1. Chemical Equations
- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
CHAPTER  1
1
CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS
* CHEMICAL EQUATIONS
CHEMICAL REACTIONS:- The process in which two or more substance combine with each other to form new substances with new properties is called chemical reaction.
There are two parts of a chemical reactions :-
(i) Reactants:- The substances which take part in a chemical reaction are known as reactants.
(ii) Products:- The new substances formed during a chemical reaction are known as products.
There are 5 ways to tell if a chemical reaction has occurred.
- Change in state.
- Change in colour.
- Change in temperature.
- Evolution of a gas.
- Formation of precipitate.
Chemical reaction in everyday life:-
- Digestion of food.
- Respiration.
- Rusting of iron.
- Formation of curd.
- Burning of magnesium ribbon.
Chemical Equations:- A chemical equation is a written representation of a chemical reaction.
The representation of chemical reaction using symbols and formulae of the substances is called chemical equation.
A + B
Reactants Products
n this equation, A and B are called reactants and C and D are called the products. The arrow shows the direction of the chemical reaction. The necessary condition such as temperature, pressure or any catalyst should be written on arrow between reactants and products.
E.g. Magnesium is burnt in air to form magnesium oxide.
(i) Word equation for above reaction would be -
Magnesium + oxygen
( Reactants ) ( Product )
Skeletal equation for above reaction would be -
Mg +
BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS:-
- LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS :- Mass can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- So number of elements involved in chemical reaction should remain same at reactant and products side.
For Example ,
Zn +
(Zinc) ( Sulphuric Acid) (Zinc Sulphate) ( hydrogen)
Let us check the number of atoms of different elements on both sides of the arrow .

As the number of atoms of each element is same on both sides of arrow. This is a balanced chemical equation.
Let us take another example :-
Fe +
STEP 1 :- Write a chemical equation.
Fe +

