Life in the city
Life in a city
Around 150 years ago, railway lines were laid for the first time in Punjab. Engineers stumped on the site of Harappa in present day Pakistan. To them it was a place which delivered good quality bricks. So they carried thousands of bricks from the old site to lay down railway lines. These bricks were from the old buildings that were destroyed in Harappa.
Harappa was excavated around 80 years ago as the oldest city of the subcontinent. It was the first city to be excavated. So similar cities having similar building were described as Harappa.
Many of the cities were divided into 2 or more parts. The part in the west were smaller but higher called the citadel, while the parts in the east were bigger but lower called the lower Town. Walls of baked bricks were laid around each part. These baked bricks of so fine quality that they last very longer. These bricks were laid in interlocking pattern which made it more strong.
Special buildings were built on citadel. In Mohejodaro, special area called Great Bath was built. Bricks coated with plaster were built and was made water tight with the layer of natural tar. There were steps leading to it from both the sides. It also had changing rooms. Well water were inlaid inside it and we’re drained out after use. It was used for holy dip by great people on some great occassions.

Cities like kalibangan and lothal had fire alters where sacrifices were made. Mohejodaro, Harappa and lothal had store houses.
Many of the cities had covered drains. There were slopes for the easy flow of water into the drains. There were holes for cleaning purposes.
A Harappan city was a busy place.
People who planned the construction of special building were called the rulers. These rulers used to sent their people to distant lands to get special metals, ornaments or any other things that they wanted. Scribes were another important people who knew to read and write and prepare seals.

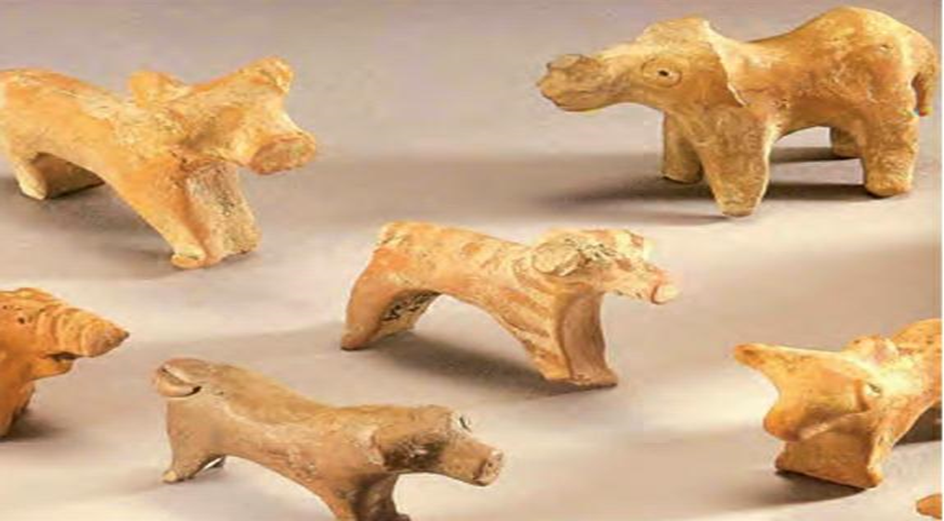
Craftpersons were people who made different types of things. Toys made of Terracotta were found.

