- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Sexual Reproduction
The type of reproduction that begins with the fusion of male and female gametes is called Sexual Reproduction.
Reproductive Parts in Humans
Male Reproductive Organs
The male reproductive system provides the sperm (male gametes) for fertilization. The male reproductive organs include the following:
Penis
It is a cylinder-shaped organ containing a small opening at its top. It secretes semen which contains the male gametes or sperms.
Scrotum
It is a sac-like structure present behind the penis. The testicles or testes are present in this organ. It provides them with the right temperature so that they can produce sperms.
Testes
Most males have a pair of testis (testes) or testicles. The testes consist of coiled tube-like structures that produce sperms. The testes also generate the male sex hormone or the testosterone that causes puberty in males.
Urethra
It is a tube-like structure that allows the flow of semen that contains sperms outside the body. The urethra and penis both are also a part of the male urinary system.
Vas Deferens
It is a tube that carries the sperms from the testicles to the urethra.
Prostate Gland
It is a gland located under the urinary bladder. It secretes prostate fluid which makes up one-third content of semen. This fluid contains some enzymes, zinc and citric acid.
Seminal Vesicles
They have a pouch-like structure. They are located above the prostate gland and connect with the vas deferens. They also secrete a fluid that provides nourishment to the sperms.
Male Sex Hormone or Testosterone
The testes produce testosterone and the pituitary gland controls how much testosterone will be produced. This hormone is responsible for the development of male sex organs and the development of secondary sexual characters in males during puberty such as deepening of voice and growth of facial and body hair.
The Sperm Cell
The testes secrete millions of sperm cells together. A sperm comprises of a single cell and has a specific structure with three main parts as given below:
Head: It consists of the nucleus which contains the DNA information of the cell.
Middle Part:: It is packed with cell organelles called Mitochondria. The mitochondria are responsible for producing energy in the cell. Hence, sperm uses this energy to move.
Tail: It allows the sperm cell to travel at a fast pace.
Female Reproductive Organs
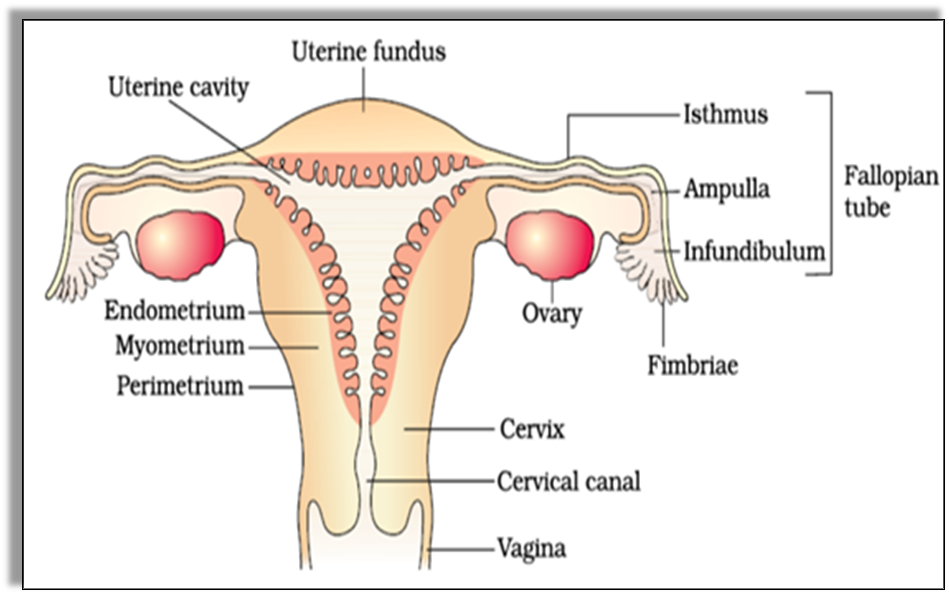
The female reproductive system provides the eggs (female gametes) for fertilization. The female reproductive organs are:
Ovaries
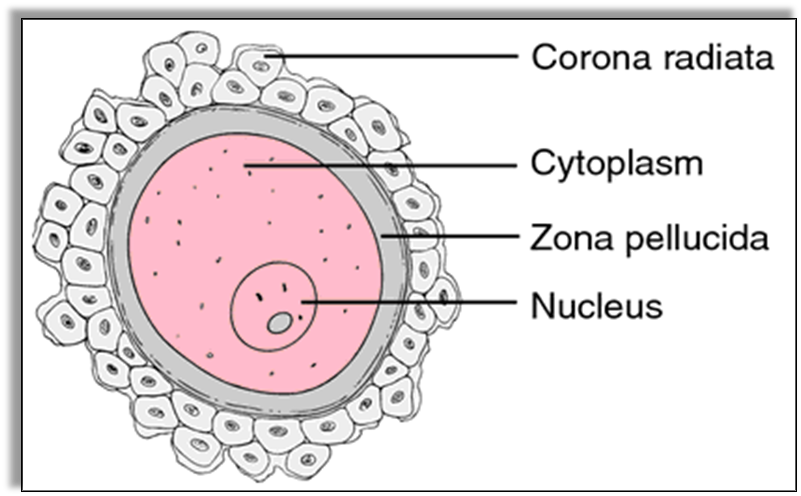
The female reproductive system comprises a pair of ovaries. These are the main female sex organs and are responsible for the production of female gametes called Eggs or Ova (ovum – singular) and female hormones. The ova or female eggs also consist of a single cell.
Estrogen and Progesterone
These are hormones or chemical substances produced by the ovaries. These hormones are responsible for the development of the female reproductive organs and the secondary sexual characteristics in women such as the development of breasts and body hair.
Oviduct or Fallopian Tubes
These are two funnel-shaped structures that extend from the superior right and left corners of the uterus to the edge of the ovaries. The ovaries release one egg every month into the oviducts. The oviducts consist of cilia that carry the ovum from the oviduct to the uterus.
Uterus
It is an inverted pear-shaped organ that allows the development of the fertilized egg into a human baby. The uterus connects with an opening called Cervix that connects it to the vagina.
Vagina
It is a muscular tube-like structure that connects with the cervix. It acts as the receptor of the penis and allows the movement of sperms to the fallopian tubes and uterus. It also allows delivery of the foetus during the birth of the child.
Menstrual Cycle
When females hit puberty, they start producing mature eggs every month indicating the ability to reproduce. This process is called the menstrual cycle. In this cycle, the ovaries produce an egg every month that travels to the uterus and attaches to its lining. If the egg is not fertilized, the uterus sheds its lining and the egg which results in bleeding in the females. On average the duration of the menstrual cycle is 28 days. The cycle starts at puberty, around the age of 10 or 11 years and lasts until the age of 45 to 55 years.
Gametogenesis
It is the process of production of gametes by the male and female primary reproductive organs. It occurs in three-phase in both males and females:
- Multiplication Phase
- Growth or maturation phase
- Meiotic Phase
Gametogenesis in males is called Spermatogenesis. It occurs in the testes and results in the formation of sperm cells.
Gametogenesis in females is called Oogenesis. It occurs in the ovaries and results in the production of female eggs or ova.
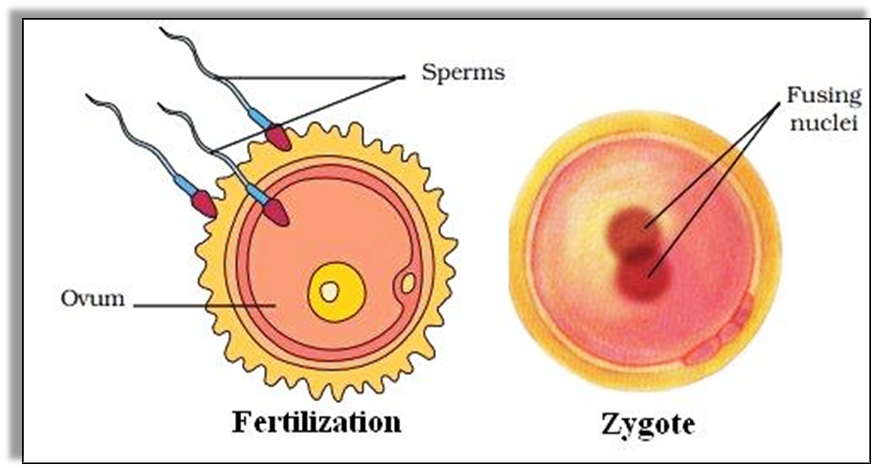
Fertilization
What is Fertilization?
- It is the fusion of male and female gametes to give rise to a single cell – zygote
- Fusion of sperm with egg to form zygote is called fertilization,
- During fertilization, the nuclei of the sperm and the nuclei of the egg fuse to form a single nucleus
- This fertilized egg is called the zygote
- The zygote is the beginning of a new individual
- Firstly, reproduction in animals begins when the sperm fuses with an ovum. This process is called Fertilization.
- The nuclei of the sperm and egg combine together and form a single nucleus.
- As a result, the zygote is formed.
- Since the zygote is formed with the fusion of male and female gametes the new individual possesses the characteristics of both the parents.
