Agricultural Practices
Farmers take this huge responsibility of cultivation of crops to provide food to the entire population.
Various tasks performed by farmers for crop production are termed as Agricultural practices. Following activities form a part of Agricultural practices:
- Preparation of soil
- Sowing
- Adding manure and fertilizers
- Irrigation
- Protecting from weeds
- Harvesting
- Storage
Agricultural Practices
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Why do we need food?
We need food because it gives us energy, keeps us healthy, and helps us to grow as well as repair and replace damaged and worn-out tissues.
We already know that:
- All living organisms require food.
- The energy from food is utilized by an organism for carrying out its various life processes such as digestion, respiration and excretion.
- Plants can make their food themselves but animals including humans cannot.
- We get our food from plants or animals, or both.
- People in the past ate raw fruits and vegetables and started hunting animals for food.
- Later, they could cultivate the land and produce rice, wheat and other food crops. Thus, was born agriculture.
How do plants and animals get their food?
What is a Crop?
Most plants make their own food through the process of Photosynthesis. Animals feed on plants or other animals to get energy. When we cultivate the same kind of plants on a large scale in one place, it is called ‘Crop’.
India is a vast country. Here climatic conditions like temperature, humidity and rainfall vary from one region to another region. There is a rich variety of crops grown in different parts of India. In India Crops can be classified on the basis of the season in which they grow:
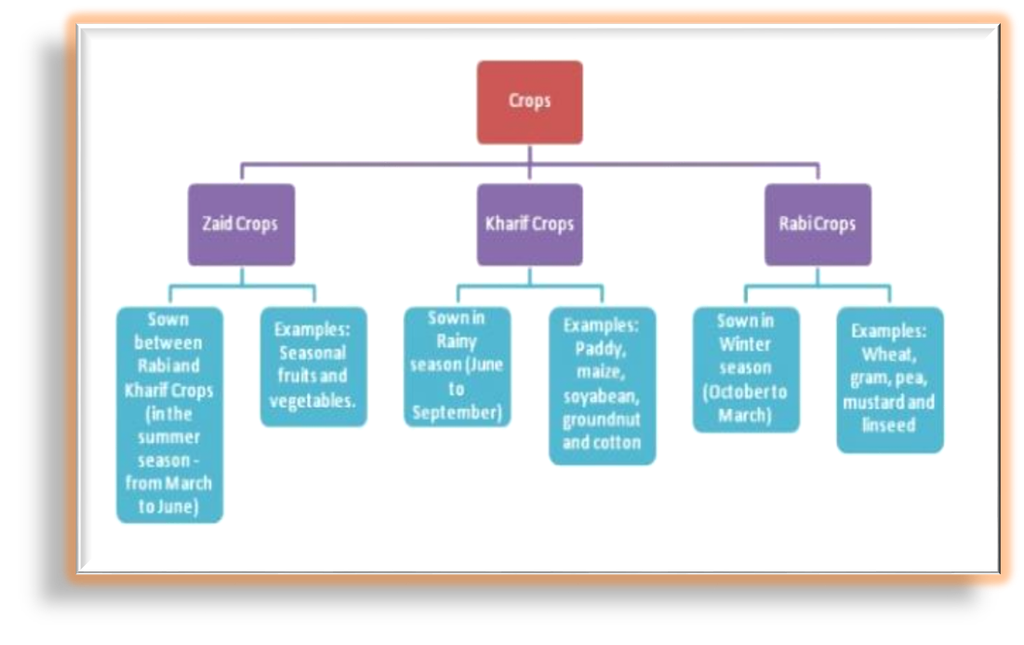
- Kharif Crops:
- The crops which are grown in the rainy season
- From June to September
- Eg: Paddy, Maize, Soyabean, Groundnut, Cotton etc.
- Rabi Crops:
- The crops that are grown in the winter season
- From October to March
- Eg: wheat, gram, pea, mustard, linseed etc.
- Zaid Crops (or Summer Crops):
- The crops are grown in the summer season
- From March to June
- Eg: Muskmelon, watermelon, cucumber, Moong etc.
Basic Practices of Crop Production
Basic practices of crop production.




Basic Practices of Crop Production
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
The several activities undertaken by the farmers for the cultivation of crops over a period of time are referred to as agricultural practices.
Basic Practices of Crop Production
Seven agricultural practices followed while growing a crop are:
- Preparation of Soil: To loosen and turn the soil.
- Sowing: Planting of seeds of a crop in soil.
- Adding Manure and Fertilizers: Adding essential nutrients to the soil for the growth and development of plants.
- Irrigation: Supplying water to plants at regular intervals.
- Protection from Weeds: Removal of unwanted plants from the cultivated field to allow crops proper access to lights, space, and nutrients.
- Harvesting: Cutting mature crops from fields.
- Storage: Keeping grains or produce safe from rats, insects, microorganisms and moisture.
Step-by-Step Agricultural Process
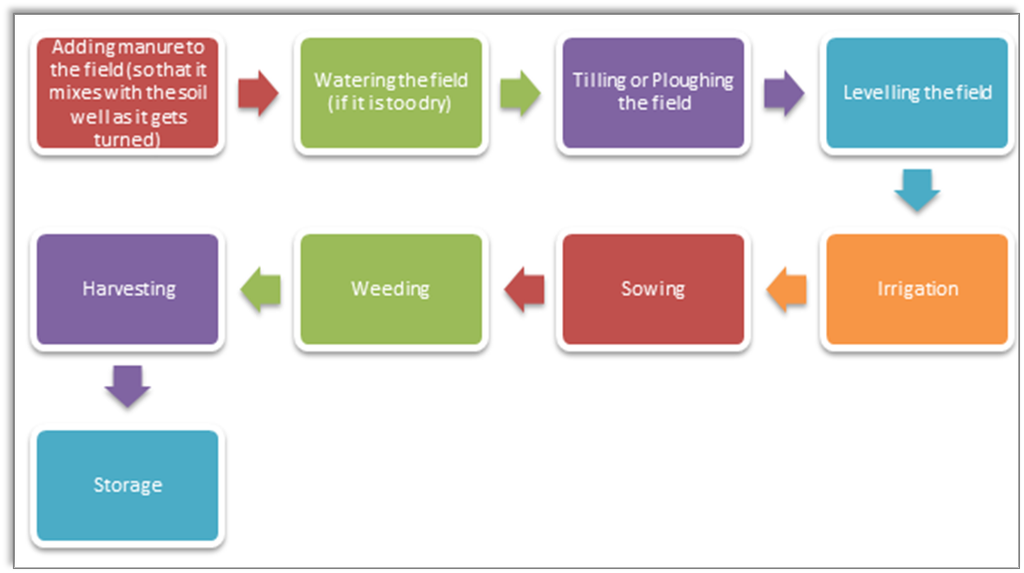
Following are the agricultural activities:

Preparation of Soil

Preparation of Soil
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Preparation of Soil

