- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Sound Produced by Humans
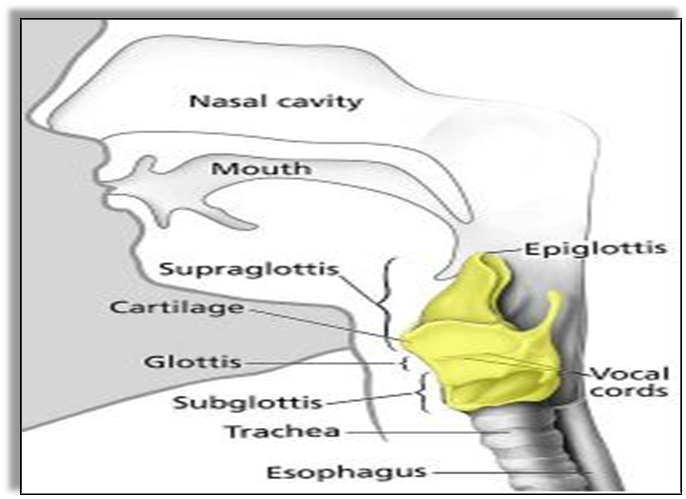
How do Humans Produce sound?
In humans, the sound is produced by the voice box or the larynx.
- The voice box is at the upper end of the windpipe.
- Two vocal cords are stretched across the larynx in such a way that it leaves a narrow slit between them for the passage of air.
- When the lungs force air through the slit, the vocal cords vibrate and produce sound.
- The type and quality of voice produced differ in each human being. It depends on the tightness and the thickness of the vocal cords.
- Adult male vocal cords are larger than a female’s and are between 17 mm to 25 mm in length. Hence, male voices are usually lower-pitched.
- Female vocal cords are between 12.5 mm to 17.5 mm in length. Hence, the women’s voices are higher in pitch.
- Children’s vocal cords have very short vocal cords.
- The human voice is used for talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, whistling, clicking and whispering
- Human beings have a voice box or larynx which is present in their throat on the upper side of the windpipe.
- The larynx has two vocal cords which have a narrow slit between them so that air can pass through them.
- As the lungs throw the air out of the windpipe, it passes through the slit and hence allows the production of sound as the vocal cords start vibrating.
- The vocal cord muscles also play a role in the production of sound.
- Their thickness and tightness describe the quality or type of voice a person has.
- The vocal cords in males are of length 20 mm and females have 15mm long vocal cords. Children, on the other hand, have very short-length vocal cords. Hence, the voices, their quality, and their type are always different in women, men, and children.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