Life in the city
HARAPPA - LIFE IN THE CITY
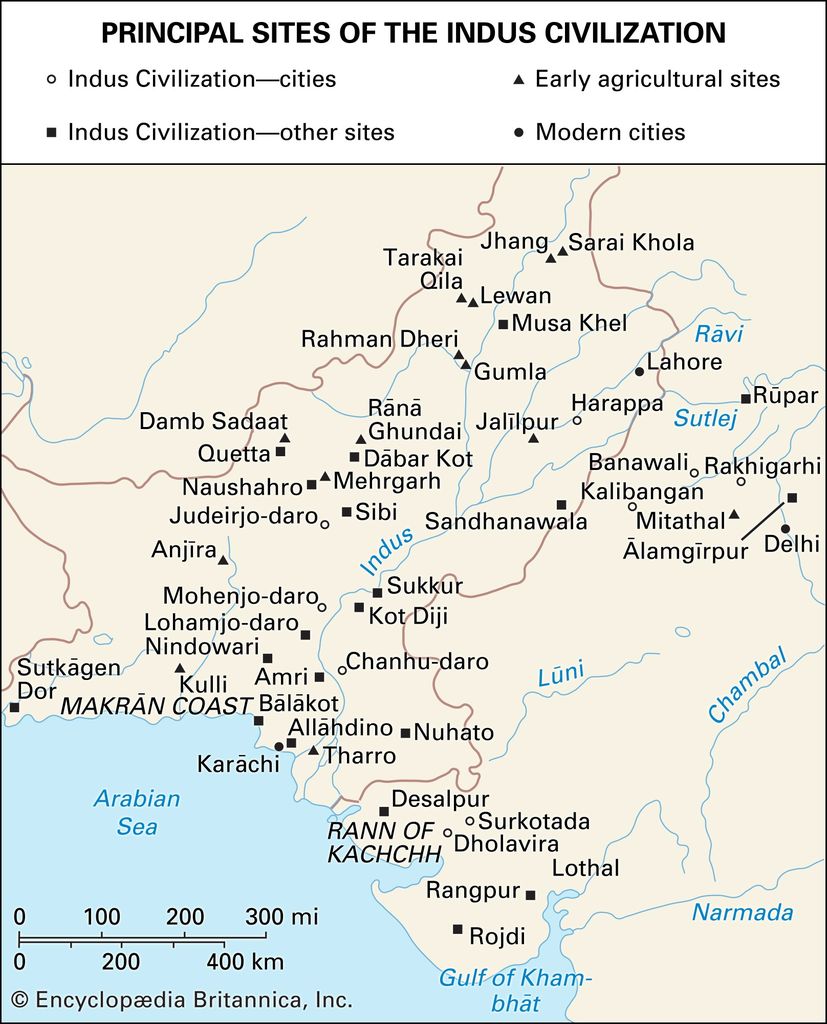
- Harappan city was a very busy place

- People involved-
-
- THE RULERS:
-
-
- Planned the construction of special buildings in the City.
- Sent people to distant places to get metal, precious stones and other things for the construction.
- Kept ornaments of gold and silver, or beautiful beads for themselves.
-
THE SCRIBES: People who knew how to write
- Prepared the seals

- Wrote on other materials but not survived
THE CRAFTS PERSONS:
-
- Making all kinds of things
-