Why do we loosen or turn the soil?
- One of the most important tasks in agriculture is to turn the soil and loosen it.
- The top layer of soil supports plant growth and is rich in nutrients.
- The loose soil allows the roots to penetrate and breathe easily, even when they go deep into the soil.
Loosening the Soil is important because it:
- Allows the toots to go deeper into the soil and yet, breathe easily (allowing air to reach the roots),
- Helps in the growth of microbes and earthworms that add humus to the soil and turn and loosen the soil further, and
- Nutrient-rich soil comes to the top and can be used by plants.
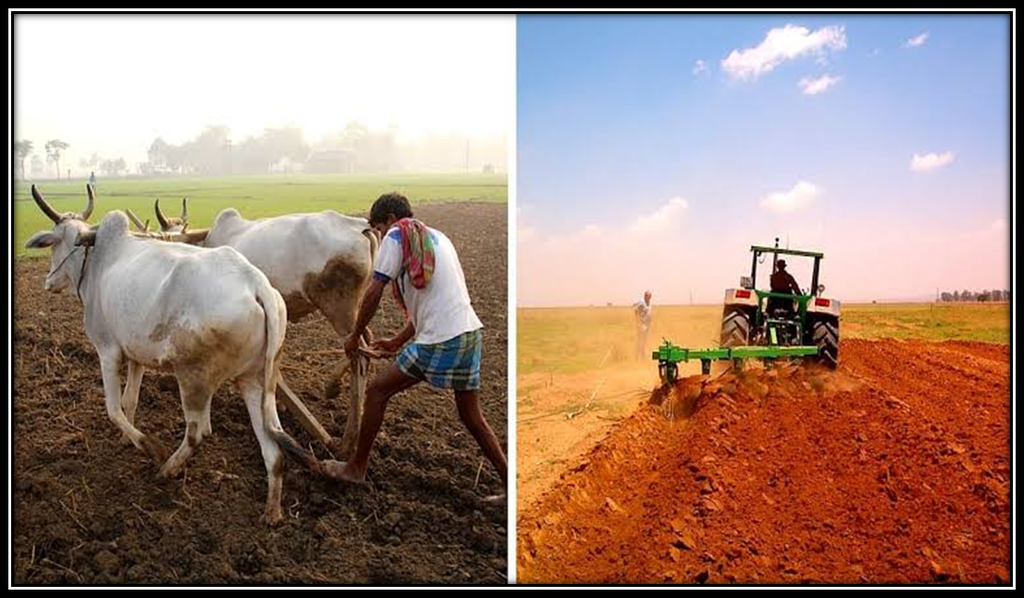
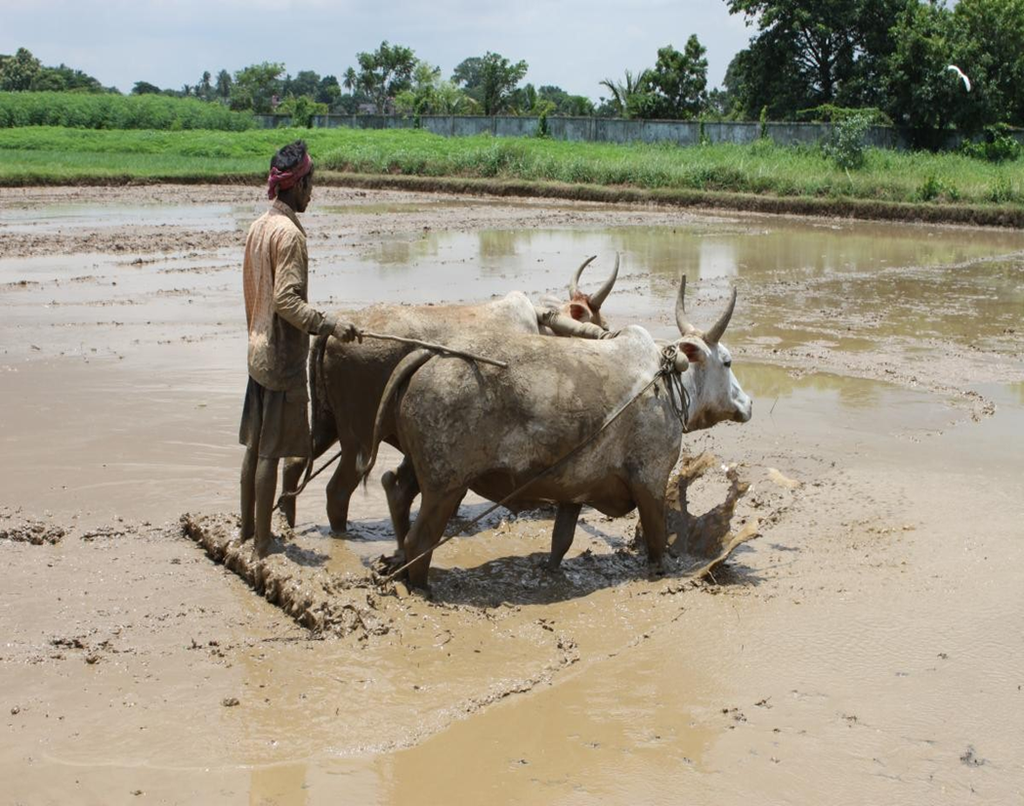
- The process of loosening and turning the soil is called tilling or ploughing. This is done by using a plough that is made of wood or iron.
The process used to loosen and turn the soil is called Tilling or Ploughing.
- If the soil is very dry, it may need watering before ploughing, break crumbs using a plank and the field is leveled using a leveler for sowing and for irrigation purposes.
After tilling, Levelling is done in which the big clumps of soil called crumbs are broken (and leveled). Leveling the field helps in the process of sowing and irrigation

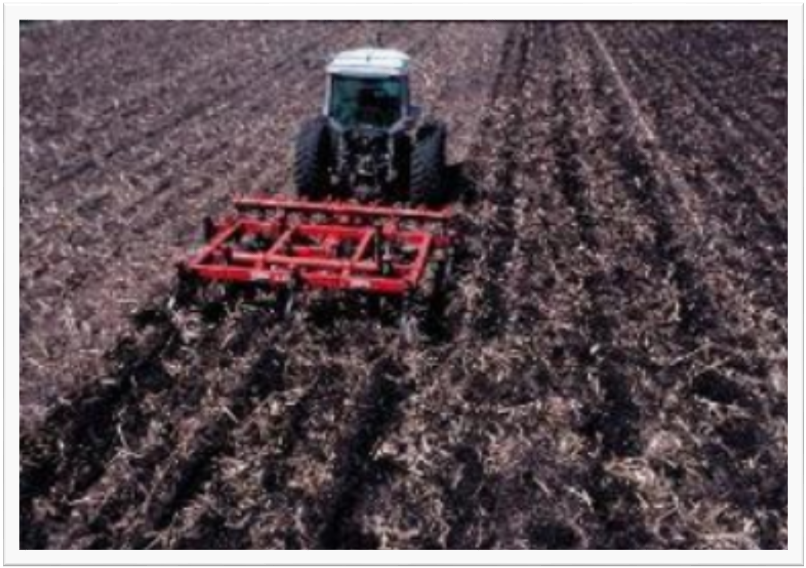
Agricultural Implements
In order to get better yields, it is necessary to break soils to the size of grains.
The main tools used for this purpose is:

A plough is a device that is used by farmers for different purposes such as adding fertilizers, tilling and loosening the soil.

A hoe is a tool that is used to dig up the soil before planting a sapling.

