Thrust and pressure.
- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Thrust and Pressure
Force acting on an object perpendicular to the surface is called thrust.
Effect of thrust depends on the area of contact.
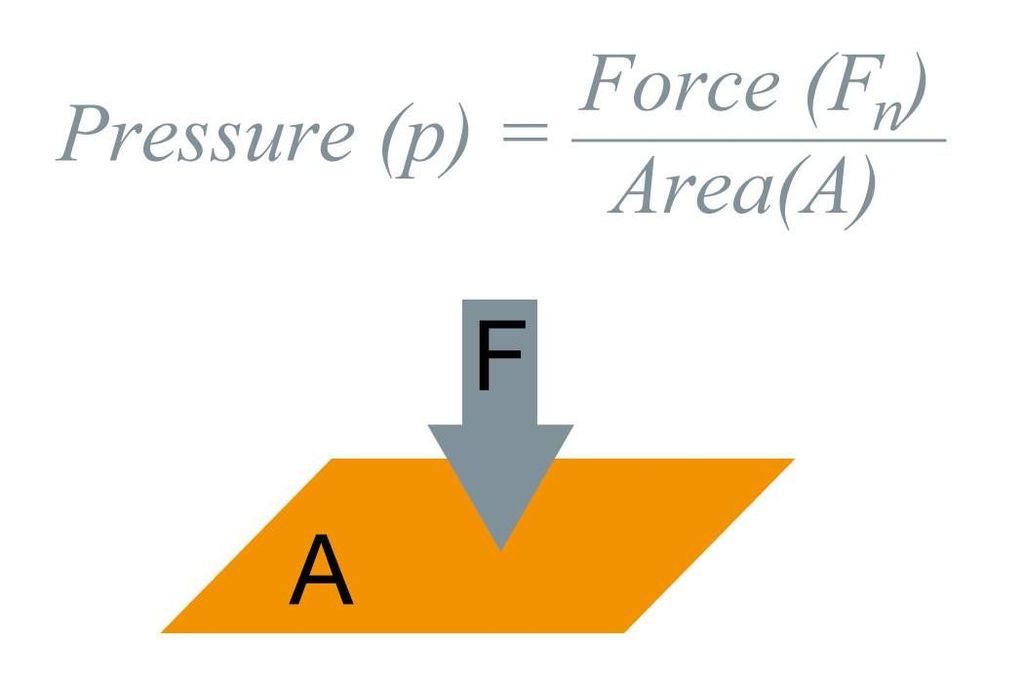
The pressure is thrust per unit area.
SI unit is the pascal (Pa).
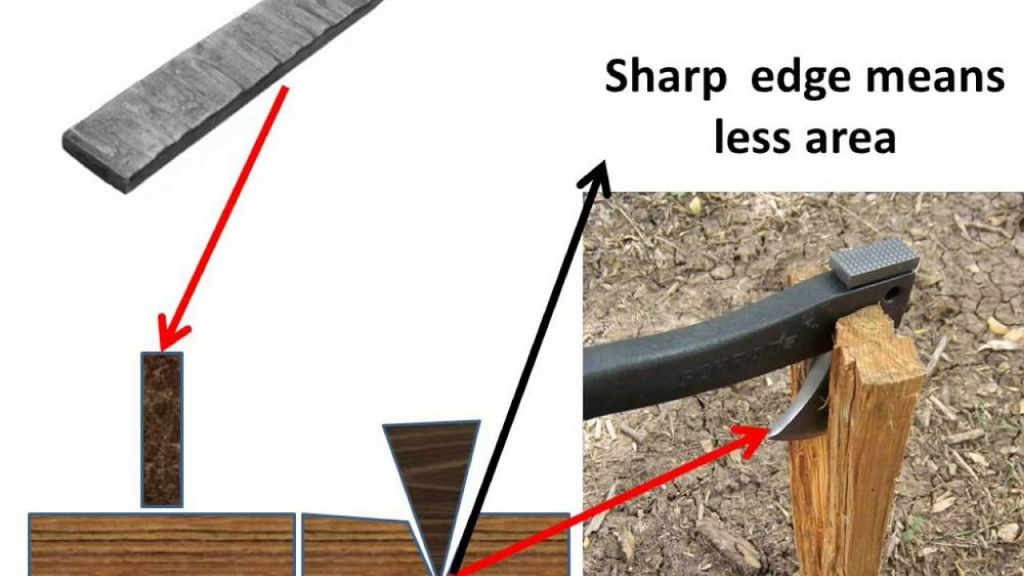
Force acting on a smaller area applies more pressure than the same force acting on a larger area.