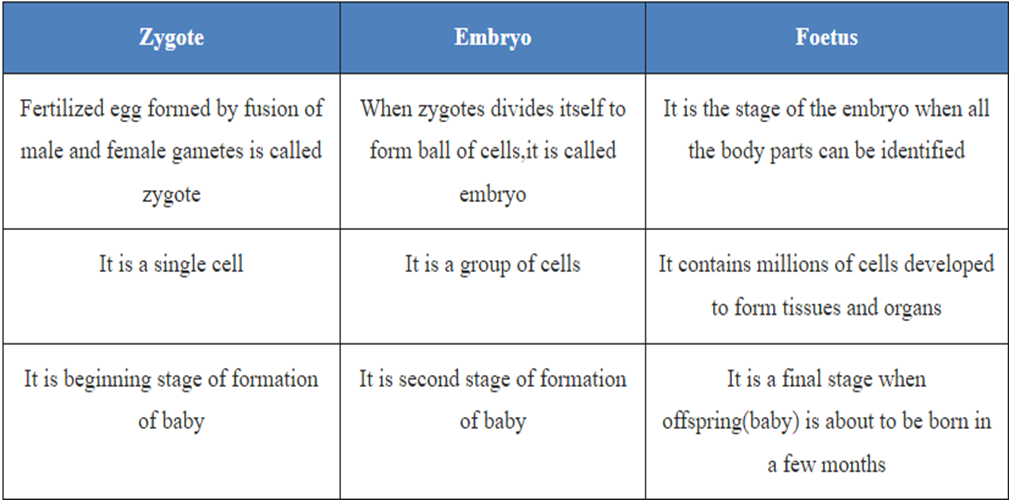
Difference between Zygote, Embryo and Foetus

External Fertilization in Frogs and Toads
- The frogs and toads reproduce by laying eggs in a slow stream or ponds.
- The female frogs first lay hundreds of eggs together in the water.
- These eggs are not covered with any hard shell instead there is a jelly-like substance that guards them all and holds them together.
- As the female frogs lay their eggs, the male frogs deposit the sperms over them.
- This results in external fertilization when the sperms come in contact with the eggs in the water.
- Though the eggs are large in numbers only a few of them manage to survive.
- There are several factors that may hinder the fertilization process such as exposure to water movement, rainfall, winds and other animals.
Internal Fertilization in Hens
- Hens reproduce by laying eggs.
- After the formation of the zygote, it keeps on dividing itself and then travels through the oviduct.
- In this process, different layers are formed over the egg that then turns into a hard shell or covering of the egg.
- When this hard shell is formed the hen lays the egg.
- Then it takes almost 3 weeks for the embryo to develop into a chick.
- In this time period, the hen often sits over the egg to provide it with warmth.
What is IVF?
- IVF Means Invitro Fertilization or ‘in Glass Fertilization’
- In IVF, fertilization of female egg and male sperm is done artificially in a glass tube
- Baby produced through IVF is called Test tube baby
Why is IVF Done?
- Fertilization of male and female gametes happens in oviducts(fallopian tubes)
- In some females, the fallopian tubes are blocked.
- So, normal fertilization is not possible
- In this case, IVF is done for fertilization
What is Procedure for IVF?
- Eggs are removed from the ovary of females
- Sperms are taken from the husband
- Sperms are mixed with eggs in a glass dish(test tube)
- When eggs are fertilized and embryos are formed
- These embryos are placed in women’s uterus
- After some time. these embryos are developed into foetus which later develops into a baby
What are Test Tube Babies?
- In some women, the oviducts are blocked and hence they are unable to hold the eggs. This means that these women are not able to bear babies because of blocked oviducts. However, due to the process of Vitro Fertilization or IVF, the freshly released eggs of females and the male sperm can be fertilized externally.
- The zygote thus formed is allowed to develop for a week outside the female body in safe conditions and is then placed in the woman's uterus.
- In this way, these women can bear babies.
- The babies that are born with the IVF process are called Test Tube Babies.
Development of the Embryo
- The zygote formed after the fertilization process divides itself in a repeated manner and forms a ball of cells.
- These cells then form different groups and each group then starts developing into different tissues and organs. This structure is called an Embryo.
- The embryo embeds itself into the uterus wall and continues to develop and grow.
- Soon the body parts such as hands, legs, feet, eyes and ears start developing.
- The embryo whose parts can be identified individually is called a Foetus.
- The foetus then completely develops and takes birth as a baby.
