- Books Name
- Chemistry Class 10 NCERT based
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
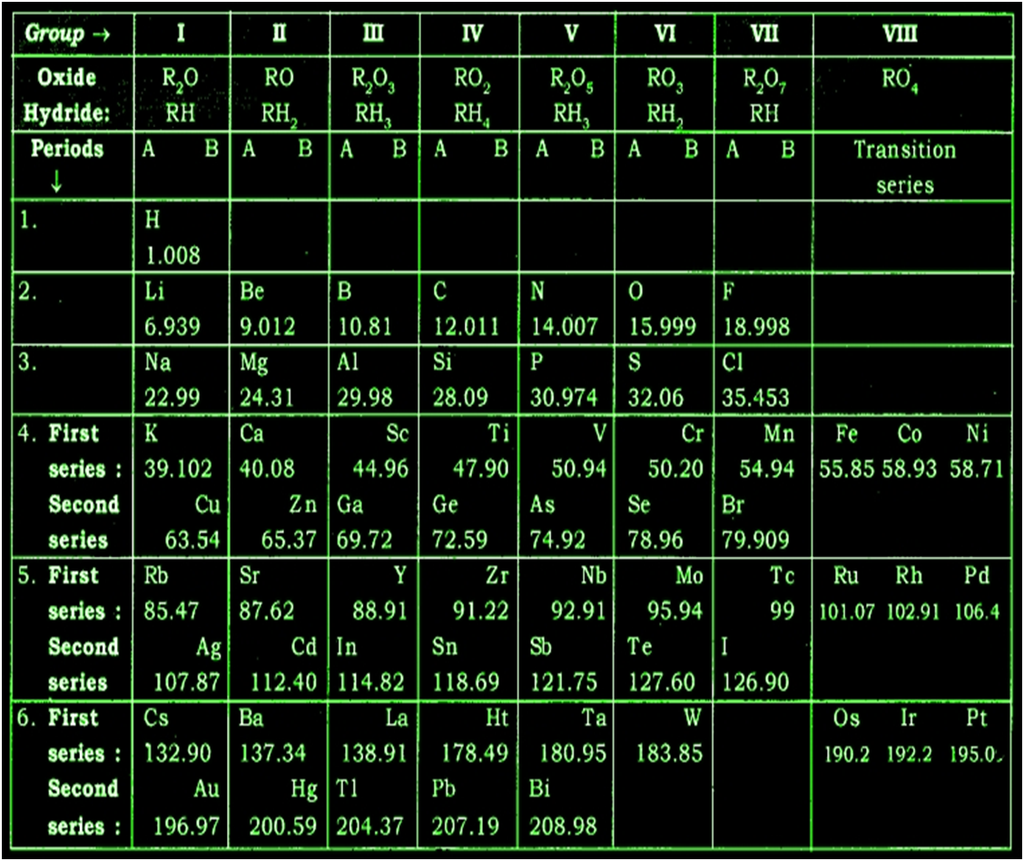
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table and Law
The physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic weights.
Features of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
● Twelve horizontal rows, which were condensed to 7, known as periods.
● Eight vertical columns known as groups.
● Groups I to VII subdivided into A and B subgroups.
● Group VIII doesn’t have any subgroups and contains three elements in each row.
● Elements in the same group exhibit similar properties.
Achievements of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
1. A systematic study of elements: Elements with similar properties were grouped together, that made the study of their chemical and physical properties easier.
2. Correction of atomic masses: Placement of elements in Mendeleev’s periodic table helped in correcting the atomic masses of certain elements. For example, the atomic mass of beryllium was corrected from 13.5 to 9. Similarly, atomic masses of indium, gold, platinum etc., were also corrected.
Limitations of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
1. Position of hydrogen: Hydrogen resembles both, the alkali metals (IA) and the halogens (VIIA) in properties, so, Mendeleev could not justify its position.
2. Position of isotopes: Atomic weight of isotopes differ, but, they were not placed in different positions in Mendeleev’s periodic table.
3. Anomalous pairs of elements: Cobalt (Co) has higher atomic weights but was placed before Nickel (Ni) in the periodic table.
4. Placement of like elements in different groups: Platinum (Pt) and Gold (Au) have similar properties but were placed in different groups.
5. Cause of periodicity: He could not explain the cause of periodicity among the elements.
Periodicity of Properties: The repetition of properties of elements after certain regular intervals is known as Periodicity of Properties.
Merits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
1.Mendeleev’s left vacant places in his table which provided an idea for the discovery of new elements. Example: Eka-boron, Eka-aluminium and Eka-silicon.
2.Mendeleev’s periodic table was predicted properties of several undiscovered elements on the basis of their position in Mendeleev’s periodic table.
3.It is useful in correcting the doubtful atomic masses of some elements.
4.Noble gases could accommodate in the Mendeleev’s periodic table without disturbing the periodic table after discovery.
Limitations of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
(a) No fixed position for hydrogen: No correct position of the hydrogen atom was in Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Example: Position of hydrogen with alkali metals and halogens (17th group).
(b) No place for isotopes: Position of isotopes were not decided.
Example: Cl-35 and Cl-37.
(c) No regular trend in atomic mass: Position of some elements with lower atomic masses before with higher atomic mass.
Example: Ni-58.7 before Co-58.9.
Mendeleev’s original periodic table is reproduced in the table below
- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
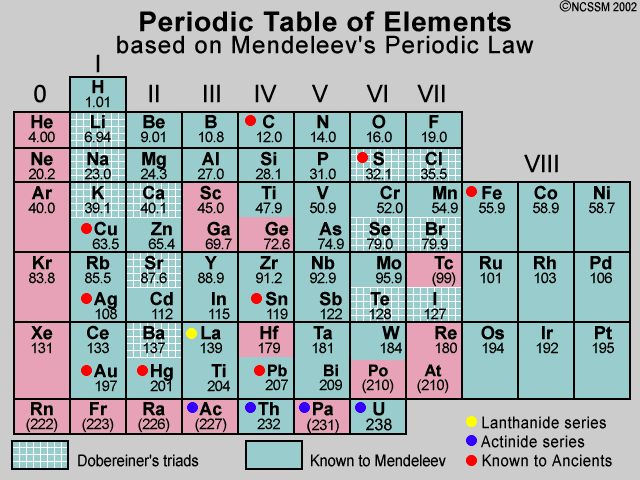
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
Mendeleev arranged 63 elements known at that time in the periodic table. According to Mendeleev “ the properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses” the table consists of eight vertical coloumn called groups and horizontal rows called periods.
Achievements :-
(I) The arrangement of elements in group and periods made the study of elements quite systematic in the sence that if properties of one element in a particular group are known, those of the other can be easily .
(II) many gaps were left in this table for undiscovered elements however, properties of these elements could be predicted in advance from their expected position. This helped in the discovery of these elements the lements silicon , gallium and germanium were ddiscovered in this manner.
(III) Mendeleev corrected the atomic masses of certain elements with the help of their excepted position and properties.
(Iv) When inert gasses were discovered they could be placed in a new group without disturbing the existing order.
Limitations :-
- He could not assign a correct position of hydrogen in his periodic table 1 as the properties of hydrogen resembles both with alkali metals as well as with halogens.
- The atomic masses do not increases a regular manner in going from one elements to the next , so it was not possible to predict how many elements could be discovered between two elements.
- The isotopes of some element will be given different position if atomic number is taken as basis which will disturb the symmetry of the periodic table.

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
