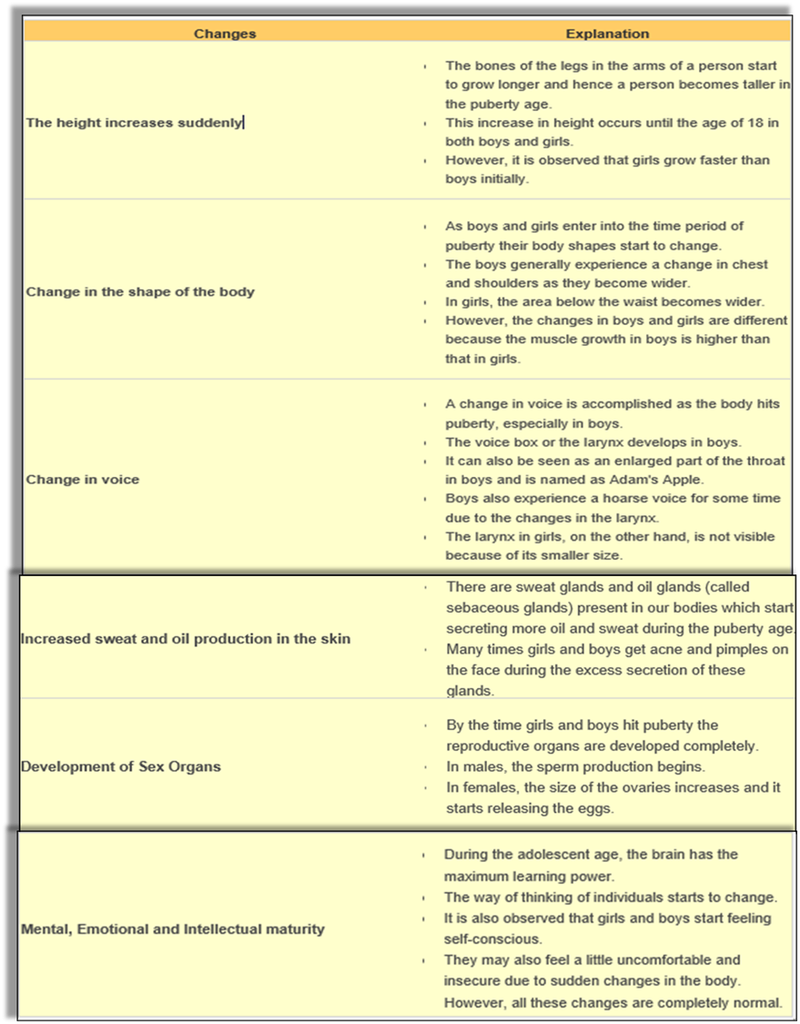
CHANGES AT PUBERTY
- Increase in Height: The most conspicuous change is a sudden increase in height of a person during puberty due to elongation of the bones of arms and legs. Initially girls grow faster than boys; both reach maximum height by the age of around 18 years.
Formula for calculating full height (cm) = Present height(cm)/ % of full height at this age X 100
- Changes in body shape: In boys, the shoulders generally broaden and muscles of the body grow more prominently than in girls.
For girls, the region below the waist becomes wider and less growth of muscles.
- Voice change: Voicebox or larynx in boy develops into larger in size.
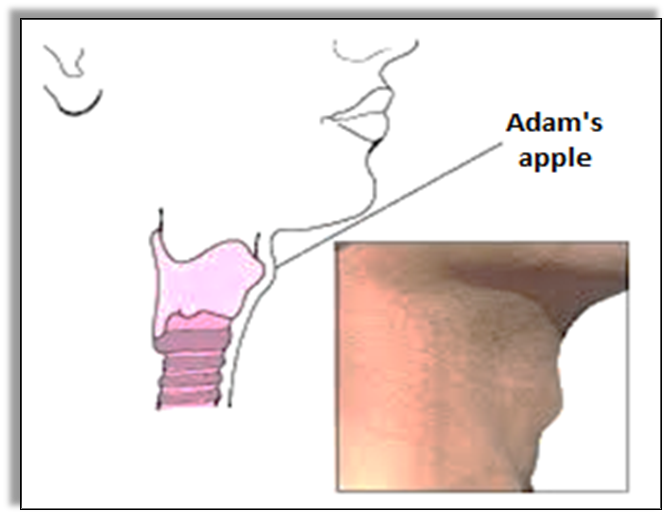
It can be seen as protruding part of the throat as ADAM'S APPLE.