• Pressure depends on two factors
(i) Force applied
(ii) Area of surface over which force acts
Examples of Pressure
→ The base of high buildings is made wider so that weight of walls act over a large surface are
pressure is less.
→ School bags are having broad strap so that the weight of school bags fall over a larger area so that student feel less pressure on shoulders.
--> liquids and gases are fluids and they exert pressure in all directions.
Archimedes' principle
- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Archimedes’ Principle
→ It states, when a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences a upward force
equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
Applications of Archimedes’ Principle
i) It is used in determining relative density of substances.
(ii) It is used in designing ships and submarines.
(iii) Hydrometers and lactometers are made on this principle.
→ It is because of this ship made of iron and steel floats in water whereas a small piece of iron
in it.
buoyancy
- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Buoyancy
→ The upward force experienced by an object when it is immersed into a fluid is called force of
buoyancy.
→ It acts in upward direction and it depends on the density of the fluid.
→ When force of gravitational attraction of the earth on the surface of the object < buoyant force
exerted by fluid on the surface of the object, object floats in the fluid.
• When force of gravitational attraction of the earth on the surface of the object > buoyant force
exerted by fluid on the surface of the object, the object sinks in the fluid.
→ This is the reason, why allpin sinks and boat/ship floats on the surface of water. (Archimedes
principle)
elementary idea of relative density
- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Relative density
→ The ratio of the density of a substance to that of the density of water is called relative density.
• Relative density = Density of a substance/Density of water
→ It has no unit as it is a ratio.
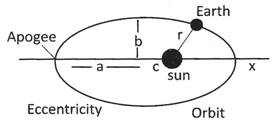
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion
Kepler observed that different planets take different time to complete one revolution around the sun. From s this observation of planetary motion he deduced that square of time period is proportional to the cube ob its distance from the sun.
Kepler’s First Law
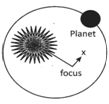
Kepler’s first law of planetary motion states that planets move around the sun in such a way that sun always remains at one of its focus.
Kepler’s second law
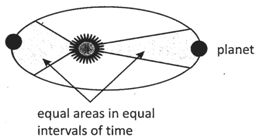
According to second law the line joining planet to the sun sweeps out equal area in equal time interval, as the planet revolve around the sun in a elliptical orbit.
Kepler's Third Law
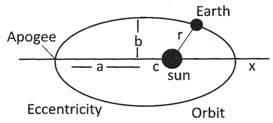
It states that square of time period is proportional to the cube of its semi major axis.
INTRODUCTION, THRUST & PRESSURE
- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Introduction
Floatation depends upon the density. If an object has density less than the density of water, it floats. Principle of floatation is stated by the Archimedes. This chapter deals with what is floatation, laws of floatation, its applications and examples.
Thrust and Pressure
Force acting on an object perpendicular to the surface is called thrust.
Effect of thrust depends on the area of contact.
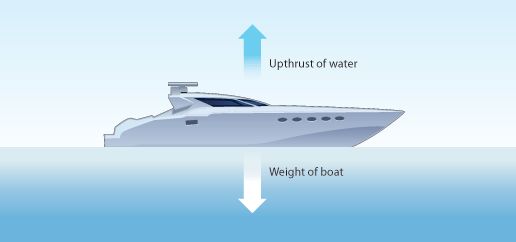
The pressure is thrust per unit area.
