lives of the earliest people and hunters and Gatherers
LIVES OF THE EARLIEST PEOPLE
ON THE MOVE: HUNTER - GATHERERS
- The evidence of human survival on the subcontinent was dated back about 2 million years ago.
- They described as Hunters – Gatherers as their lives depended on hunting the wild animals and gathering the forest produce such as fruits, roots, nuts, seeds, leaves, stalks and eggs.


- But they could not stay too long at one place.
The reasons for their movement:
- In search of food, move to another place – Staying long at one place means eaten all the available resources (forest produce and animals) and unavailability of food at that place.

- Trace the path of animals' movement – Hunters followed the movement of the animals.


- Seasonal fruits/ flowers on plants and trees – People had to move from season to season in search of different kinds of plants.
- Availability of water: Water is essential for the survival of people, plants and animals and it found in lakes, streams and rivers. Early people lived around these places. If these water bodies were not perennial (water throughout the year), they moved in search of water to another place.

KNOWING THE EARLIEST PEOPLE LIVES
Archaeological findings tell us -
- The things used by hunters –gatherers.
- People made tools of wood, bone and stone.
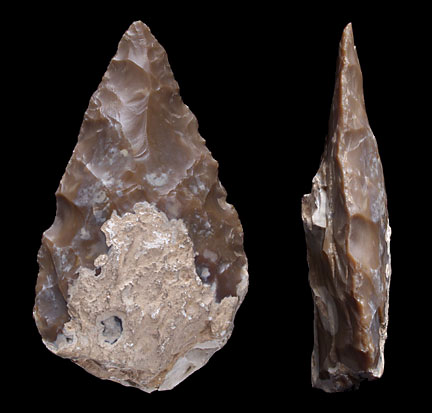


- Stone tools have survived best and used
- to cut meat and bone
- scrape bark(from trees) and hides(animal skin)
- chop fruits and roots
- to make spears and arrows (bone/wooden handle attached ) for hunting
- to chop wood used as firewood

- Wood was used to make huts and tools.

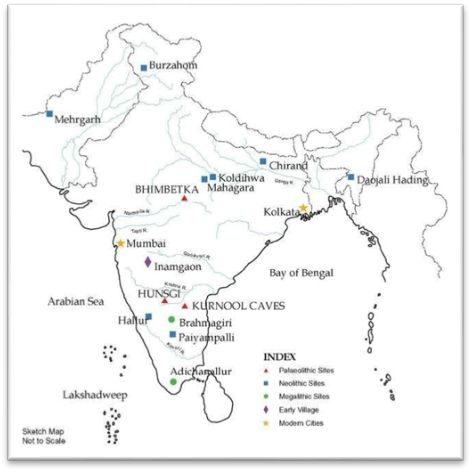
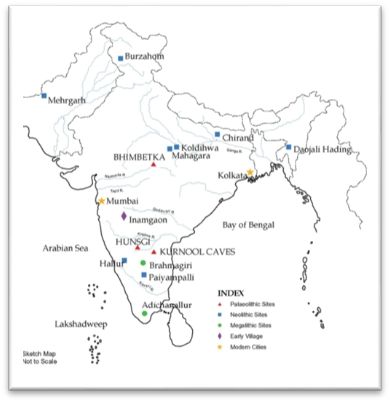
SITES OF HUNTERS – GATHERERS
Sites:
- The places where the remains of things (tools, pots, buildings etc.) were found, which were used and left behind by people.
- May be found
- on the surface of the earth
- buried under the earth
- under water
Archaeologists have found sites of hunter – gatherers:
-
- Bhimketka
- Hunsgi
- Kurnool caves
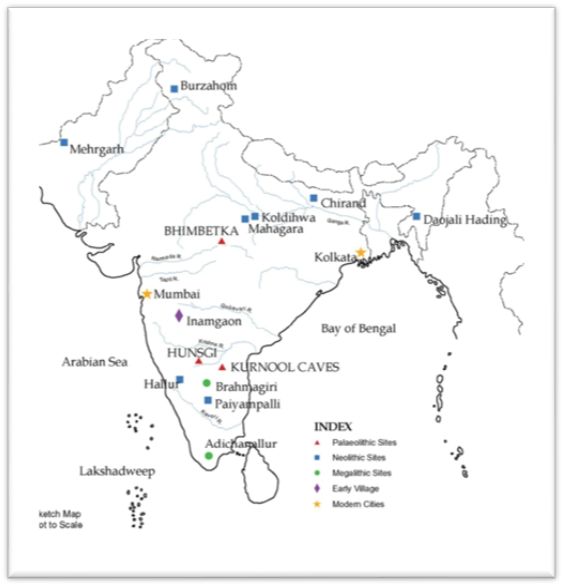
Location of the sites:
- Near sources of water
- rivers
- lakes

- Places where good quality stones available(as stone tools were important)
Bhimbetka ( Madhya Pradesh):

- An old site with caves and rock shelters.
- Close to the Narmada river
- Natural caves chosen by the people as they provided shelter from rain, heat and wind.
- People did paintings on the walls of these caves.