In girls, the larynx is hardly visible due to smaller size in growth. Boys have deep voices whereas girls have high pitch voices.
- Increased activity of sweat and sebaceous glands: During puberty, there is an increase in the secretion of sweat glands and sebaceous glands which may lead to the appearance of acne and pimples.
- Development of sex organ : At puberty, male sex organs like the testes and penis develop completely and begin to produce sperms. In girls, the ovaries enlarge and start releasing eggs or ova.
- Reaching mental, intellectual and emotional maturity: During adolescence, they tend to think more. Feel insecure when while trying to adjust to the changes in mind and body. During adolescence, a person's brain has the greatest capacity for learning.
What happens due to a sudden increase in height of adolescents?
- It may not happen that all the parts of the body would grow at the same rate at this age.
- Hence, sometimes the legs and arms of teenagers appear oversized or not in proportion to their bodies.
- But with time everything comes in proportion.
Why height of family members is generally similar?
- The height of a person is a characteristic that they receive from their parents.
- Hence, in general, the height of a person is similar to the height of a family member.
- But it is also recommended that adolescents should eat a proper diet that is rich in vitamins, minerals and other nutrients that can help in their growth.
Secondary Sexual Characters
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
SECONDARY SEXUAL CHARACTERS
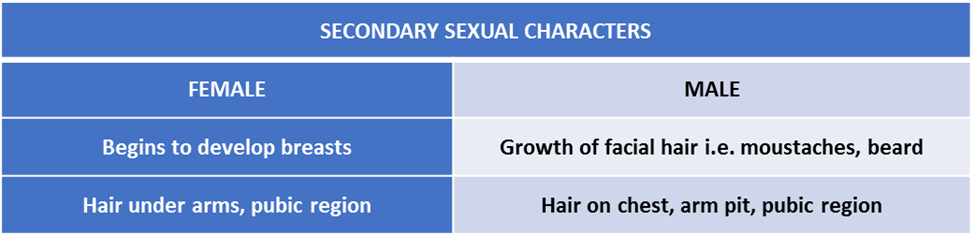
- A character that develops during adolescence and helps to distinguish the male from the female is known as a secondary sexual character. Some of these characters are as listed below
- Hormones are chemical substances secreted by the endocrine system/ endocrine glands (Ductless gland i.e. endocrine glands release hormone directly into the bloodstream to reach a particular body part/TARGET SITE).
- Hormones control the changes during adolescence. The pituitary gland (found attached to the brain) secretes hormones which in turn control the production of hormones from other endocrine glands.
What are Secondary Sexual Characters?
- At puberty, some changes occur in both males and females that distinguish them from each other. The features that develop in them are called Secondary Sexual Characters.
- In boys some secondary sexual characters are:
- Facial hair growth.
- Growth of hair on the chest, under the arms and pubic area.
- Some secondary sexual characteristics in girls are:
- Development of breasts.
- The growth of hair under the arms and the pubic area.
