- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
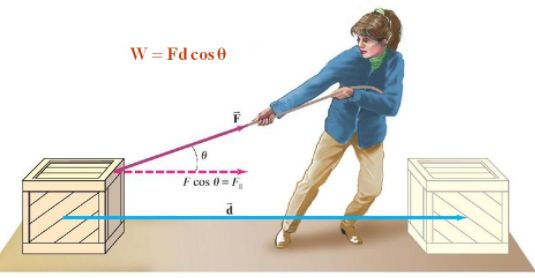
Work
Work done on an object is defined as the product of the magnitude of the force acting on the body and the displacement in the direction of the force.
W = F.s
If a force acting on a body causes no displacement, the work done is 0. For example, pushing a wall.
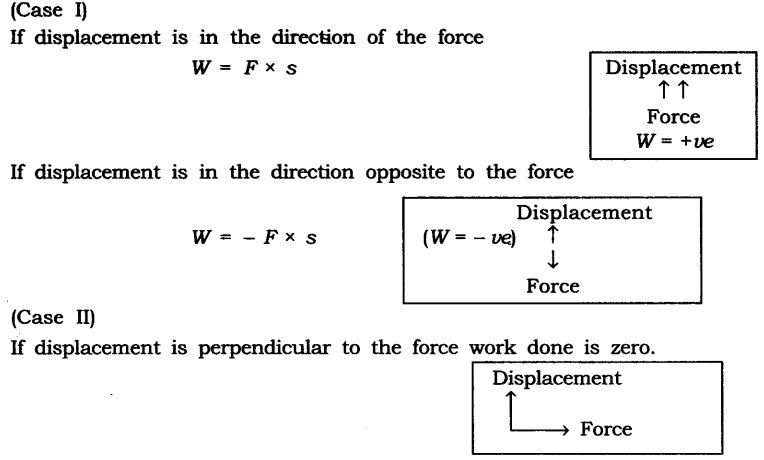
Two conditions need to be satisfied for work to be done:
(i) A force should act on object
(a) The object must be displaced
Work = Force x Displacement
Unit of workdone = Joule = Newton x metre
1 Joule work is said to be done when 1 Newton force is applied on an object and it shows the displacement by 1 meter.
Types of work
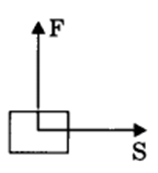
(i) Zero work: If the angle between force and displacement is 90°, then work done is said to be zero work.
Example: When a man carries a load on his hand and moves on a level road, work done by the man on the load is zero.
(ii) Positive work: Work done is said to be positive if force applied on an object and displacement are in the same direction.
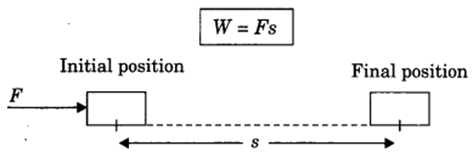
Example: Work done by the force of gravity on a falling body is positive.
(iii) Negative work: Work done is said to be negative if the applied force on an object and displacement are in opposite direction.
W = -Fs
Here displacement is taken to be negative (-s).
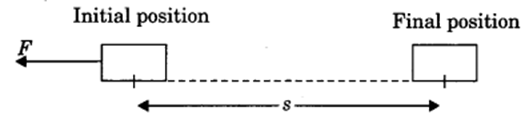
Example: Work done by friction force is usually negative on a moving body.

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