- Terracotta toys for children
-
- Either in their own homes
- Or in special workshops
THE TRAVELLERS:
-
- Travelled distant lands
- Returned with raw materials
- With stories
crafts , raw materials and food
New crafts
Most of the things found there were made of stone, gold, silver, metal. Copper and bronze were used to make vessels, tools , weapons. Gold and silver were used to make ornaments and vessels.
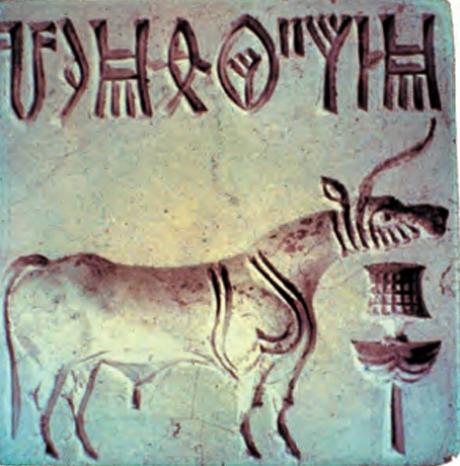
Harappans made seals made of stone. These were basically rectangle and had animals carved on it. The Harappans made beautiful pots with black designs.
Cotton was generally grown at Mehergarh. People such as specialists were skilled to make different things.
Faience was produced unlike stone and shells that were produced naturally. A gum used to shape sand and powered quartz. Colours like blue or sea green were used to glaze objects. Faiaence was used to make beads, earings, neckpiece, bangles, etc.
Raw materials & Food
Raw material and food
Raw materials were substances that were found naturally such as wood, or metal ore or produced by the farmers. These raw materials are then processed into finished goods. For example, cotton is the raw material processed into cloth. some raw materials were available locally while some were asked to be brought from distant lands like copper, gold, silver or some precious stones.
The Harappan have got copper from Rajasthan or Oman in West Asia. Tin were mixed with copper to produce bronze which were brought from Afghanistan and Iran. Gold were brought from Karnataka and precious stones from Gujarat Afghanistan and Iran.
People living in cities used to produce crops and reared animals. Wheat, barley, rice, pulses, lentils were crops produced.
Plough was used for turning the soil and cultivating. Plough were made of wood.
Rainfall were scarce, so the irrigation system was practiced. This means that water were provided to the fields artificially. The Harappan reared cattle, sheep , goat , buffalo. Fruits like ber were collected and fish were caught. They hunted animals like antelopes.
Raw materials & Food
RAW MATERIALS
Raw materials:
Substances that are
- found naturally
- Wood
- Ores of metals
- Produced by farmers and herders
Raw materials + process = finished goods
cotton(raw material produced by the farmers) + processes = cloth
The Harappans used locally available raw materials as well as brought from distant places such as copper, tin, gold, silver, and precious stones.
- Copper from present-day
- Rajasthan
- Oman in West Asia
- Tin from present-day
- Afghanistan
- Iran
(tin was mixed with copper to produce bronze)
- Gold from present-day Karnataka
- Precious stones from present-day
- Gujarat
- Iran
- Afghanistan
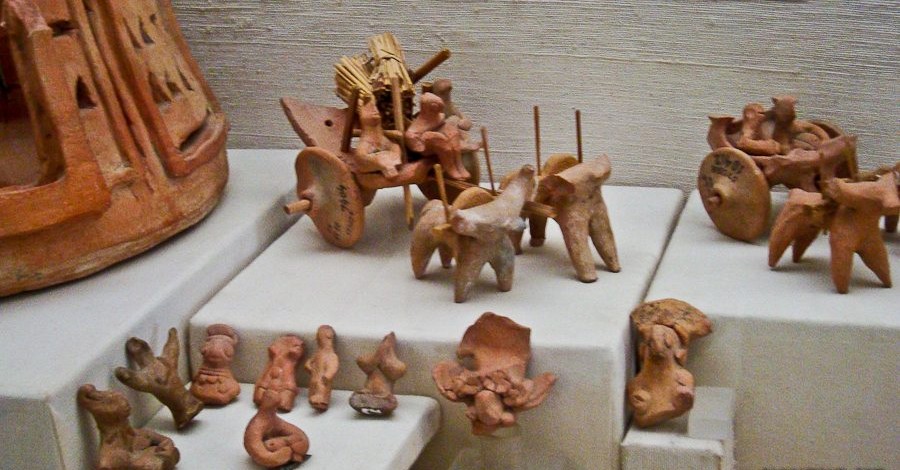
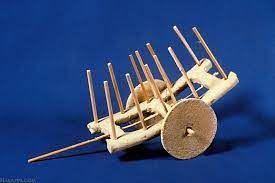
- Toy cart shows that carts were used to transport things from one place to another.
- Seals show that the trading of goods flourished at that time.