Role of Hormones in Initiating Reproductive Function
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Role of Hormones in Initiating Reproductive Function
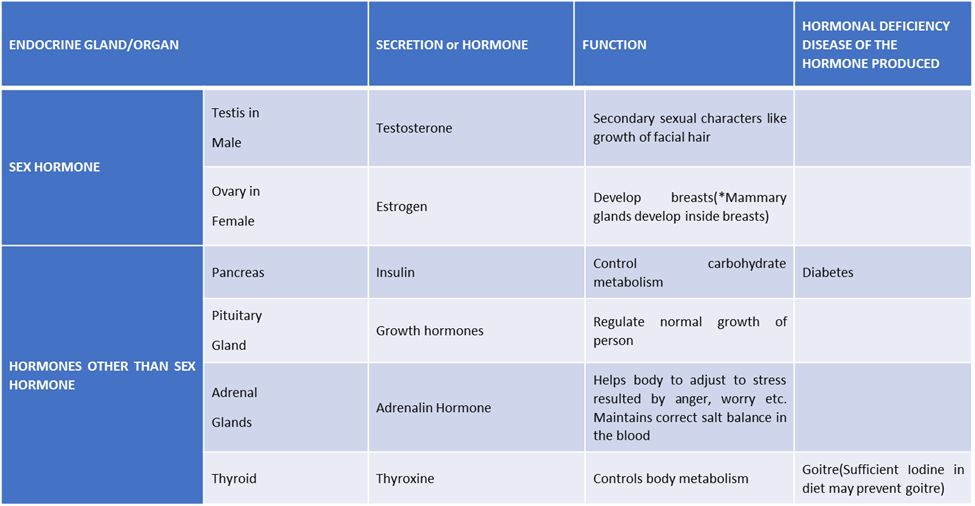
Pituitary gland – growth hormone - Needed for normal growth of a person, controls secretion of other glands.
Thyroid gland – thyroxine - Needed for metabolism. Its deficiency causes goiter. In frogs, it controls metamorphosis (In insects also, hormones control metamorphosis).
Pancreas – insulin - Needed for sugar breakdown. Deficiency causes diabetes.
Adrenal glands – adrenaline - Needed for adjustment to stress, maintain the salt balance of the body.
Ovaries – estrogen - (secondary sexual features in females, egg production).
Testes – testosterone - (secondary sexual features in males, sperm production).
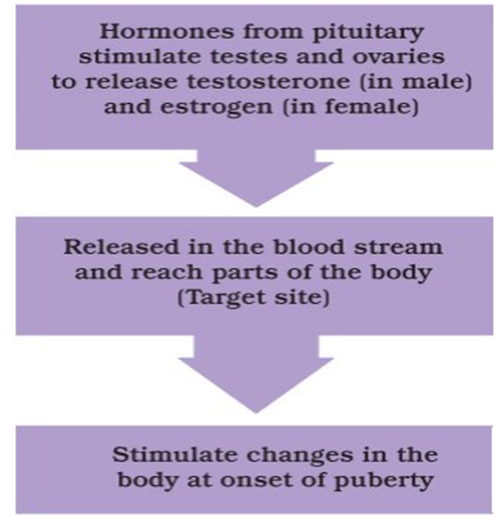
What are Hormones?
Hormones
The chemical substances secreted by endocrine glands are known as hormones. They control the changes occurring in adolescence. The onset of puberty is controlled by sex hormones.
Role of Hormones during Adolescence:-
The pituitary gland releases hormones to stimulate testes in males and ovaries in females.
Testosterone and Estrogen (Produced by testes and ovaries respectively) are released into the bloodstream which reaches the target site and produces puberty changes.
- There are endocrine glands present in humans with secrete chemical substances in the body is called the Hormones. These chemical substances are responsible for changes in the human body at the time of puberty.
- The hormones act as messengers and are responsible for transporting signals from one cell to another. Hence they evoke responses from various organs of the body and tissues. Hormones have certain properties or characteristics such as:
- They are secreted by the endocrine glands.
- They circulate in the body fluids.
- They are responsible for regulating the behavior of the target cells.
- They cause long-term effects in the body like change in behavior, change in growth, development of organs, puberty menopause, etc.
- Hormones are secreted in limited quantities from time to time whenever they are required by the body.
- Different glands present in the body are responsible for the secretion of different hormones.
- The nervous system regulates the flow of hormones in the body.
- The endocrine glands are also called Ductless Glands because they secrete the hormones directly into the blood. In males, the testes secrete the male hormones or testosterone. In females, the ovaries secrete the female hormones or Estrogen.
What are Pituitary glands?
- There are pituitary glands present in the body switch control the production of the hormones by endocrine glands in both males as well as females.
- The part of the body for which a particular hormone is meant is called the Target Site.
- The endocrine glands secrete the hormones in the blood and it reaches the target site. Then the target site response accordingly.
Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
REPRODUCTIVE PHASE OF LIFE IN HUMANS
- Adolescents become capable of reproduction when their testes and ovaries begin to produce gametes.
