- Books Name
- Chemistry Class 10 NCERT based
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
Ionic Compounds
The electrostatic attractions between the opposite charged ions hold the compound together.
Example: MgCl2, CaO, MgO, NaCl etc.
Properties of Ionic Compound
Ionic compounds
- Are usually crystalline solids (made of ions).
- Have high melting and boiling points.
- Conduct electricity when in aqueous solution and when melted.
Physical Nature
Ionic solids usually exist in regular, well-defined crystal structures.
Electric Conduction of Ionic Compounds
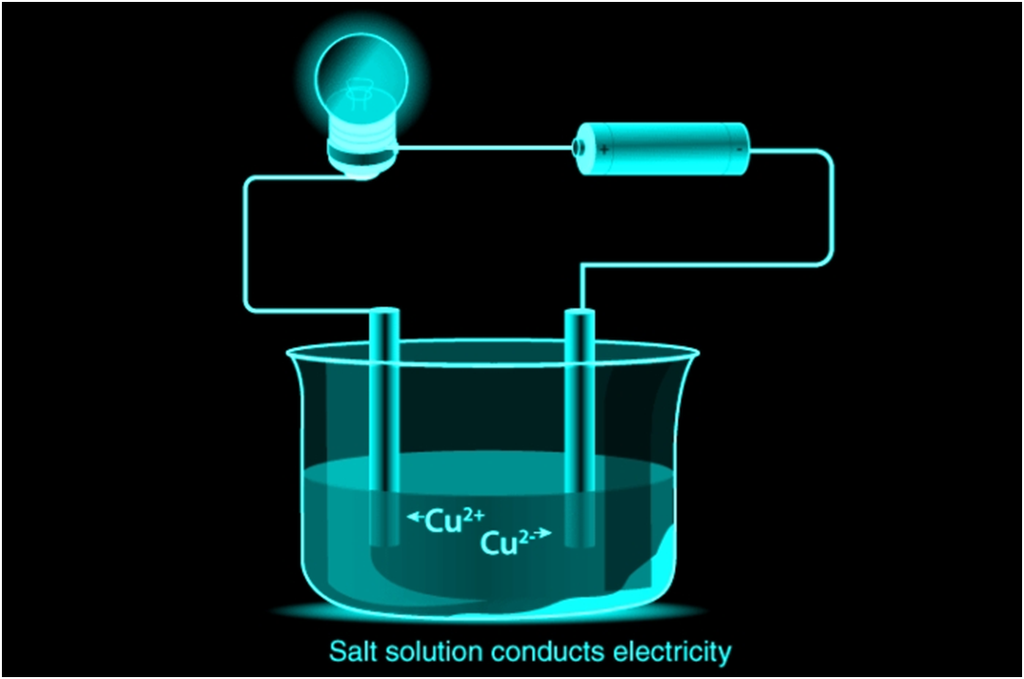
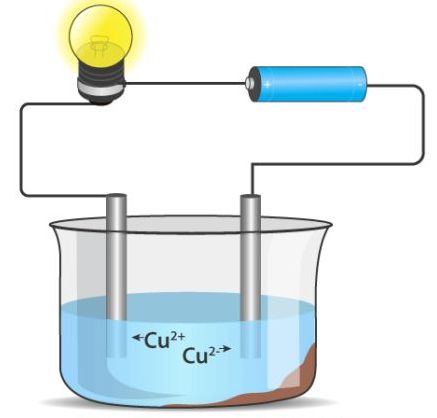
Ionic compounds conduct electricity in the molten or aqueous state when ions become free and act as charge carriers.
In solid form, ions are strongly held by electrostatic forces of attractions and are not free to move; hence do not conduct electricity.
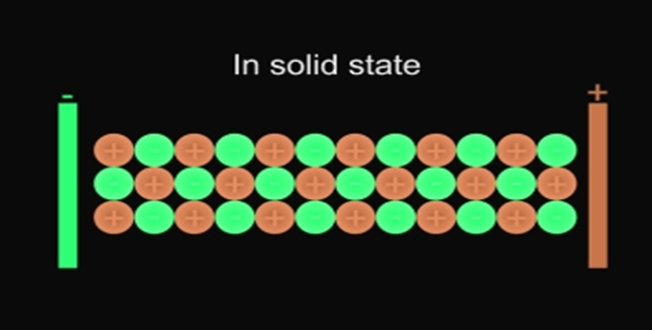
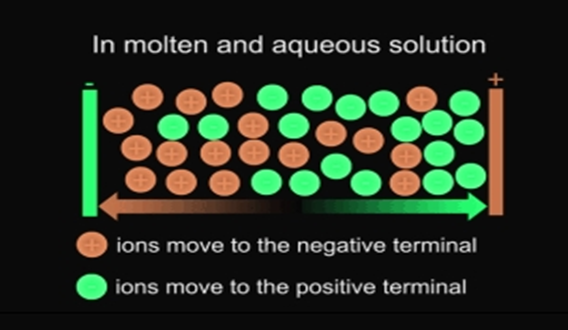
For example, ionic compounds such as NaCl does not conduct electricity when solid but when dissolved in water or in a molten state, it will conduct electricity.
