- Books Name
- Chemistry Class 10 NCERT based
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chemical Properties of Metals
1. Reaction with oxygen: Most of the metals form respective metal oxides when reacting with oxygen.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal Oxide
Examples:
Reaction of Potassium with Oxygen: Potassium metal forms potassium oxide when reacts with oxygen.
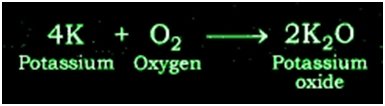
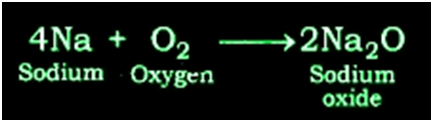
Reaction of Sodium with Oxygen: Sodium metal forms sodium oxide when reacts with oxygen.
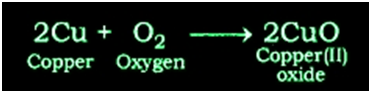
Reaction of Copper metal with Oxygen: Copper does not react with oxygen at room temperature but when burnt in air, it gives oxide.
Silver, gold and platinum do not combine with the oxygen of air even at high temperature. They are the least reactive.
2. Reaction of metals with water: Metals form respective hydroxide and hydrogen gas when reacting with water.
![]()
Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen
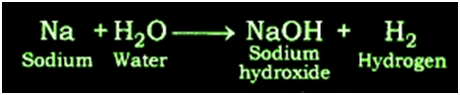
Reaction of Sodium metal with Water: Sodium metal forms sodium hydroxide and liberates hydrogen gas along with lot of heat when reacting with water.
Reaction of Iron with Water: Reaction of iron with cold water is very slow and comes into notice after a long time. Iron forms rust (iron oxide) when reacts with moisture present in the atmosphere. Iron oxide and hydrogen gas are formed by passing of steam over iron metal.
3. Reaction of metals with dilute acid: Metals form respective salts when reacting with dilute acid. Reaction of Sodium metal with dilute hydrochloric acid: Sodium metal gives sodium chloride and hydrogen gas when react with dilute hydrochloric acid.
![]()
![]()
Hydrogen gas is not when metal is treated with nitric acid (HNO3):
Nitric acid is strong oxidising agent and it oxidises the hydrogen gas (H2) liberated into water (H2O) and itself get reduced to some oxide of nitrogen like nitrous oxide (N2O)3 nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
Copper, gold, silver are known as noble metals. These do not react with water or dilute acids.
The order of reactivity of metal towards dilute hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid is in the order;
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu > Hg > Ag
Metal Oxides
Chemical Properties: Metal oxides are basic in nature. The aqueous solution of metal oxides turns red litmus blue.
Reaction of Metal oxides with Water: Most of the metal oxides are insoluble in water. Alkali metal oxides are soluble in water. Alkali metal oxides give strong base when dissolved in water.
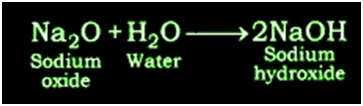
Reaction of Sodium oxide with Water: Sodium oxide gives sodium hydroxide when reacts with water.
Reaction of Zinc oxide and Aluminium oxide: Aluminum oxide and zinc oxide are insoluble in water. Aluminium oxide and zinc oxide are amphoteric in nature. An amphoteric substance shows both acidic and basic characters. It reacts with base like acid and reacts with an acid like a base.

When zinc oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide, it behaves like an acid. In this reaction, sodium zincate and water are formed
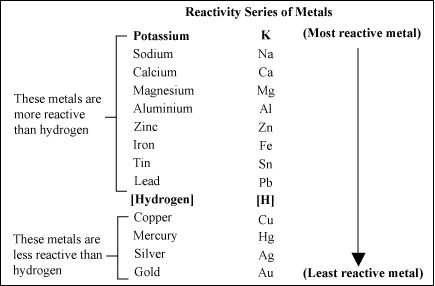
Reactivity Series of Metals: The order of intensity or reactivity of metal is known as Reactivity Series. Reactivity of elements decreases on moving from top to bottom in the given reactivity series. In the reactivity series, copper, gold, and silver are at the bottom and hence, least reactive. These metals are known as Noble metals.
Reactivity of some metals are given in descending order :
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu
- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chemical properties of Metals
(i) Reaction with air :-
All metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxide .
Metal +
For example,
2
4Al + 3
- Sodium and potassium react so vigorously that they catch fire in open so they are kept immersed in kerosence
- Surfaces of Mg , Al, Zn pb are covered with a thin layer of oxide whish prevent them from further oxidation. Anodizing is a process of forming a tick oxide layer of aluminium.
- Iron does not burn on heating but iron filling burn vigorously.
- Copper does not burn but the hot metal is coated with a black coloured layer of copper (ii) oxide
- Silver and gold do not react with oxygen even at high temperatures.
Amphoteric oxide
Example ;
A
A
(SODIUM ALUMINATE )
Most metal oxides are insoluble in water but some of these dissolve in water to form alkalis. Sodium oxide and potassium oxide dissolved in water to produce alkali.
N
(ii) Reactions of metals with water:-
Metal+ water
Metal oxide + water
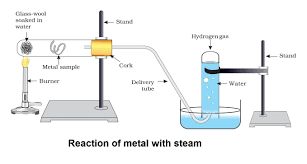
Metals like potassium and sodium react violenty with cold water.
Na + 2
The reaction of calcium of water is less violent
Ca + 2
Magnesium react with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen.
Mg + 2
Metals like aluminium iron and zinc do not react with cold or hot water. But they react with steam to form metal oxide and hydrogen.
2 Al + 3
3 Fe + 4
Metal such as lead ,copper, silver and gold do not react with water at all.
(ii) Reaction of metals with acids.
Metal + Dilute acid
Copper and silver do not react wit dil acids.
For example
Fe + 2HCl
Mg + 2HCl
Zn + 2HCl
(iii) Reaction of metals with solution of other Metal salts ;
Metal A+ Salts solution B
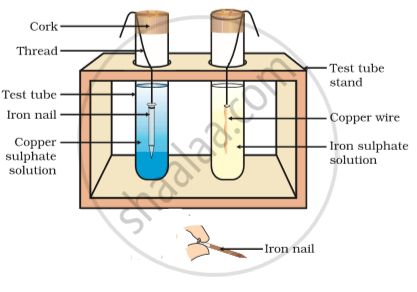
Reaction of metals with salt solutions.
More reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution form.
Fe + CuS
Fe displaces Cu because Fe is more reactive metals than Cu .
REACTIVITY SERIELS ;
The reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in the order of their decreasing activities.

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