Reproductive Phase in Females
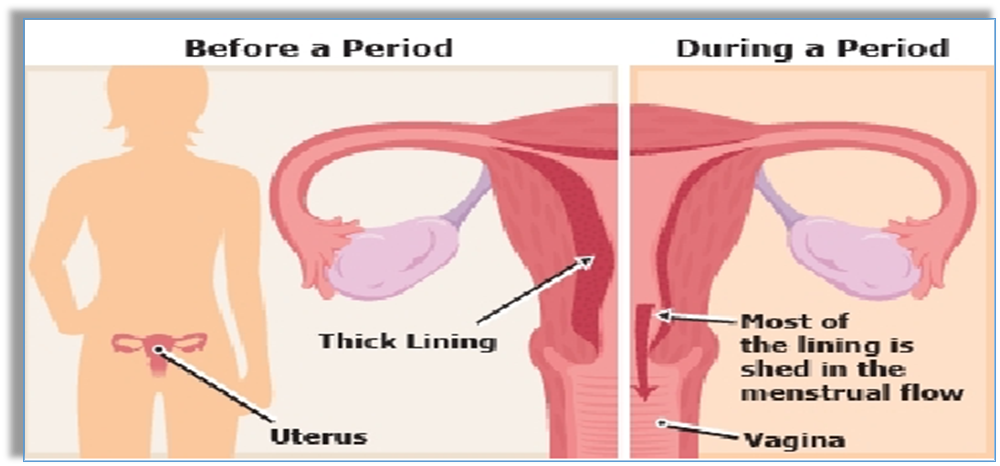
- In Females, the reproductive phase of life begins at puberty (10-12 years of age and generally lasts till the age of approx 45-50 years).
- Ova matures and is released by one of the ovaries once in about 28-30 days. A fertilized egg develops pregnancy.
- Unfertilized eggs along with the thickened lining of the uterus and blood vessels are shed off in the form of bleeding in women once in about 28-30 days is termed MENSTRUATION.
- Initial menstrual flow begins at puberty and is termed MENARCHE.
- Stoppage of the menstrual cycle at 45-50 years of age is called MENOPAUSE.
The ability of production of gametes in humans lasts until a certain time period only. This time period varies between males and females.
- It begins from the age of 10 to 12 years and lasts until the age of 45 to 50 years.
- When females hit puberty, the eggs or ova start getting mature.
- One of the ovaries then releases the mature ovum around 28 to 30 days.
- The wall of the uterus at this time, when the egg is released, becomes thick to hold the egg in case fertilization occurs and the egg develops.
- When the fertilization does not take place, the lining of the uterus sheds along with the egg and the blood vessels.
- This results in menstruation or bleeding in females.
- The first menstrual flow occurs at puberty and is called the Menarche.
- When the menstrual flow stops, it is termed Menopause.
- The whole menstrual cycle occurs because of female hormones.
How is the Sex of the Baby Determined?