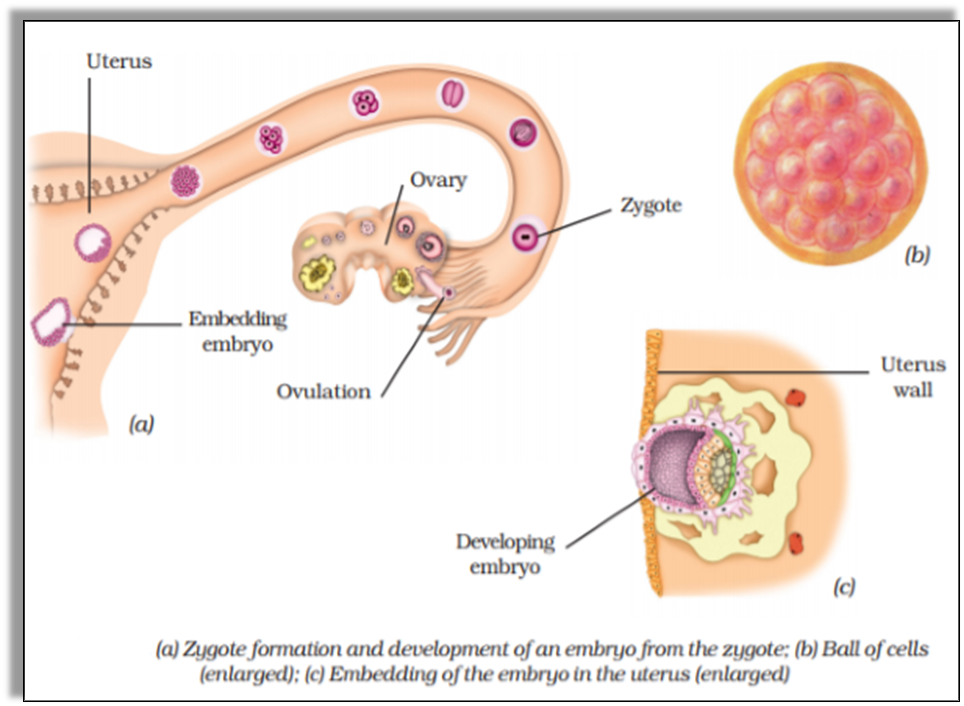
How is an embryo different from a zygote?

Based on the way how the organisms give birth to their offspring, they are classified into two categories:

What is Metamorphosis?
Metamorphosis:
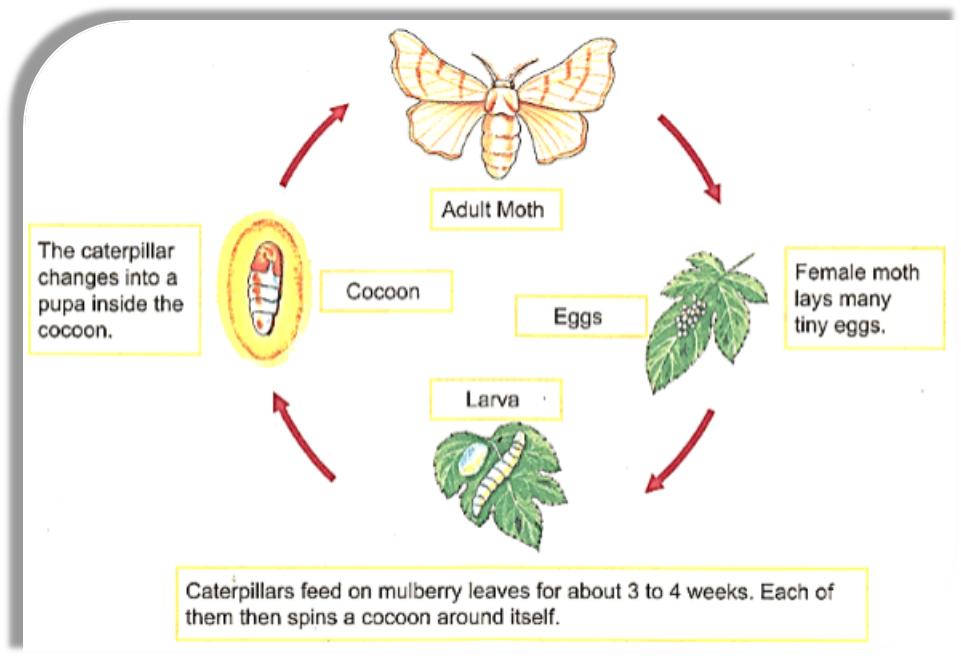
The process of transformation from an immature form to an adult in two or more distinct stages is called metamorphosis. In other words, drastic changes which occur when the fertilized egg develops into an adult are called metamorphosis.
Example:- Life cycle of Frog:
Egg ----- Larva ------ Adult
Turning into adults from young ones
- As individuals are born they continue to grow until they turn into adults.
- The young ones may or may not look like the same when they become adults. For instance, in the case of frogs and silkworms, the adults and young ones are completely different.
- The process in which the young ones undergo drastic changes as they develop into an adult is called Metamorphosis.
- Human beings do not undergo metamorphosis. This is because their body parts remain the same from childhood to adulthood.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