FOOD FOR PEOPLE IN THE CITIES
PEOPLE IN THE CITIES:
- The rulers, the scribes, and the crafts persons lived in the cities.
- The farmers and the herders lived in the countryside and supplied the food to the city.
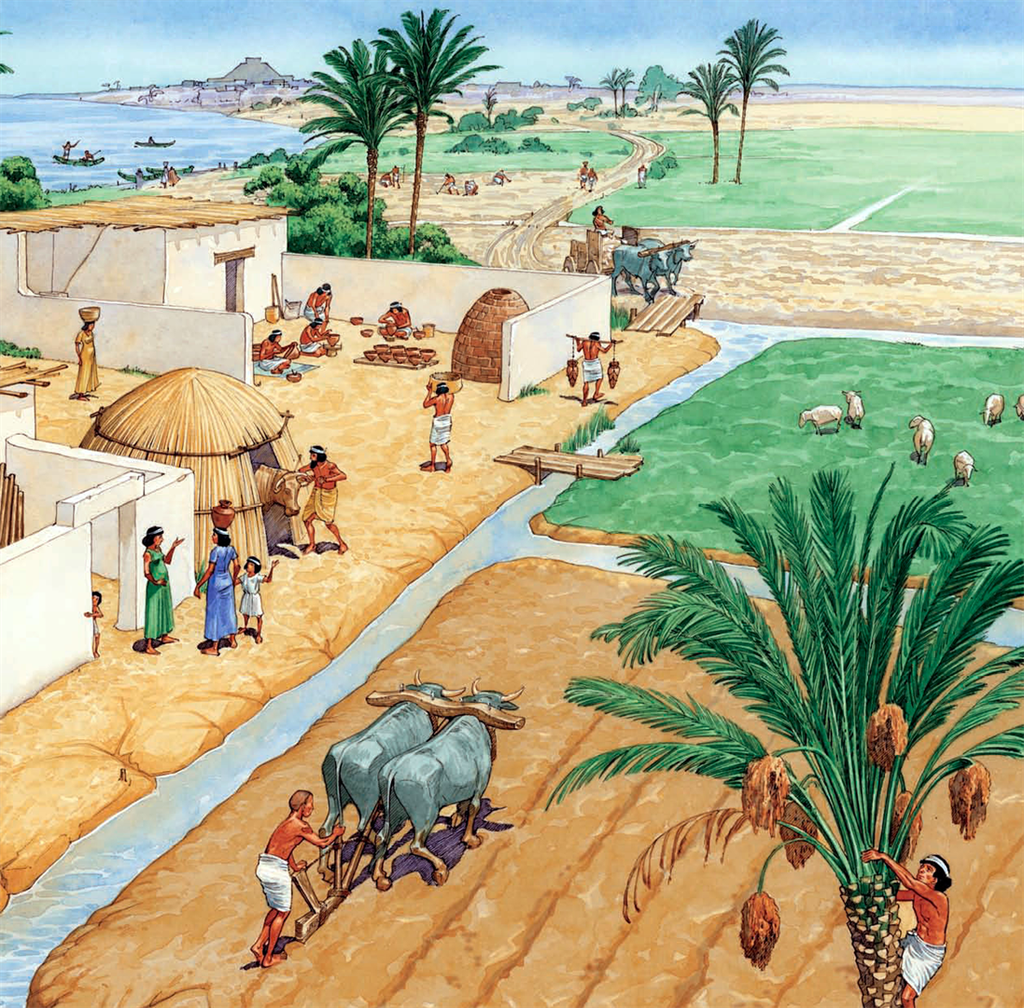

THE FARMERS:
We got to know through the remains that-
- The Harappans grew
- Wheat
- Barley
- Pulses
- Peas
- Rice
- Sesame
- Linseed
- Mustard
- A new tool.the plough was used to dig the earth and planting seeds.