STEP 3 :_ Select the element which has the maximum number of atoms . now equalize the number of atoms by putting coefficient in front of it.
Fe + 4
STEP 4 :- Fe and H atoms are still not balanced choose any elements now to balance. To equalize the number of H atoms,
Fe + 4
STEP 5 :- Now, take Fe and equalize the number of Fe atoms.
3 Fe + 4  F
F
Now all the atoms of elements are equal on both sides.
STEP 6 :- To make the chemical equation more information ,write the physical states of reactants and products.
Solid state = (s)
Liquid state = (l)
Gaseous State = (g)
Aqueous state = (aq)
3 Fe (S) + 4
STEP 7:- Write necessary conditions of temperature pressure or catalyst on above or below arrow.
For Example:-
![]()
2. Types of Chemical Reactions
- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
TYPE OF CHEMICAL REACTION
There are five type of chemical reactions.
COMBINATION REACTION:- The reaction in which two or more reaction combine to form a single product is called combination reaction They are represented by equation of the following term.
Reactant product
For Example :-
Burning of coal
C(s) +
(carbon) (oxygen) (carbon dioxide)
Formation of water
2
(Hydrogen) (oxygen) (Water)
Formation of slaked line
CaO (s) +
(calcium oxide) (water) (calcium Hydroxide)/ slaked lime
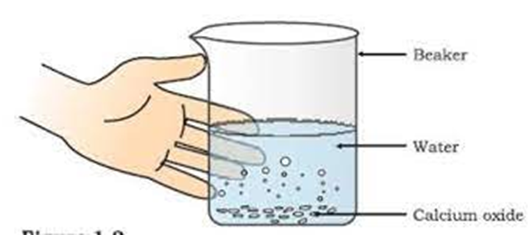
Formation of slaked lime by the reaction of calcium oxide with water.
DECOMPOSITION REACTION :- The reaction I which single compound breaks down to simpler product is called decomposition reaction. They are represented by equation of the following term .
AB
(i) Thermat decomposition :- when decomposition is carried out by heating.
For example
(i) 2 Fe S
(Ferrous sulphate ) (Ferric Oxide)
Green colour Red brown colour
(ii) CaC
(calcium carbonate) ( calcium oxide ) (Carbon dioxide ) Limestone quick lime
(iii) 2Pb (N
(Lead nitrate ) (lead oxide) (Nitrogen dioxide) oxygen
Brown fumes
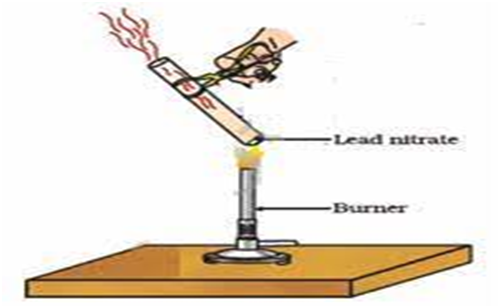
Heating of lead nitrate and emission of nitrogen dioxide
ELECTRONIC DECOMPOSITION :- When decomposition is carried out by passing electricity .
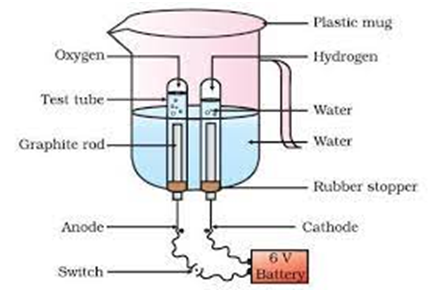
For Example:- (i) Electrolysis of water.
Electric current
2
(Water) (Hydrogen) (Oxygen)
Electrolysis of water is done as follows:-
When decomposition is carried out in presence of sunlight .
For Example:-
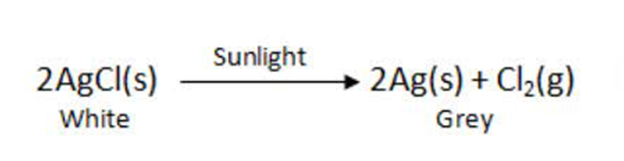
This is why silver chloride turns grey in sunlight because of the decomposition of silver chloride into silvers and chloride by light.
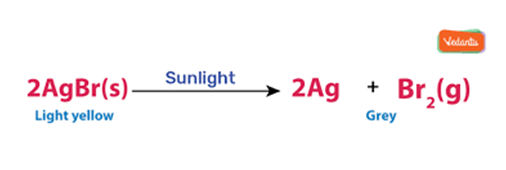
This reaction is used in black and write Photography.
DISPLACEMENT REACTION :- This reaction in which more reactive element displace less reative element from its salt solution is called displacement reaction . they aare represented by equation of the following term.
A + BC
For example :-
(i) Fe (s) + CuS
(Iron ) (copper Sulphate) ( iron Sulphate) ( Copper)
Fe is more reactive than therefore iron (Fe) has displaced copper (Cu) from copper sulphate solution.
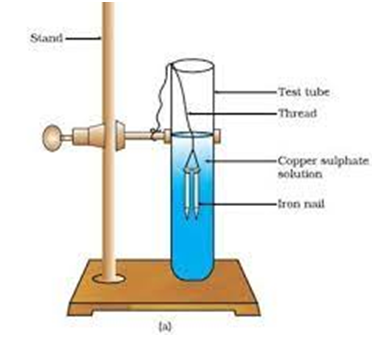
Iron nails dipped in copper sulphate solution.
(ii) Zn(s) + CuS
(Zinc) (copper sulphate) ( Zinc sulphate ) copper
Zinc is more reactive than copper , therefore it displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
(iii) Pb (s) + CuC
(Lead) (copper chloride) ( lead chloride) copper
Lead is more reactive elements than copper, therefore it displaces copper from copper chloride solution.
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIVE :- The reaction in which the reactant ions exchange to form new products is called double displacement reaction . they are represented by equation of the following term.
AB + CD
For Example :-
N
(sodium sulphate) (barium chloride) (barium sulphate) (sodium chloride)
White precipitate of BaS
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION :-
OXIDATION
(i) The addition of oxygen to reactant
(ii) the removal of hydrogen from reactant
For Example :-
2 Cu +
(Copper) (oxygen) (copper oxide )
Black substance
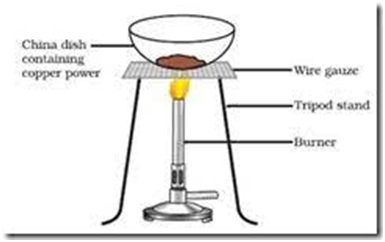
Oxidation of copper to copper oxide
Reduction : - (i) the addition of hydrogen to reactant
(ii) the removal of oxygen from a reactant.
Redox Reactions :- The reaction on written one substance gets oxidisied and other get reduced is known as redox reaction
For example :-
CuO +
In this reaction CuO is reduced to Cu and
ZnO + C
Here, C is oxidized to CO because oxygen is being added and ZnO IS REDUCED TO Zn because O is being removed.
NOTE :
* If a substance loses oxygen during a reactant , it is said to be reduced.
ENDETHERMIC REACTION:- Reaction in which energy is absorded are known as endothermic reaction.
For example :-
CaC
FXOTHERMIC REACTION :- Reaction in which heat is released along with formation of products.
For Example,
C
3. Effects of Oxidation Reactions in Everyday Life
- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
EFFORTS OF OXIDATION REACTIONS IN EVERYDAY LIFE
1) COROSION :- When a metal is exposd to moisture ,air, acid eyc. For some time , a layer of hydrated oxide, is formed which e weaknes the metal and hence metal is said to be corroded.
Example of corrosion are:-
- Rusting of iron .
- Black coating on silver
- Green coating on copper.
• Rusting of iron :- when iron is exposed to oxygen in the presence of moisture, reddish brown power is formed.
This is process is knon as rusting of iron.
• Method to prevent corrosion are:-
- Galvanization
- Electroplating
- By putting paints
2) RANCIDITY:- The oxidation of fats and oils when exposed to air is known as rancidity . due to rancidity, bad smell and bad taste of food occurs
Method of prevent rancidity are :-
- By adding antioxidants.
- Refrigeration.
- Replacing air by nitrogen.
- Keeping food in air tight containers.
• Chips manufactures fill bag of chips with nitrogen because it is non reactive gas and it prevent the chips from getting oxidized.

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