A cultivator is attached to the tractor and helps in loosening soil. Cultivators are used instead of plough since they are faster.
Why is leveling the field important?
Land leveling is typically done in mildly sloping lands where farmers use surface irrigation methods such as furrows, borders, basins, or floods. It ensures uniform distribution of irrigation water in the root zone of the crop. It also helps in seeding and managing the crop better, which means that the yield and quality of the crop are better.
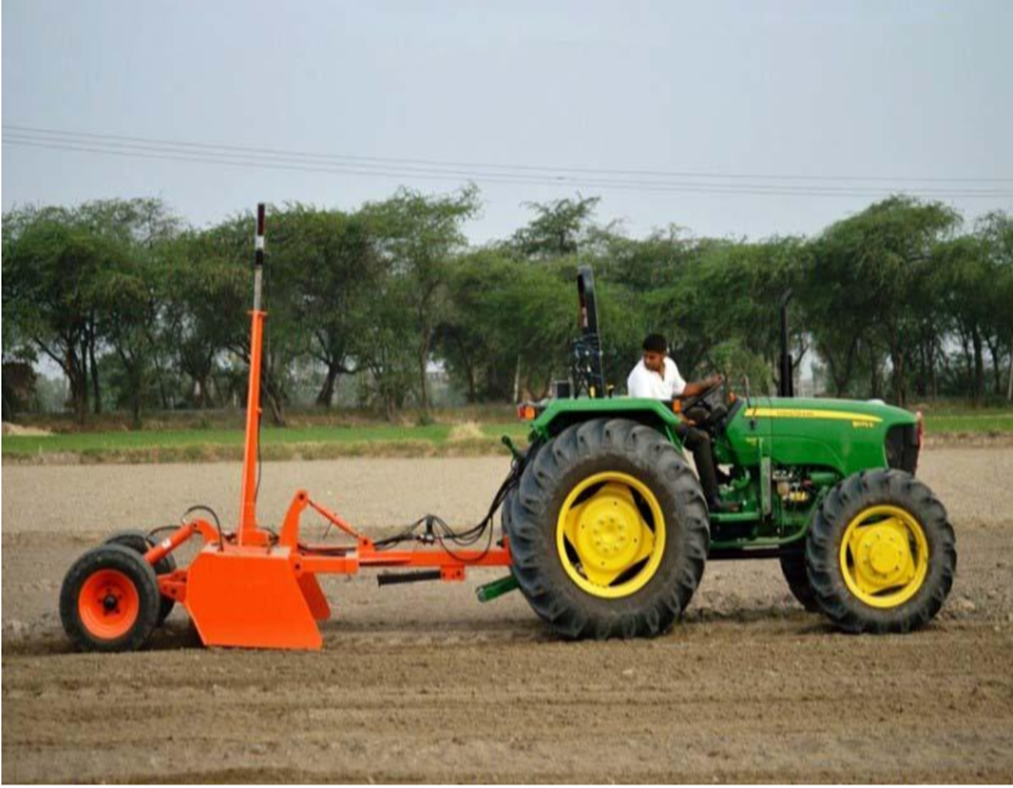
Agricultural Implements used for Levelling
Traditionally, farmers used ox-drawn scrapers to level the land but today, a laser land leveler is being used to make sure that the surface of the field is even and flat. The laser-guided levelers save time, increase productivity, and save water (as it minimizes water-logging or run-off problems.


Sowing

Sowing
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Sowing is the most important part of crop production. Before sowing good quality seeds are selected. These are clean and healthy seeds of a good variety. Farmers prefer to use seeds that give a high yield.
Sowing
Which kind of seeds should farmers use?
Farmers should use good-quality seeds that are clean, healthy and give a high yield. The selection of the right variety of seeds depends on the soil, climate, irrigation method, and other regional factors.
The Ministry of Agriculture in India has set up a national-level organization called the National Seeds Corporation (NSCC) that tests the quality of seeds. State Seeds Corporations and Agricultural Universities have also set up seed testing laboratories throughout India.
These labs test seeds for their:
- purity,
- resistance to diseases and pests,
- germination and vigour,
- suitability to regional climatic conditions, and general seed health. (olympiad)
How to separate damaged seeds from healthy seeds?
Put the seeds in water. Damaged seeds are hollow and lighter and thus, float on water. Good and healthy seeds sink in water and settle down.
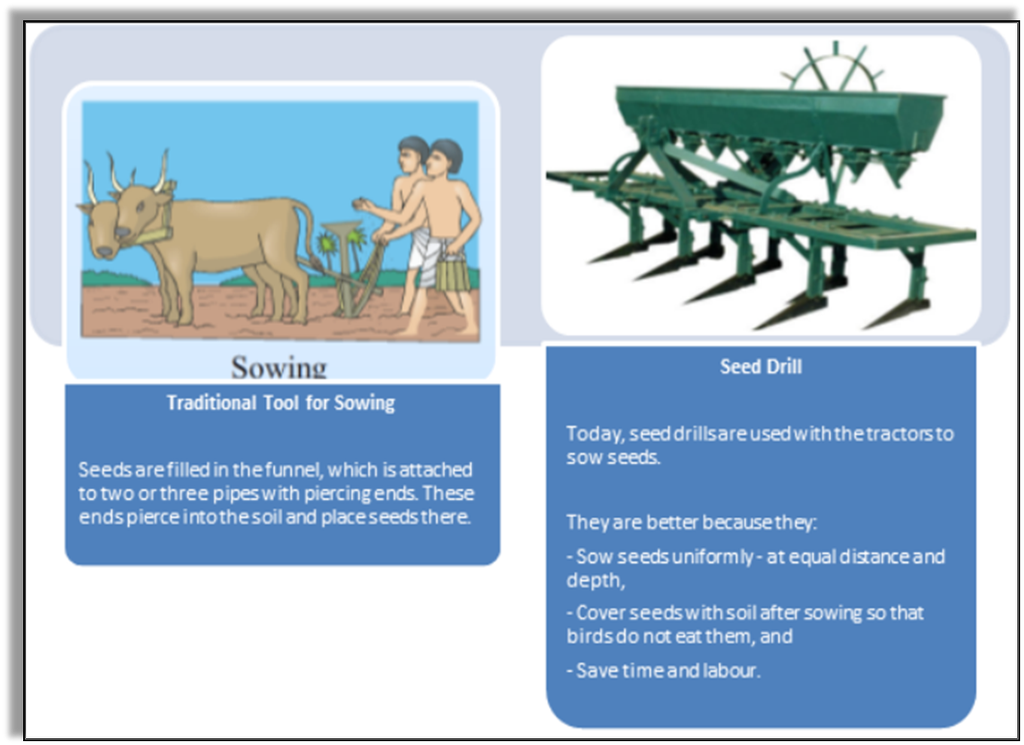
Agricultural Implements used for Sowing
What precautions should be taken while sowing?
While sowing seeds, it is essential to make sure that:
- Seeds are healthy and of high quality.
- They are planted at the correct distance from each other so that they can get proper light, water and nutrients from the soil.
- They must be sown deep enough to protect them from animals and birds (which might eat them) and wind (which might blow them away) but not so deep that they may not get enough air to germinate.
Why it is better to sow seeds uniformly?
Seeds should be planted at an appropriate distance to avoid overcrowding of plants. It allows plants to get proper sunlight as well as sufficient water and nutrients from the soil.
Why are plants kept in small bags in the nursery?
Few plants (like paddy, forest plants, and flowering plants) are first grown in a nursery into seedlings and then, transplanted to plants manually. Keeping the seedlings in bags makes it easier to transfer them to another place.
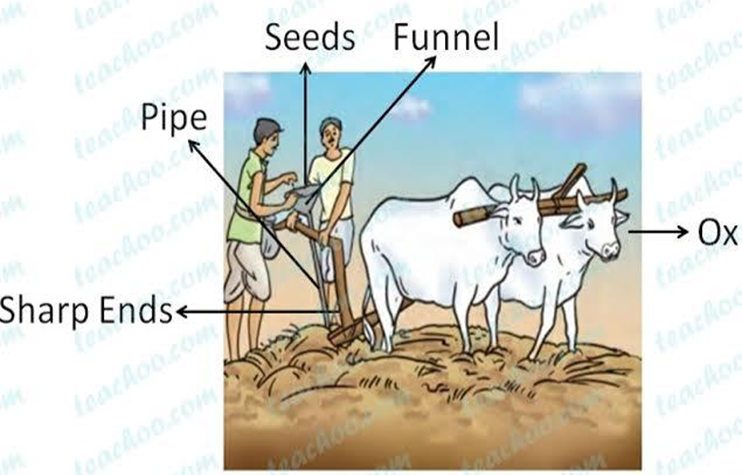
It is a tool shaped like a funnel used traditionally for sowing seeds. The seeds are filled into the funnel, passed down through two or three pipes having sharp ends. These ends pierce into the soil and place seeds there. Some of the crops are first grown in the nurseries and then transferred to the main field. This process is known as Transplantation.
Important tools used for sowing seeds are:

