- Books Name
- Chemistry Class 10 NCERT based
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chemical Properties
Combustion Reactions
Combustion means burning of carbon or carbon-containing compounds in the presence of air or oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, heat and light.
Flame Characteristics
Saturated hydrocarbons give clean flame while unsaturated hydrocarbons give smoky flame. In the presence of limited oxygen, even saturated hydrocarbons give smoky flame.
Oxidation
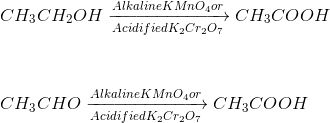
Addition
The reactions in which two molecules react to form a single product having all the atoms of the combining molecules are called addition reactions.
The hydrogenation reaction is an example of the addition reaction. In this reaction, hydrogen is added to a double bond or a triple bond in the presence of a catalyst like nickel, palladium or platinum.
![]()
Substitution
The reaction in which an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced or substituted by different atoms or group of atoms is called substitution reaction. In alkanes, hydrogen atoms are replaced by other elements.
CH4+Cl2+Sunlight → CH3Cl+HCl
- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CARBON COMPOUND .
(i) Combustion :- carbon burns in oxygen to give carbon dioxide along with the release of heat and heat .
C +
C
C
Saturated hydrocarbon will give a clean flame unsaturated carbon compounds will give a yellow flame with lots of balck soke. The gas slove used at home has inlets for air so that a sufficiently oxygen-rich mixture is burnt to give a clean blue flame. Fuel such as coal and petroleum have some amount of nitrogen and sulphur in them. The combustion results in the formation of oxides of sulphur and nitrogen which are major pollutants in the environment.
• Coal Coal and petroleum has been formed from biomass. Coal is the remains of trees, forms that lived millions of year ago . oil and gas are the remains of millions of tiny plants and animals that lived in the sea.
(ii) Oxidation :- The substance which are used for oxidation are known as oxidizing agent.
E.g alkaline kMn
C
(iii) Addition Reaction unsatured hydrocarbons ( alkenes and alkynes) add hydrogen in the presence of catalysts to give saturated hydrocarbons.
Catalyst are substance that cause a reaction to occur or proced ata different rate without the reaction itself being affected
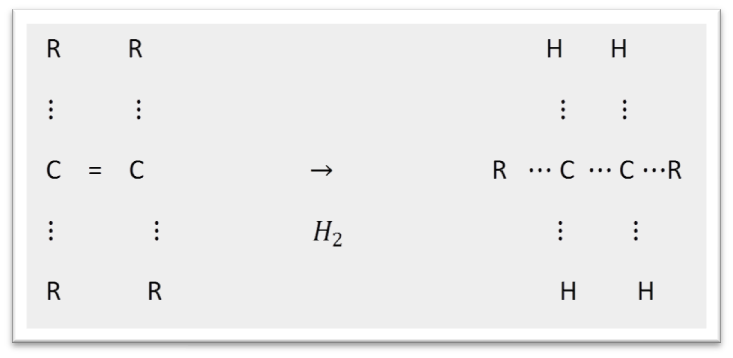
(IV) Substitution Reaction
Saturated hydrocarbons give substitution reaction e.g methane in presence of sunlight undergo chlorination.
C

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION

