1. The Ratio
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Ratio and Proportion
Ratio
A ratio is the comparison of two or more quantities of same kind using division or we can define ratio of two quantities a and b of the same kind in the same units as a fraction ![]() which is written generally as a : b (read as ‘a’ is to ‘b’). In the ratio a : b, ‘a’ is called the first term or antecedent and ‘b’ is called the second term or consequent.
which is written generally as a : b (read as ‘a’ is to ‘b’). In the ratio a : b, ‘a’ is called the first term or antecedent and ‘b’ is called the second term or consequent.
RATIO IN SIMPLEST FORM OR LOWEST TERM
A ratio is said to be in its simplest form or lowest terms when its terms do not have common factor except 1.
Note :
1. Ratio only exists between quantities of same kind :
(i) There exists no ratio between the height of a child and the weights of a child.
(ii) We cannot write a ratio between the age of a student and the marks obtained by the student.
2. To find a ratio between the quantities of same kind, quantities should be expressed in same units.
3. Ratio has no unit.
(I) Comparison of Ratio: Two ratios can be compared by converting them to like fractions. If the two fractions are equal, we say that two given ratios are equivalent.
Illustration 1
Express the ratio 36 : 81 in the simplest form.
Solution
H.C.F. of 36 and 81 is 9
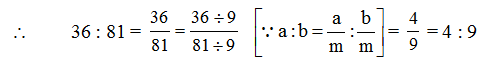
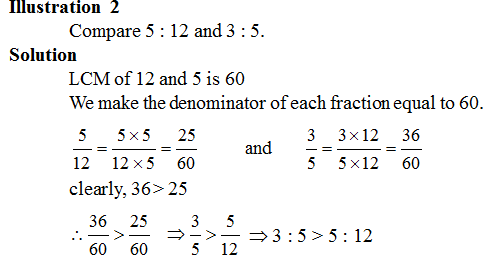
2. Percentage
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Equivalent Ratio
A ratio obtained by multiplying or dividing the numerator and denominator of a given ratio by the same non-zero number is called an equivalent ratio. A ratio remains unchanged if both of its terms are multiplied or divided by same non zero quantity.
If n ≠ 0, then :
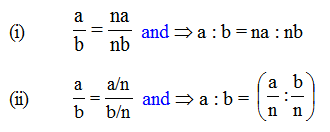

3. Percentage Application
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics

Illustration 9
In an examination, 96% of the candidates passed & 50 failed. How many candidates appeared ?
Solution
Let the number of candidates appeared be x
Percentage of those who passed = 96%
Percentage of those who failed = (100 – 96)% = 4 %
Number of failures = 4% of x.
∴ 4% of x = 50
![]()
Hence, the number of candidates appeared is 1250.
Illustration 10
(i) Chalk contains calcium, carbon and oxygen in the ratio 10 : 3 : 12, find the % of carbon in chalk.
(ii) If in a stick of chalk, carbon is 3g, what is the weight of the chalk stick ?

4. Simple interest
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
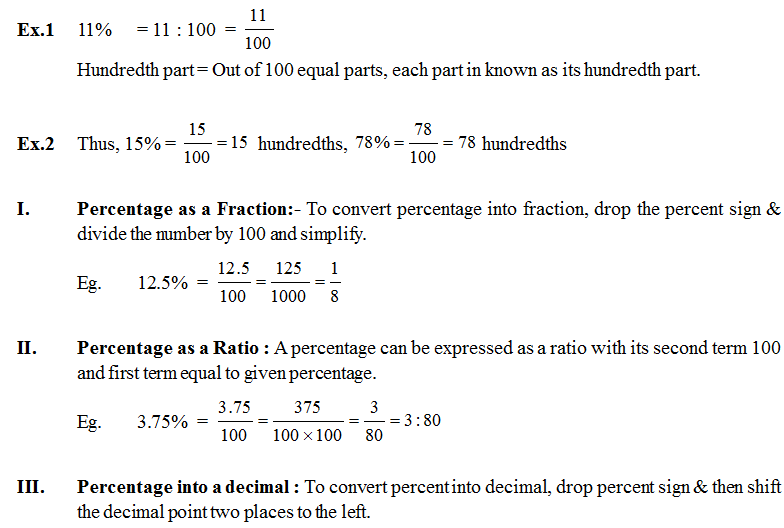
Percentage
The word ‘Percent’ is derived from Latin word ‘per centum’ meaning ‘per hundred’. The symbol for percent is %.
When we take 100 as the denominator of fractions, the numerator are called percentages. Per cent can also be expressed as a ratio with its second term 100 & first term equal to the given percent.
![]()
5. Charge given on borrowed money or simple interest
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
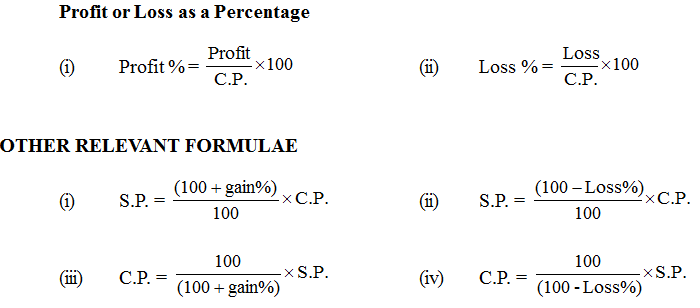
Profit, Loss & Discount
Cost price : The money paid by the shopkeeper to buy the goods from a manufactures or a wholesale is called the cost price of the shopkeeper & it is abbreviated as C.P.
Selling price : The price at which a shopkeeper sells the goods is called the selling price of the shopkeeper, it is abbreviated is S.P.
Shopkeeper makes gain or profit if S.P. > C.P.
Profit = S.P. – C. P.
S.P. = Profit + C.P.
C.P. = S.P. – Profit
Loss = C.P. – S.P.
S.P. = C.P. – Loss
C.P. = S.P. + Loss
Gain or loss is always calculated on C.P.
Overhead Charges : Shopkeeper has to bear some additional expenses such as sales tax, labour charges, maintenance charges for the goods before they are sold. Such charges are called overhead charges. Overhead charges becomes a put of cost price.
Illustration 12
An article was purchased for M400 and sold for M336. Find the loss & loss percent.
Solution
C.P. of article = M400
S.P. of article = M336
Since S.P. < C.P., so there is a loss
Loss = C.P. – S.P.
= M(400 – 336) = M64
![]()
Hence, loss = M64
Loss % = 16%.
Illustration 13
Selling price of a toy car is M540. If the profit made by shopkeeper is 20%, what is the cost price of this toy?
Solution
![]()
Illustration 14
A fruit seller bought bananas for M40 out of them, 20 bananas were spoiled and thrown away.
He sold the remaining bananas at a profit of 10%. Find the selling price of the bananas.

Charge Given on Borrowed Money or Simple Interest
- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Simple Interest
Sometimes we need to borrow money from a bank or a money lender for a specific period of time.
At the end of this period, we have to pay back the money which we had borrowed plus some additional money for using the lender’s money.
In this connection, we use the following terms.
(i) Principal : The money borrowed by a borrower from a lender is known as principal or sum.
(ii) Interest : The additional money paid by the borrower to the lender for using his money is called the interest.
(iii) Amount : The total money which the borrower pays back to the lender at the end of the specific period is called amount.
Amount = Principal + Interest
A = P + I
(iv) Rate : The interest on Rs. 100 for 1 year is known as the rate per annum.
(v) Simple Interest : If interest is calculated uniformly on the original principal throughout the loan period, it is called Simple Interest.
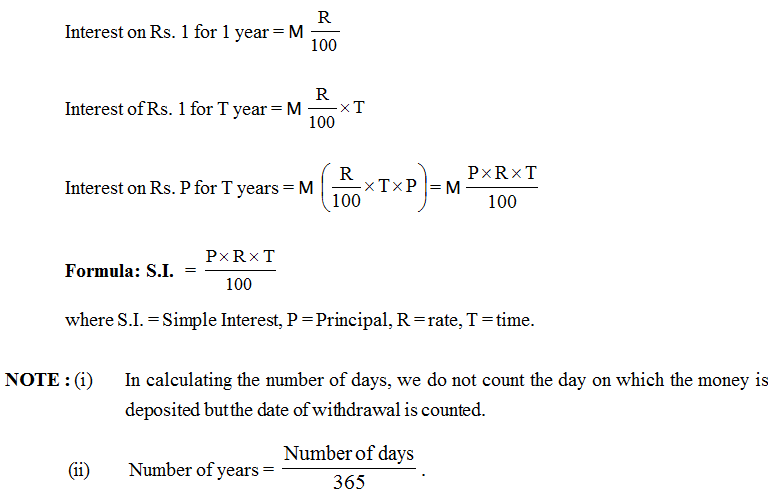
Illustration 16
Sudhir borrowed Rs. 3,00,000 at 12% per annum from a money-lender. At the end of 3 years, he cleaned the amount by paying Rs. 2,60,000 and a gold necklace. Find the cost of necklace.


 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
 Param Publication
Param Publication