Nowadays seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. With the help of this tool sows the seeds uniformly at proper distance and depths. It ensures that seeds get covered by the soil after sowing and prevents damage caused by birds. It saves time and labor.
Adding Manure and Fertilizers

Adding Manure and Fertilizers
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Adding Manure and Fertilizers
Why are manure and fertilizers added to the soil?
When crop after the crop is grown in the same field, the soil becomes poor in certain nutrients. Manure and fertilizers are added to the soil to replenish it with nutrients to ensure the healthy growth of plants.
What are the different types of manure that farmers can use?
Manure can be of various types, such as:
- Natural Organic Manure: This includes raw manure, compost, and green manure:
- Raw manure is a mixture of cattle and domestic waste.
- Compost is well-rotted plant and animal residue.
- Green Manure is crops grown in the field as the pure crop or as an intercrop between the main crops - and then, buried in the field to enrich the soil.
- Biofertilizers: These are the nitrogen-fixing organisms that are widely used in organic farming and make agriculture sustainable. These include Rhizobium, Azotobacter, blue-green algae, and Mycorrhizae (a type of fungi that increases phosphorus uptake in fruit crops like papaya and citrus fruits).
- Vermi-Compost: It is a type of compost that is made using earthworms.
What are the three methods of replenishing the soil with nutrients?
The three methods of replenishing the soil are:
- Adding organic manure to the soil.
- Adding chemical fertilizers to the soil.
- Leaving the field uncultivated (or fallow) between two crops.
- Crop rotation is a practice in which different crops are grown alternately to allow the soil to replenish with different nutrients.
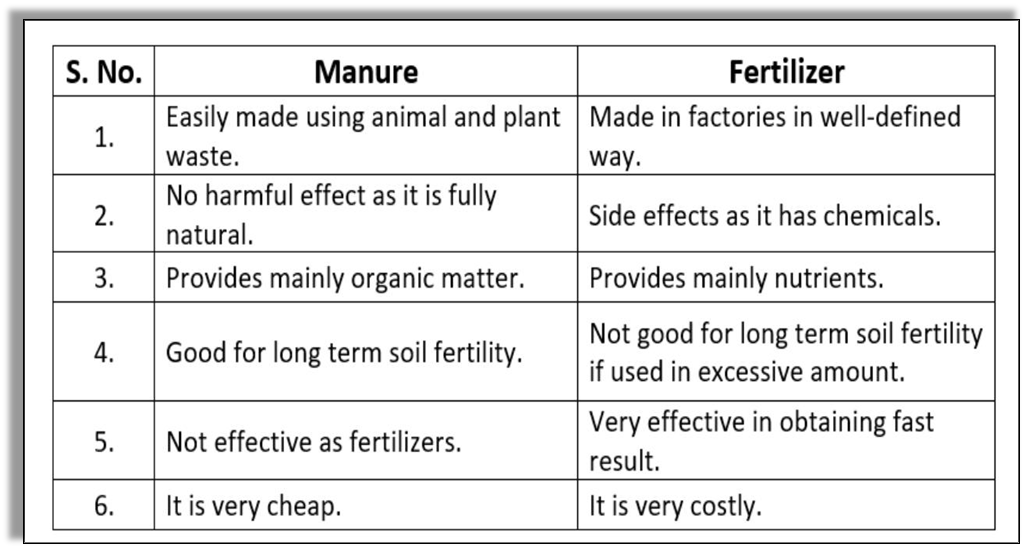
Difference between Manure and Fertilizers
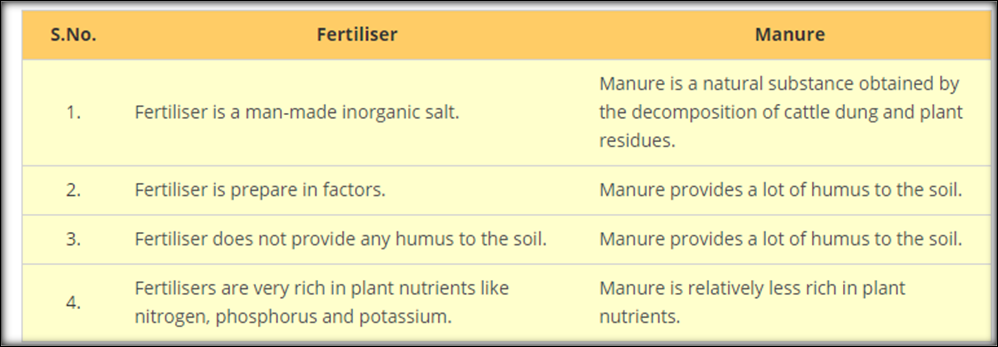
- When crop after the crop is grown in the same field, the soil becomes poor in certain nutrients.
- Manure and fertilizers are added to the soil to replenish it with nutrients to ensure the healthy growth of plants.
- Fertilizers are chemicals used to add minerals like potassium, phosphorus and nitrates to the soil.
Manure are of various types such as:
- Natural organic manure
This includes:
- Raw manure – is a mixture of cattle and domestic waste.
- Compost – it is well-rotted plant and animal residue.
- Green manure – these are crops grown in the field as a pure crop or as an intercrop between the main crops and then buried in the field to enrich the soil.