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
How is the Sex of the Baby Determined
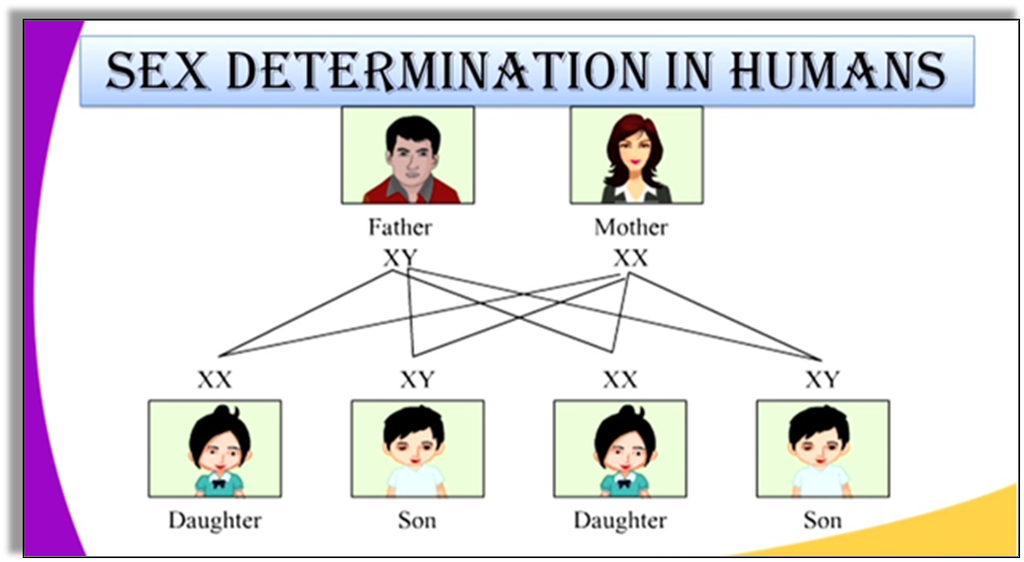
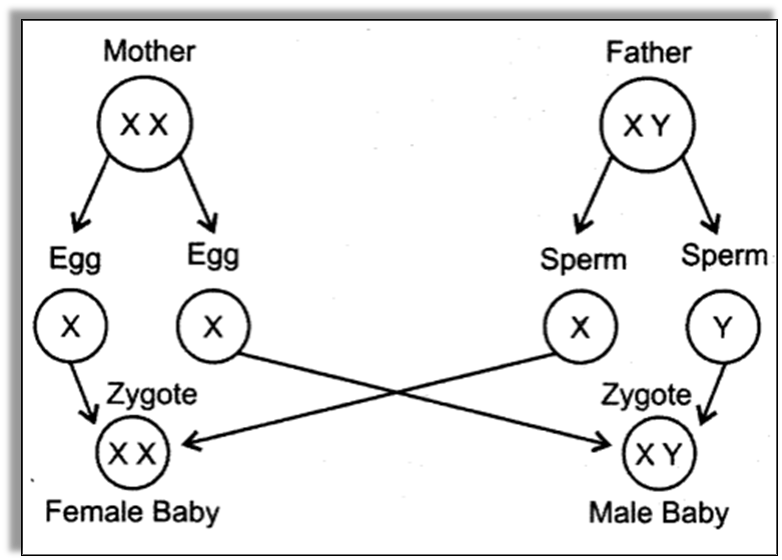
Determining the Sex of the Baby
- We know that there are 23 pairs of chromosomes present inside the nucleus of every human cell.
- These chromosomes have a thread-like structure and they always occur in pairs.
- The chromosomes help in determining the sex of the child.
- Out of the 23 pairs of chromosomes, 2 of them are sex chromosomes called X and Y.
- Females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y chromosome.
- The gametes contain only one set of chromosomes that is either an X or a Y.
- The egg of the female contains an X chromosome always.
- However, the sperm can contain only one of the X and Y chromosomes.
- So if the sperm that contains a Y chromosome fertilizes with the egg which contains the X chromosome, the zygote develops into a male.
- On the other hand, if the sperm contains an X chromosome and fertilizers with the egg which contains an X chromosome, the zygote develops into a female.
- Hence the sex of the child depends upon the chromosomes of the father and not the mother
Hormones other than Sex Hormones
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Hormones other than Sex Hormones
Other endocrine glands that are present in the Human Body are:
Hormones: Thyroxine
Location and Function:
- It is found at the front of the neck between the windpipes.
- It has a brownish-red color and secretes a collection of hormones called Thyroid Hormones.
- The thyroid hormone controls the rate of metabolism in the body.
- Lack of Thyroxine results in Goitre.
Hormones: Insulin Glucagon
Location and Function:
- The Pancreas is almost a 6-inch long gland located behind the stomach.
- It produces digestive enzymes, glucagon, and insulin.
- The insulin maintains glucose levels in the blood.
- The glucagon prevents the insulin levels from getting too low in the body.
- The insulin activates when the blood glucose levels are high while the glucagon activates when the blood sugar levels are low.
- Lack of insulin in the body leads to diabetes
Hormones: Adrenaline
Location and Function:
- Adrenal glands have a size almost of a walnut and are located above the kidneys.
- They secrete more than 150 hormones in the human body for various purposes.
