- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Introduction
→ Gravitational Force of Earth: If we release a small stone without pushing it from a height, it
accelerates towards earth. Earth attracts everything towards it by an unseen force of attraction. This force of attraction is known as gravitation or gravitational pull
Universal Law of Gravitation
→ Sir Isaac Newton in 1687 proposed a law about the force of attraction between the
objects in the universe which is known as Newton’s law of gravitation.
According to Universal law of Gravitation
→ Every mass in this universe attracts every other mass with a force which is directly proportional to
the product of two masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
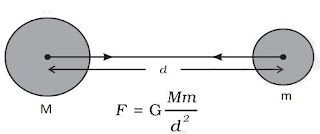
• Let masses (M) and (m) of two objects are distance (d) apart, then force of attraction (F) between
them
F ∝ M×m
F ∝ 1/d2
F ∝ Mm/d2
F = (GMm)/d2
where,
G is a constant and is known as Gravitational constant.
Value of G = 6.67×10-11 Nm2/kg2
G is called universal gravitational constant.
→ If unit of F is in Newton, m is in kg, d is in mere, then unit of G can be calculated as :
G = (F×d2)/Mm, therefor unit will be Nm2/kg2
Importance of universal law of gravitation
(i) The force that binds us to the earth.
(ii) The motion of moon around the earth.
(iii) The motion of earth around the sun.
(iv) The tides due to moon and the sun.
Chapter 10
Gravitation
Introduction
Gravitational force of Earth:
- If we release a small stone without pushing it from a height it accelerates towards Earth. The stone is when accelerated towards earth, means some force is acting on it.
- The force which pulls the object towards the centre of earth is known as gravitational force of the earth. Here, stone also attracts the earth.
- It means every object in universe attracts every other object.
- When a body undergoes circular motion, it experiences a force that acts towards the centre of the circle. This centre-seeking force is called a centripetal force.
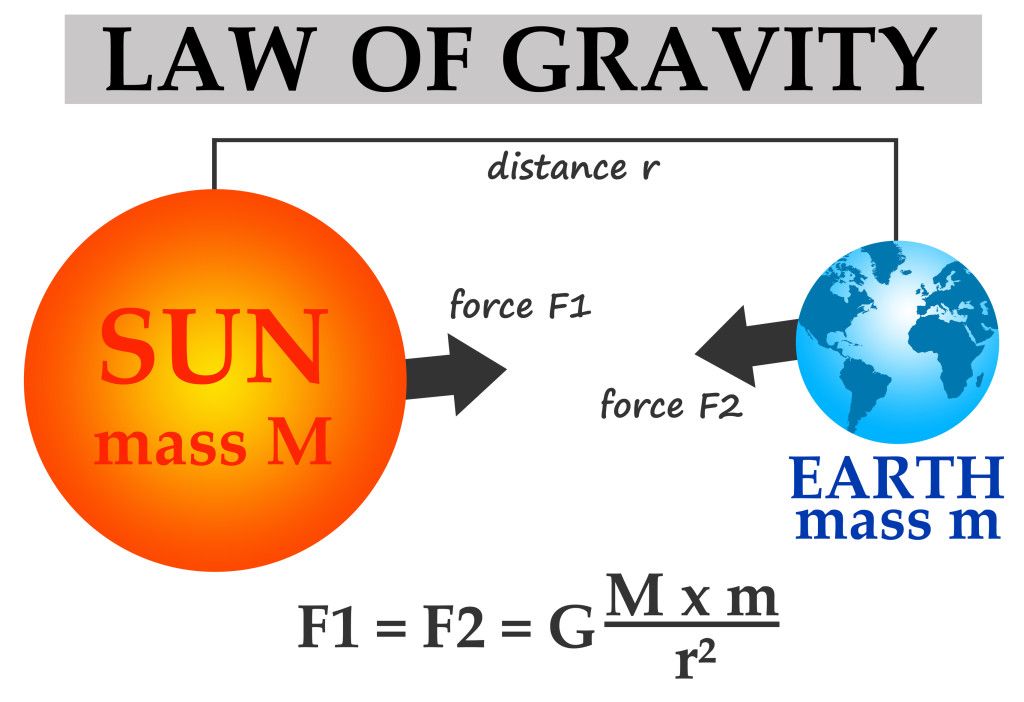
Universal Law of Gravitation
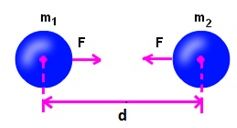
- According to the universal law of gravitation, every object attracts every other object with a force.
- This force is directly proportional to the product of their masses.
- This force is inversely proportional to the square of distances between them.
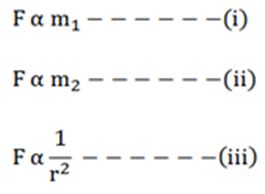
From the above equation we can rewrite them as the following:
![]()
If we remove the proportionality, we get proportionality constant G as the following:
![]()
According to, Newton’s universal Law of gravitation
G = Fr2/ m1 m2
SI Unit: Nm2 kg-2
Value of G = 6.673 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2
The proportionality constant G is also known as the Universal Gravitational Constant.
Importance of universal law of gravitation
It explains:
- the force that binds us to the earth.
- the motion of moon around the earth
- the motion of planets around the sun.
- the tides due to the moon and the sun.

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