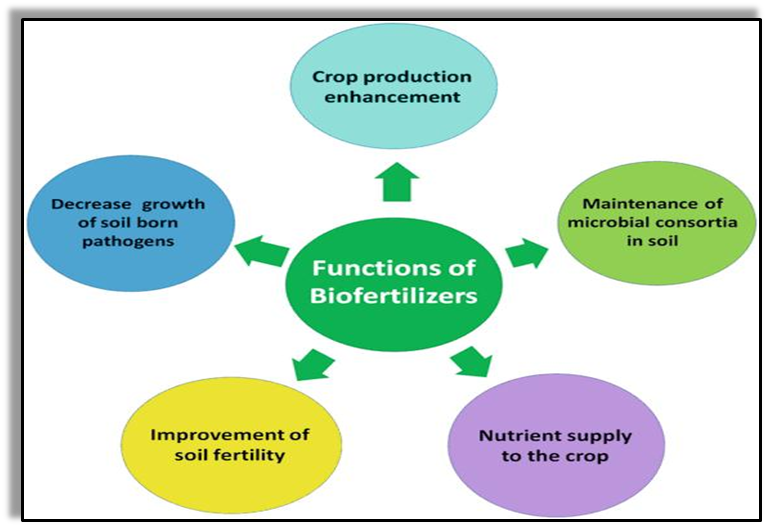
- Biofertilizers:
- These are the nitrogen-fixing organisms that are widely used in organic farming and make agriculture sustainable.
- These include Rhizobium, Azotobacter, Blue-green algae.
- Vermicompost:
- It is a type of compost that is made using earthworms.

Methods of Replenishing the soil with nutrients are:

Examples of Fertilisers

Pros and Cons of using Fertilizers
Pros: They are chemicals, rich in particular nutrients and help farmers get a better yield of crops like wheat, paddy and maize.
Cons: They make the soil less fertile and also cause water pollution.
Why is Manure better than Fertilisers?
Organic Manure is better than Fertilisers because:
- It adds humus to the soil and increases its water holding capacity,
- Improves soil texture,
- Makes soil porous which makes the exchange of gases easier, and
- Increases the number of friendly microbes.
State an example of Crop Rotation
In North India, farmers used to grow legumes in one season as fodder and wheat in the next season. This helped the soil to get replenished with nitrogen*.
*Root nodules of leguminous plants have Rhizobium bacteria that fix atmospheric nitrogen and make it usable by plants.
Irrigation

Irrigation
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
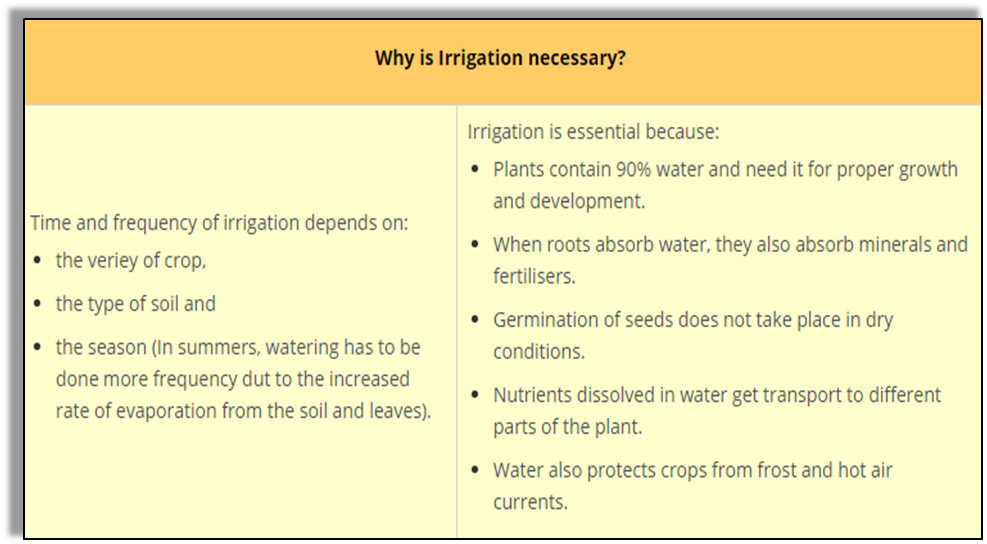
Sources of irrigation:
Wells, tube wells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals.







Water is important for the proper growth and development of plants.
- Water is essential because the germination of seeds does not take place under dry conditions.
- Water also protects crops from both frost and hot air currents.
- The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation.
- A proper irrigation system will ensure timely and adequate water for crops. This will lead to more yield.
- The water available in wells, lakes and canals is lifted by different methods in different regions, for taking it to the fields.
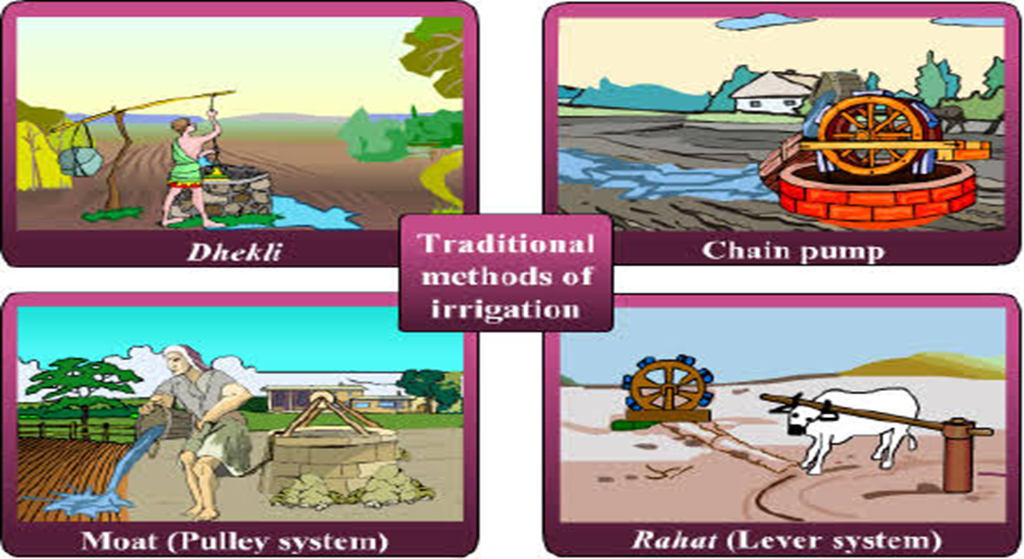
Traditional methods of irrigation:
Traditional irrigation methods can be of two types:
Ones that use cattle and human labor:
- They are cheaper but less efficient. These include:
- Ones that use pumps: To lift water, pumps can be powered by:
- Diesel,
- Biogas,
- Electricity, and
- Solar Energy.




Video Reference:

Modern Methods of Irrigation
They are best for saving water. Two main irrigation methods in use today are:
- Sprinkler System
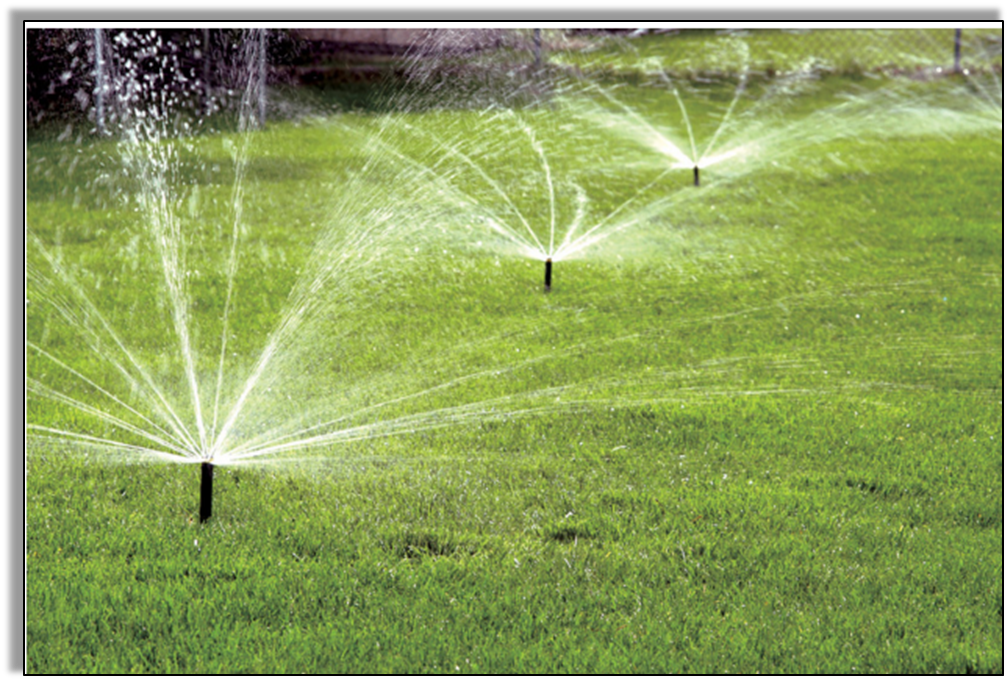