SI unit is the pascal (Pa).
Force acting on a smaller area applies more pressure than the same force acting on a larger area.
FACTORS AFFECTING PRESSURE
- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
• Pressure depends on two factors
(i) Force applied
(ii) Area of surface over which force acts
Examples of Pressure
→ The base of high buildings is made wider so that weight of walls act over a large surface are
pressure is less.
→ School bags are having broad strap so that the weight of school bags fall over a larger area so that student feel less pressure on shoulders.
--> liquids and gases are fluids and they exert pressure in all directions.
BUOYANCY
- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Buoyancy
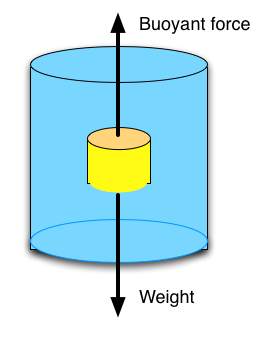
→ The upward force experienced by an object when it is immersed into a fluid is called force of
buoyancy.
→ It acts in upward direction and it depends on the density of the fluid.
→ When force of gravitational attraction of the earth on the surface of the object < buoyant force
exerted by fluid on the surface of the object, object floats in the fluid.
• When force of gravitational attraction of the earth on the surface of the object > buoyant force
exerted by fluid on the surface of the object, the object sinks in the fluid.
→ This is the reason, why allpin sinks and boat/ship floats on the surface of water. (Archimedes
principle)
DENSITY AND RELATIVE DENSITY
- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Density
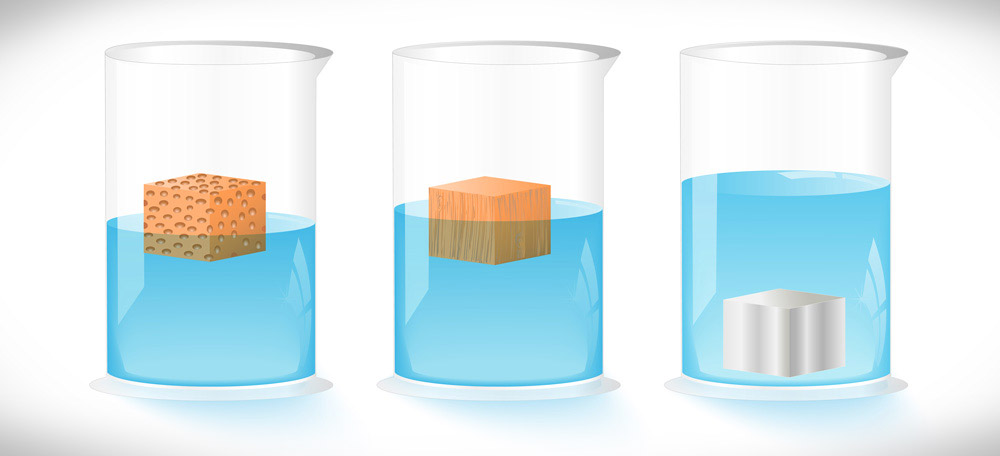

→ The mass per unit volume is called density of an object.