- Adrenaline helps in managing stress as it increases the blood sugar levels, dilates the pupils, increases the heart rate, enhances the blood supply to the muscles
- It also maintains a balance of salt in the blood.
Hormones: Growth Hormone
Location and Function:
- The pituitary gland has a size as small as a pea and is located inside the skull.
- It is also called the master gland as it controls the function of all other glands.
- It also secretes prolactin that stimulates the production of milk.
- The growth hormone is responsible for the growth of a person.
Hormones: Parathormone
Location and Function:
- The parathyroid glands are located behind the thyroid glands.
- The parathormone maintains the level of calcium in the body.
- If they produce excess hormones it can lead to severe effects such as kidney stones and brittle bones.
Hormones: Melatonin
Location and Function:
- It is also known as the Third Eye and is located between the two halves of the brain.
- Melatonin is responsible for the working of the internal clock of the body. This means it influences the cardiac rhythm or the sleep-wake cycle of the body.
Role of Hormones in Completing the Life History of Insects and Frogs
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Role of hormones in completing the life history of insects and frogs
Metamorphosis
- The change from larva to adult is known as metamorphosis.
- In insects it is controlled by insect hormones.
- In frog, thyroid produce thyroxin hormone for metamorphosis (change from tadpoles to adult frog).
- Sufficient iodine in the water is also important for metamorphosis.
- Insects like silk moths and some animals like frogs undergo the process of metamorphosis which results in drastic changes in their bodies.
- The insect hormones control the process of metamorphosis in the insects.
- In frogs, the thyroid releases thyroxine which controls the process of metamorphosis in them.
- The thyroxine only produces with the help of iodine that is present in the water.
- If there is a lack of iodine in water the tadpoles would never turn into adult frogs.
Reproductive Health
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Reproductive Health
Factors that lead to overall well being in adolescents:
Reproductive Health:-
A healthy individual is a person with overall physical and mental well-being. Reproductive health refers to the personal hygiene and proper caring of the reproductive organs. An adolescent needs to keep personal hygiene and predominantly the reproductive organs as all the body parts will be very active at this stage.
Some of the steps to be taken to maintain good reproductive health during adolescence are:
- Eating a balanced diet.
- Maintaining personal hygiene.
- Adequate physical exercise.
- Avoiding drugs.

1. Nutritional Health of Adolescents
- The adolescent age requires a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients such as proteins and carbohydrates along with vitamins and essential minerals.
- This is needed because the bodies of adolescents are changing and developing at a rapid rate at this time.
- Healthy and nutrition-rich diets are essential for their right growth.
- Also, they should avoid foods such as chips, soft drinks and soda as they have low nutritional value.

2. Personal Hygiene
Personal hygiene also plays a role in maintaining the mental and physical well-being of adolescents. Here are a few ways they can maintain their hygiene:
- Having bath daily as the sweat glands and the oil glands secrete high amounts of sweat and oil in the skin which can lead to bad odour.
- Maintaining cleanliness of the body as there can be chances of getting a bacterial infection otherwise.
- Females should take note of the menstrual cycle and prepare themselves accordingly.
3. Physical Exercise
- Exercising not only keep the body fit but also helps in relieving stress and maintaining mental well-being.
- Therefore, adolescents should indulge in sports, exercise, walking, cycling, and other physical activities.
4. Say “No” to Drugs
- Adolescent age incorporates different changes in the mind and body of the individual.
- As a result, the adolescents may feel a little uneasy sometimes.
- However, they should understand that this is natural and they should not be worried about it.
- But many times adolescents are fooled by others by saying that taking drugs would bring relief to them.
- They should always say NO to that as taking drugs can be dangerous for their health.
- Drugs should be taken only if a doctor prescribed them otherwise not.
- This is because the drugs are addictive and once a person takes them they feel like taking them again and again.
- As a result, the mental and physical health of the person starts getting affected due to drugs.
- Also, taking drugs through syringes can cause AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Disease).
- This disease is caused by a hazardous virus that can get transmitted from one infected person to another through the use of the same syringes.
- Along with this, it can transmit through sexual contact or from the infected mother's milk.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