- The plough was probably made of wood that’s why not survived but toy models have been found.
- The Harappan region did not receive heavy rainfall, irrigation needed in some parts.
- This means that water once stored then supplied to the fields where plants grow.
THE HERDERS:
- The Harappan reared cattle, sheep, goat and buffalo.
- They settled around the water resources and the pasture lands.
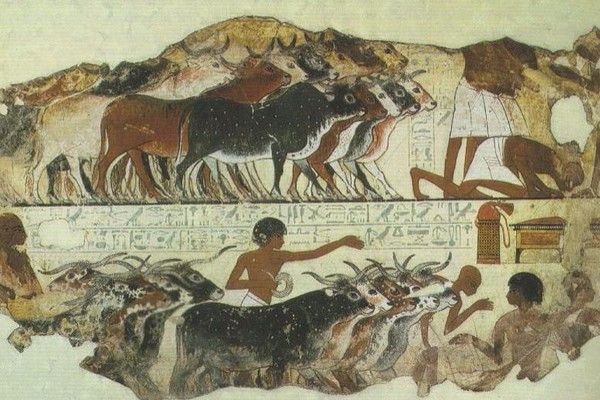

- And moved to far off places in search of water and pastures during the summers.
- They collected fruits like ber, caught fish and hunted wild animals like the antelope.
End of first civilization
End of first civilization
The city of Dholavira is located in the Rann if Kutch where one would find fresh water and fertile soil land. The city of Lothal was found near the tributary of Sabarmati, in Gujarat close to the Gulf of Khambet. It’s the place where semi precious stones were found. It is believed to be an important centre where objects were made out of stone, shell and metal. There were storehouses also in the city. Harappan script carved on white stone and then inlaid in wood were found. Seals and sealings were found in the storehouses.
Seals were used to stamp the bags or packets having goods inside it. When the packets are tied, a clay layer is placed on the top of the know and then the seals are pressed on it. Thus ensured security and safety of the goods being sent from one place to another. If the seals are intact the receiver would be assured the goods have reached him safely. The impression on the seal is known as sealing.
Seals are used even today.
Dockyard were also found in the city of Lothal. It’s the place where boats and ships would have come to rest from the seas and the river channels. Goods from the ship’s were loaded and unloaded here.
Around 3900 years ago, the lives begin to change. There were fewer people living in the cities, fewer raw materials were been brought, seals and sealings, weights were no longer in use. However no body knew the reasons behind these changes, but there were many assumptions and believes. Some believed that rivers were getting dried up. While some believed there were large scale deforestation. The need for fuel for baking, burning, cooking were the reason behind deforestation. Some believed grazing by the herds and cattle would have destroyed the green cover. Some areas were flooded. Flooding or drying up if the rivers were believed to have effected some areas. But no body could cite the exact reason of the end of all the city lives.
It was seen that in Mohejodaro, the streets were piled up with garbage, drainage system is poorly maintained, houses were being constructed over the streets hence lacked planning.
Rulers lost their control over their subjects. People residing in Sindh and West Punjab abondoned the cities and moved to newer settlement towards South and East.
New city life cropped up around 1400 years later.
End of first civilization
END OF FIRST CIVILIZATION
- The cities of Harappa developed about 4700 years ago.
- These cities were fully flourished.
- The construction of the houses, drains and streets reflected the well planned architecture of that period.

But around 3900 years ago ,major changes were seen .
-
- People stopped living in many of the cities.
- Writing, seals and weights were no longer used.
- Raw materials were rarely brought from distant lands.
- In Mohenjodaro,
- Garbage piled up on the streets
- The drainage system broken down
- Less impressive houses were built
The reason behind these changes were not sorted out till date but scholars suggested that-
- The rivers dried up
- There was deforestation
- As fuel was required for baking bricks and smelting copper ores
- Grazing by large herds of cattle, sheep and goat
- There were floods in some areas.
- The rulers lost their control over the region.
These reasons are not accepted at all as it would only affect some areas, not the whole civilization together.
Whatever the reasons were, here was the end of this flourished civilization .
Now people moved into newer and smaller settlements to the east and the south.
New cities emerged about 1400 years ago.

 Indira Gandhi Memorial High School
Indira Gandhi Memorial High School