Best for places where:
- the land is uneven
- sufficient water is not available.
- Sprinkler system: In this system, the perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. When water is allowed to flow through the main pipeline under pressure with the help of a pump, it sprinkles from the rotating nozzles. It gets sprinkled on the crops as if it is raining.
It has perpendicular pipes, with rotating nozzles on top, joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. Water flows through the main pipeline under pressure (created with the help of a pump). It escapes from rotating nozzles and sprinkles on the crop like rain.
Often used in watering:
- Lawns, and
- Coffee plantations.
- Drip system: In this system, the waterfalls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. So it is called the drip system.
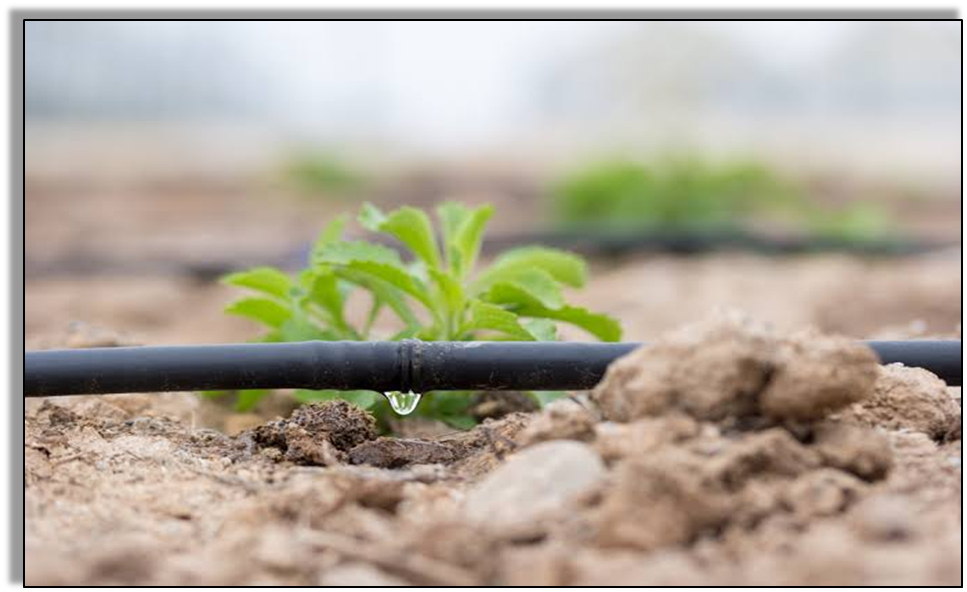
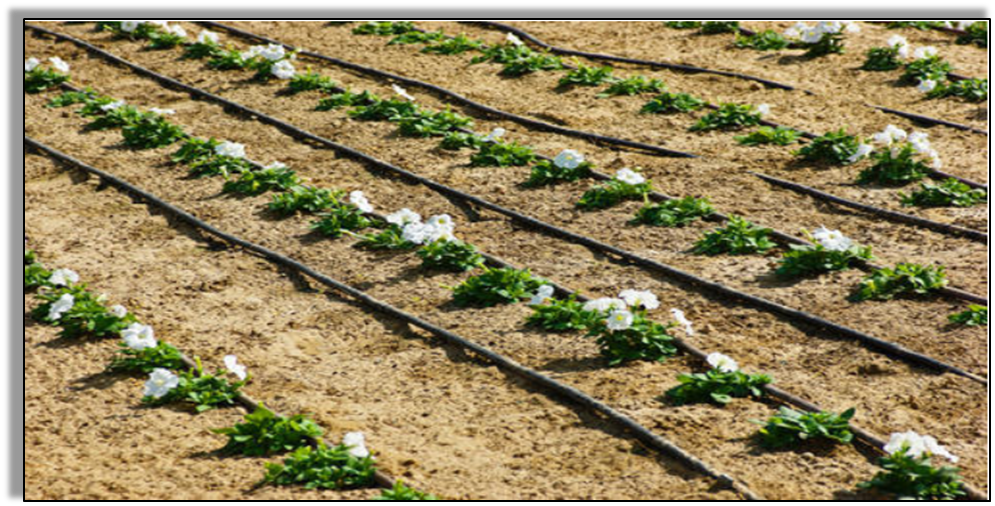


Best for places where:
- availability of water is poor.
Waterfalls drop-by-drop directly near the roots of the crop. There is no wastage of water at all.
Often used in watering:
- Fruit Plants,
- Gardens
- Trees
How does over-irrigation harmful to crop production?
Like irregular or under-irrigation, excessive water can also damage crops. In a waterlogged field:
- Seeds do not germinate properly as they do not get sufficient air to respire,
- Roots do not grow properly due to lack of proper soil aeration,
- Water evaporates more which leads to the accumulation of salt which in turn damages soil fertility, and
- Roots do not go deep in the soil and hence, plants are not able to get full nutrients from the soil. Roots are also unable to anchor the plants properly and the crop can easily get damaged by strong winds.
Protection from Weeds

Protection from Weeds
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Weeds are undesirable plants that may grow naturally along with the crop grown in the field.
Removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary because they affect the growth of the crop by competing with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light.
Protection from Weeds
Undesirable plants that grow naturally along with the crop are called weeds. Removal of weeds is called Weeding.
Why is weeding necessary?
Removal of weeds is essential because:
- Weeds compete with crops for space, light, water, and nutrients.
- They may interfere in harvesting and can be poisonous for animals and human beings.
How do farmers remove weeds?
Farmers remove weeds by:
- Tilling before sowing of crops (to uproot and kill weeds),
- Manually removing them using khurpi to uproot them or cut them close to the ground,
- Spraying weedicides (chemicals that kill weeds but do not damage crops), such as 2, 4 Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid (2, 4-D), Naphthalene acetic acid, and Atrazine.
What should farmers keep in mind while using weedicides?
The best time to remove weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds.
Weedicides are diluted with water and sprayed in the fields. Farmers should cover their noses and mouth with a piece of cloth while spraying them.
Farmers use many ways to remove weeds and control their growth:
- Tilling before sowing of crops: helps in uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed up with the soil.
- The best time to remove weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds. Manual removal includes the physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground from time to time.
- Weeds are also controlled by spraying certain chemicals called weedicides, in the fields to kill the weeds. They do not damage the crops.
Harvesting