Melting and Boiling Points of Ionic Compounds
In ionic compounds, the strong electrostatic forces between ions require a high amount of energy to break. Thus, the melting point and boiling point of an ionic compound are usually very high.
Solubility of Ionic Compounds
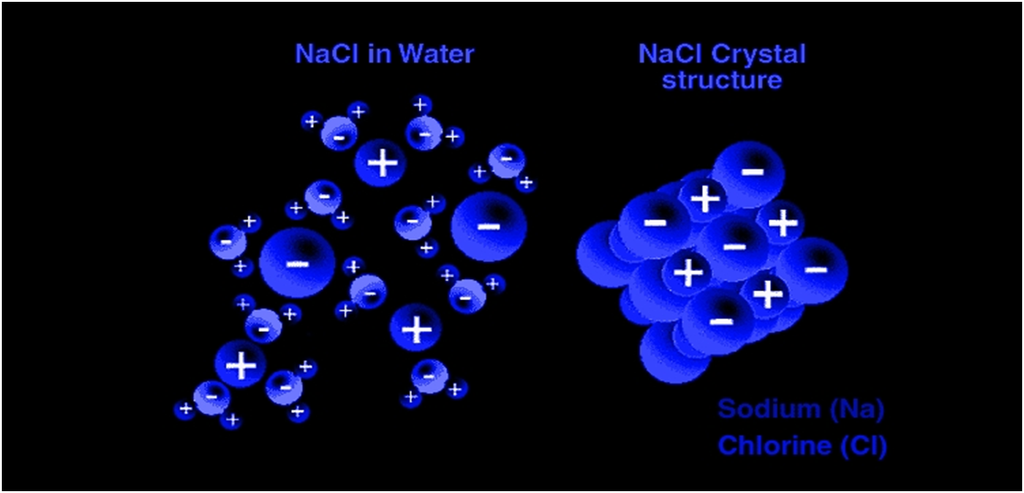
Most ionic compounds are soluble in water due to the separation of ions by water. This occurs due to the polar nature of water.
For example, NaCl is a 3-D salt crystal composed of Na+ and Cl− ions bound together through electrostatic forces of attractions. When a crystal of NaCl comes into contact with water, the partial positively charged ends of water molecules interact with the Cl− ions, while the negatively charged end of the water molecules interacts with the Na+ ions. This ion-dipole interaction between ions and water molecules assist in the breaking of the strong electrostatic forces of attractions within the crystal and ultimately in the solubility of the crystal.
.Properties of Ionic compound
- Ionic compounds are solid. Ionic bond has a greater force of attraction because of which ions attract each other strongly. This makes ionic compounds solid.
- Ionic compounds are brittle.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because force of attraction between ions of ionic compounds is very strong.
- Ionic compounds generally dissolve in water.
- Ionic compounds are generally insoluble in organic solvents; like kerosene, petrol, etc.
- Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in the solid state.
- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
METALS AND NON- METALS REACTIONS
- Atoms of the metals lose electron from their valence shell to form cation.
- Atoms of the non- metals gain electrons in the valence to form anion.
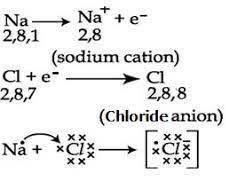
Formation of sodium chloride.
Formation of magnesium chloride
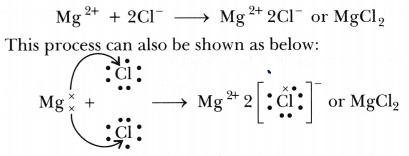
Properties of ionic compound
- PHYSICAL NATURE :- They are solid and hard (because of the strong force of attraction between the positive and negative ions) . They are brittle.
- Melting and boiling point:_ They have high melting and boiling pont.
- Solubility :- soluble in water and insoluble in solvents such as kerosene , petrol etc.
- Conductor of electricity :- Ionic compound conduct electricity in molter (ions move to the opposite electrodes when electricity is passed )
- They do not conduct electricity in solid state as movements of ions is not possible in solid They conduct electricity in molten state.

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