Stone tools & uses of Fire
STONE TOOLS AND USES OF FIRE
- Archaeologists describe the time period of Hunters-Gatherers as STONE AGE.
- Stone was used as tools and weapons and they took shelters in the caves in diverse climatic conditions.
- Stone age can be divided into three periods-
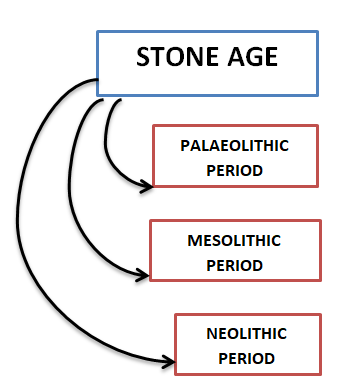
PALAEOLITHIC PERIOD:
- The earliest period.
- Comes from two Greek words, 'palaeo' means old, and 'lithos' means stone.
- Period extends from 2 million years ago to about 12,000 years ago.

- The long span further divided into three parts –
- Lower Palaeolithic
- Middle Palaeolithic
- Upper Palaeolithic
- This period covers 99% of human history.
MESOLITHIC PERIOD:
- It is also called Middle Stone Age.

- The period of environmental changes.
- Began about 12,000 years ago till about 10,000 years ago.
- Tiny stone tools found in this period, called MICROLITHS.
- Handles of bone or wood attached with the Microliths to make tools i.e. saws and sickles.

- Old tools continued with the new ones.
NEOLITHIC PERIOD:
- 'Neo' means new, it's a New stone age.
- From about 10,000 years ago

EVOLUTION OF FIRE AND ITS USES:
- Traces of ashes have been found in the Kurnool Caves of Andhra Pradesh.
- The people were familiar with the use of fire.
- a source of light
- to roast meat
- to scare away animals
- The first reported use of fire in the Indian subcontinent was from 18,000-20,000 years ago.
Changing environment
CHANGING ENVIRONMENT
- Around 12,000 years ago major changes were seen in the climate of the world.
- It was a shift to relatively warm conditions.
- This led to the development of the Grasslands.

- Which increased the number of dependent on grasslands, such as
- antelope
- deer
- cattle
- goat
- sheep
- Hunters of these animals now started following them.
- Learning about their food habits.
- Their breeding seasons.
- Now people started herding and rearing animals.
- Fishing was also an important activity.

Farmers:
- Several grain bearing grasses grew naturally
- wheat
- barley
- rice

- This led them to grow plants on their own and became farmers.
Herders:
- People started taming animals by leaving food near their shelters.
- The first tamed animal was the wild ancestor of the dog.
- Later, relatively gentle animals who ate grass lived in herds-
- sheep
- goat
- cattle and
- pigs
Domestication: A process in which people grow plants and look after animals.

- Gradually plants and animals looked different from their wild variety as they were tamed.
- Then people selected plants and animals for domestication.
- People selected them wisely
- those plants and animals that are not prone to disease
- plants that yield large-
- size grain
- have strong stalks
- capable of bearing the weight of the ripe grain
- Seeds preserved of those plants and sown to ensure new plants with the same qualities.
- Relatively gentle animals were selected for breeding.
- Gradually, domesticated animals and plants become different from their wild ones.
- For example- teeth and horn of the wild animals differ from those of domestic animals.

- Domestication began about 12,000 years ago in various parts of the world.
- All the plants and animal product which we use today is a gradual result of domestication.
- The earliest domesticated plants were wheat and barley whereas domesticated animals were sheep and goat.
Paleolithic site-Hunsgi
PALEOLITHIC SITE – HUNSGI
- Hunsgi is a village in Yadgir district, Karnataka.
- Numerous early Palaeolithic sites found here.
- Many stone tools, and weapons that are made of reddish-brown chert (a stone) are found at these sites.
- The tools found include long blades with sharp edges and many other instruments for multi-purpose usages.
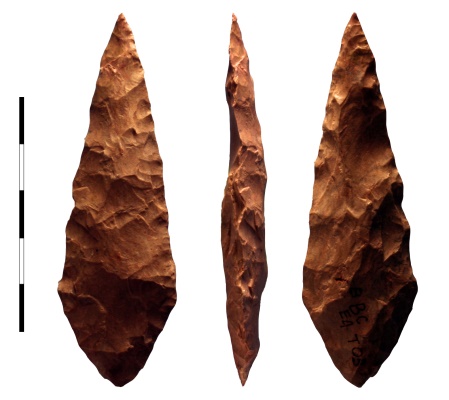

- Most tools were made of limestones which were locally available.


 Indira Gandhi Memorial High School
Indira Gandhi Memorial High School