Harvesting
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Harvesting
Cutting of crop after it matures is called Harvesting*.
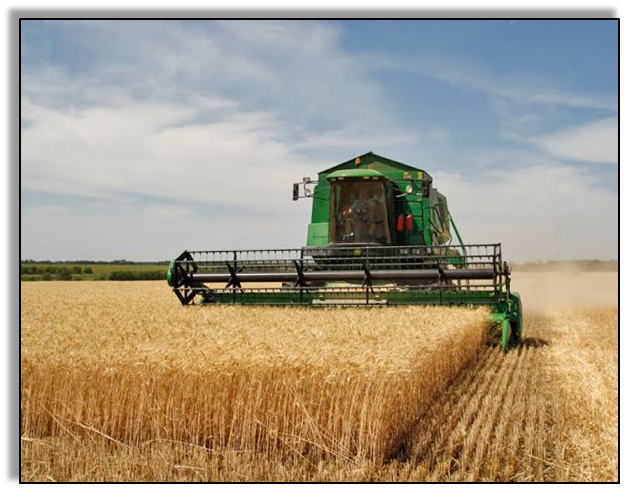
Cutting the crops after it has ripened and gathered the grains is known as Harvesting. Harvesting can be done manually (using sickle) or by machine (called Harvester).
- Cereal crops usually take 3-4 months to mature.
- In India, many festivals are associated with harvestings, such as Pongal, Baisakhi, Holi, Diwali, Nabanya and Bihu.
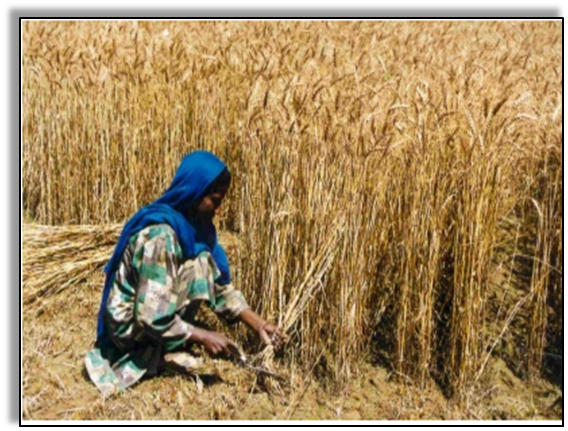

- A sickle is used for cutting the crop. A harvester is a machine that helps to cut the ripened crop from the fields.
- Threshing is the process of separating the grains from the straw and chaff. A thresher is used for threshing.
- Winnowing is a process in which we allow natural wind to blow through the grains so the lighter grains fly away, whereas heavier grains fall to the ground

Winnowing
After harvesting, separating the chaff from grain can be done through threshing and winnowing.
Threshing
Threshing is separating the chaff from grain by beating the crop against a stone or wooden bar. In this process, grains fall from the stalk due to force.
After threshing, winnowing separates the husk from the seeds by blowing air through it. In this process, the husk (which is lighter) flies away and the seeds (which are heavier) fall down.
There is a machine called ‘Combine’ which works as a harvester as well as a thresher.
Storage

Storage
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Storage:
It is done to protect food items from Pests, Bacteria and Fungi
How are grains protected from pests, bacteria and fungi?
- Grains (seeds) are dried in the sun to reduce their moisture.
- On small scale, grains are stored in jute bags or metallic bins.
- On large scale, they are kept in silos and granaries.
- Dried neem leaves are used at home to protect food grains.
- In big godowns, chemical treatments are done to protect large quantities of grain.
- They should be stored in completely dry gunny bags.
- The bags should be kept in a place that is completely moisture-free.
- Storage areas should be well ventilated.
- In larger godowns, care should be taken that chemicals used to repel or kill insects and rats do not contaminate food grains.
- Grains are dried in sun to reduce their moisture.
- On large scale, they are kept in silos or granaries. On small scale, grains are stored in jute bags or metallic bins.
What precautions should be taken during the storage of grains?
Precautions to be taken during storage of food grains are:
- Grains should be dried properly or they might rot easily.
- They should be stored in completely dry gunny bags.
- The bags should be kept in a place that is completely moisture-free.
- Storage areas should be well-ventilated.
- In larger godowns, care should be taken that chemicals used to repel or kill insects and rats do not contaminate food grains.
Food from Animals


Key points of crop production and management.

Food from Animals
- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
- Animal husbandry is the management and care of farm animals for milk, meat, egg.
- Animal husbandry has been practiced for thousands of years since the first domestication of animals.
Humans are dependent on animals in innumerable ways. Then animals are domesticated by humans for many purposes.
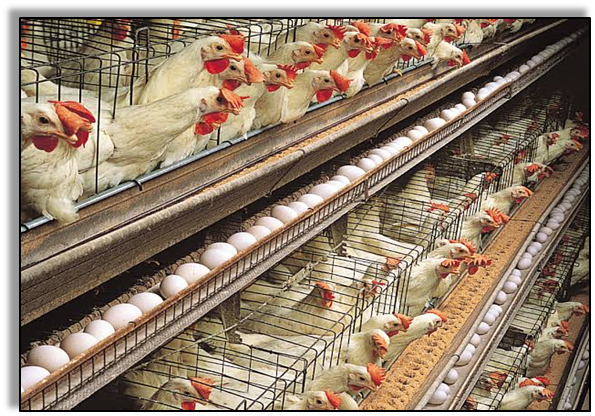
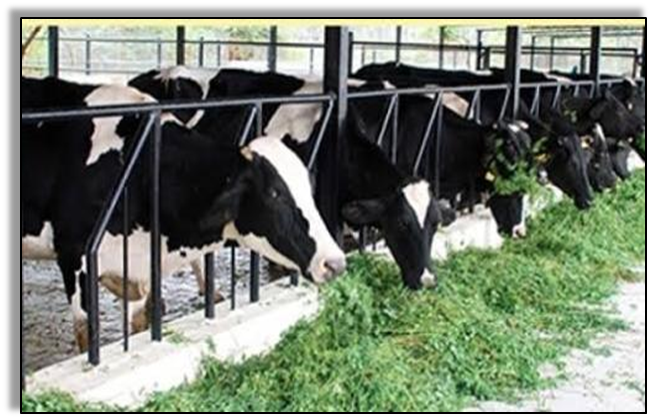