→ If M is the mass and V is the volume, then
• Density (d) = Mass(M)/Volume(V)
• SI unit = kg/m3
ARCHIMEDES PRINCIPLE
- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Archimedes’ Principle
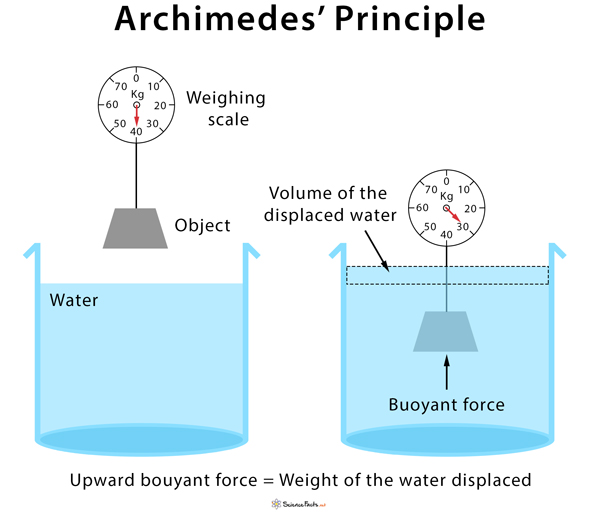
→ It states, when a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences a upward force
equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
Applications of Archimedes’ Principle
i) It is used in determining relative density of substances.
(ii) It is used in designing ships and submarines.
(iii) Hydrometers and lactometers are made on this principle.
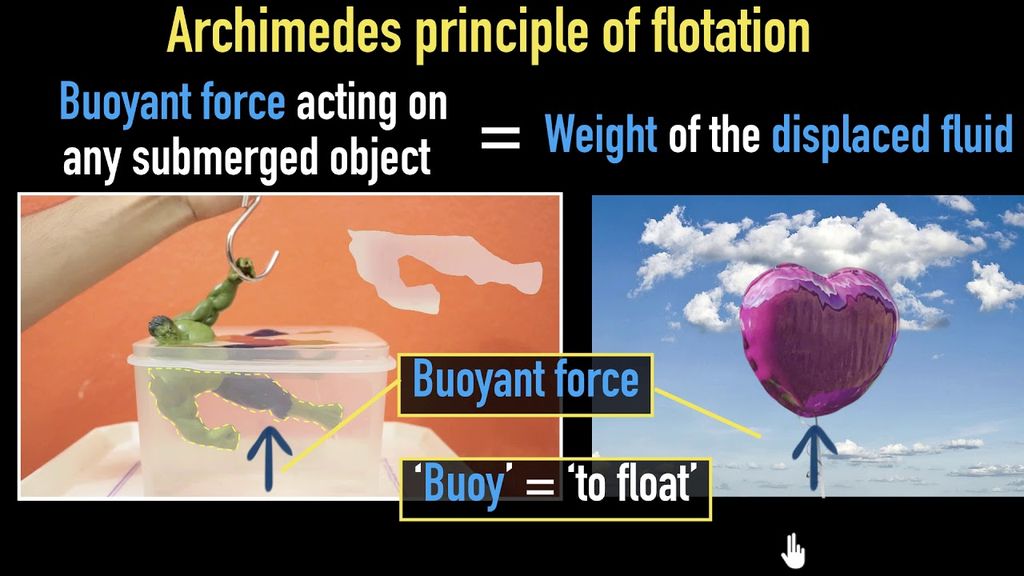
→ It is because of this ship made of iron and steel floats in water whereas a small piece of iron
in it.
Relative density
→ The ratio of the density of a substance to that of the density of water is called relative density.
• Relative density = Density of a substance/Density of water
→ It has no unit as it is a ratio.
KEPLER'S LAWS
- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion
Kepler observed that different planets take different time to complete one revolution around the sun. From s this observation of planetary motion he deduced that square of time period is proportional to the cube ob its distance from the sun.
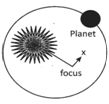
Kepler’s First Law
Kepler’s first law of planetary motion states that planets move around the sun in such a way that sun always remains at one of its focus.
Kepler’s second law
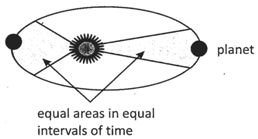
According to second law the line joining planet to the sun sweeps out equal area in equal time interval, as the planet revolve around the sun in a elliptical orbit.
Kepler's Third Law
It states that square of time period is proportional to the cube of its semi major axis.

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