When animals are reared at a large scale to obtain food from them, it is called Animal Husbandry.
Animal husbandry includes taking care of animals, breeding them, and domesticating them for different purposes such as meat, wool, milk, eggs, honey etc. Types of animal husbandry popular in India include:
- Beekeeping or Apiculture
- Cattle farming
- Dairy farming
- Fish Farming or Aquaculture
- Poultry farming
- Sheep farming
Breeding means mating animals with superior characters to create a new breed (or offspring that is more useful to us than its parents). Breeding can be of two types:
- Inbreeding
- Outbreeding
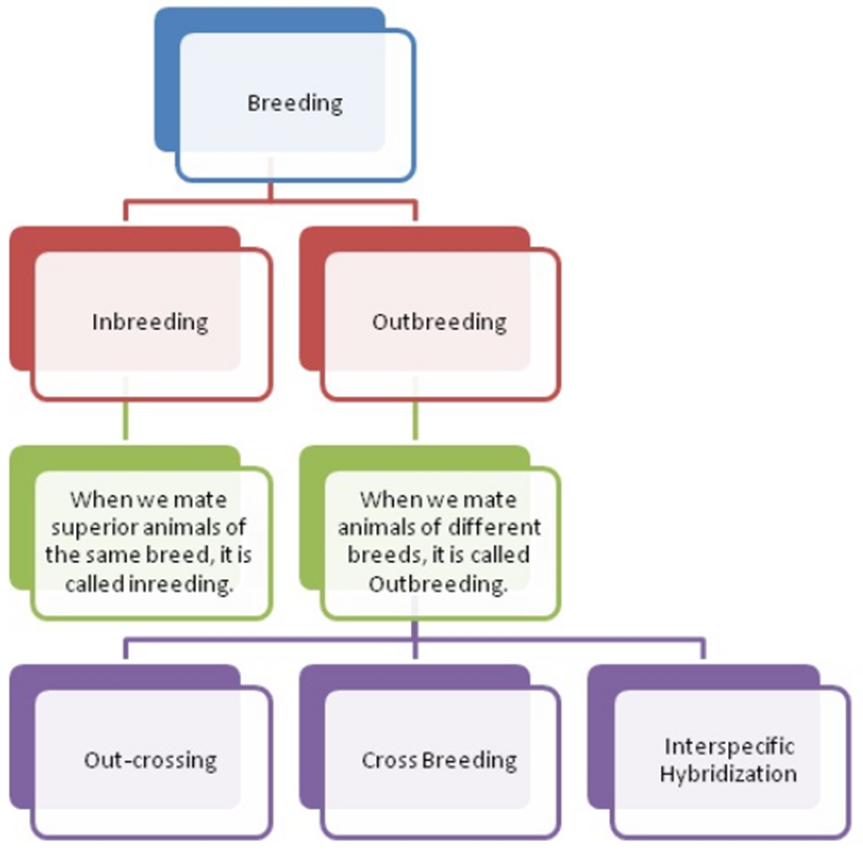
What are the advantages and disadvantages of inbreeding?
Inbreeding allows us to eliminate the harmful recessive genes in a breed and selectively choose and nurture superior genes. In the case of cattle, a superior female produces more milk per lactation while a superior male produces superior progeny than other males.
However, continuous inbreeding can reduce the fertility and productivity of animals that are bred. This is called inbreeding depression. It can be overcome by outbreeding.
What are the three types of outbreeding programs?
- Out-crossing: When animals of the same breed are mated together but have no common ancestors (on either side of the pedigree) for four to six generations, it is called Outcrossing. The resultant offspring is called Outcross.
- Cross Breeding: When superior males of one breed are mated with superior males of another breed, it is called Cross Breeding. This helps scientists to combine the desirable qualities of the two breeds. In Punjab, Bikaneri ewes were mated with Marino rams to create a new breed of sheep called Hisardale.
- Interspecific Hybridization: When a male and a female of two different species of animals are mated together, it is called Hybridization. For Example, when a donkey and a horse are mated, a new breed called Mule is born. (Olympiads)
What are the advantages and disadvantages of hybridization?
Hybridization passes along the favorable traits of the two chosen species. It can also prolong the survival of a species that is considered threatened or endangered at present.
However, successful breeding through hybridization and finding suitable mates for the purpose is difficult. Moreover, whether done naturally or through human initiation, the hybridization often fails to pass on the life-sustaining genes to offspring which means that most of the offspring do not survive for long after birth.
Green Revolution in India
Prime Minister Lal Bahadur Shastri, the second Prime Minister of India, started the Green Revolution in India with the slogan 'Jai Jawan, Jai Kisan'. His vision was that the soldiers bear the responsibility of making the country powerful from a security point of view while farmers bear the responsibility to make the country self-sufficient in terms of food and other agricultural produce.
Eight Main achievements of the Green Revolution are:
- Increase in Crop Yield per Hectare: The use of modern agricultural implements increased the yield or production of crops per hectare.
- Increase in Overall Crop Production: The new implements and agricultural methods not only increased the production of food grains but also of commercial crops such as jute, cotton, oilseeds etc. Due to the Green revolution, the country has become less dependent on imports for food and its exports have increased which means that our country is more self-sufficient now.
- Commercialization of Agriculture: The status of agriculture increased from being just a means of livelihood to a profit-making enterprise. This led to rapid development in this field.
- Increased Use of Fertilizers and Insecticides: The scientific knowledge about new agricultural practices helped farmers adopt the use of chemical fertilizers and insecticides which increased the quantity and quality of their crops.
- Increase in Irrigation Facilities: Emphasis was laid on making irrigation accessible to everyone and hence, India has a total irrigated crop area of 82.6 million hectares which is the largest in the world.
- Less dependence on Monsoons: Earlier, farmers used to depend on monsoons to be able to produce a good crop. Natural calamities, pests, diseases, hails, and storms are used to damage crops easily. Now, more and more farmers are using new scientific methods to produce a healthy crop and keep it safe.
- Multiple Crop Program: Since 1867-68, the multiple crop program has been introduced which ensures that farmers can produce more than one crop every year increasing their income considerably.
- Rural Electrification: Under Green Revolution, more than 70% of rural India has already been electrified. The Rural Electrification Corporation was established to make sure that electricity is provided to farmers for agricultural purposes and the quality of rural life improves in general.
SUMMARY
Food from Animals: Like plants, the animals also provide us with different kinds of food like fish, meat and eggs.
Fumigation: Fumigation is the most effective method for checking the growth of insects by providing smoke or chemicals in the gaseous state without affecting the grain.
Agricultural practices: There are various activities that have to be performed, before sowing and up to harvesting. These are called agricultural practices.
Animal husbandry: Animals reared at home or on a farm, have to be provided with proper food, shelter and care, when this is done on a large scale it is called animal husbandry.
Crop: When plants of the same kind are grown at a place in a regular manner on a large scale, it is called a crop.
Fertilizer: Fertilisers are chemicals that are rich in particular nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
Granaries: The harvested grains, usually are stored in huge stores, after they are properly dried in sunlight. Such stores are called granaries.
Harvesting: The cutting of the crop after it is mature is called harvesting.
Irrigation: The supply of water to crops at appropriate intervals is called irrigation.
Kharif Crops: The crops which are grown in the rainy season, that is from June to September are called Kharif crops.
Manure: Manures are decomposed organic matter obtained from plant or animal waste.
Plough: The device used for tilling or ploughing is called plough.
Rabi Crops: The crops are grown in the winter season, that is from October to March are called rabi crops.
Seeds: A plant’s fertilized ovules, from which a new plant may grow, are called seeds.
Silo: Harvested grains are usually dried before being stored because moisture encourages the growth of microorganisms. They are then stored in metal or earthen containers, gunny bags. Such stores are also called silos.
Sowing: It is a process to put seeds in the soil.
Storage: It is to keep crop grains safe from moisture, insects and rats for a long time.
Threshing: The process of separation of grains from the chaff in the harvested plant is called threshing.
Weeds: Some undesirable or unwanted plants may grow naturally along with the crop such plants are called weeds.
Weedicides: Those certain chemicals which are used to control weeds are called weedicides. For example, 2, 4-D (2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid), metolachlor.
Winnowing: A process to bring out the separation of grain and chaff is called winnowing

 Izram
Izram
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
