- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
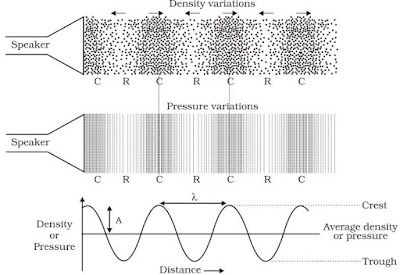
Characteristics of Sound Wave
• The characteristics of sound waves are : wavelength, frequency, amplitude, time period and
velocity.
→ When a wave travel in air the density and pressure of air changes from their mean position.
→ Compression is shown by crest while rarefaction is shown by trough.
→ Compression is the region of maximum density or pressure.
→ Rarefaction is the region of minimum density or pressure.
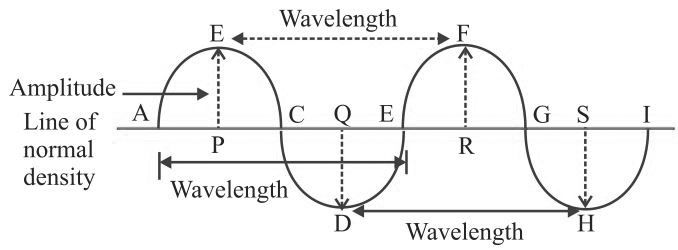
Wavelength
→ In sound waves the combined length of a compression and an adjacent rarefaction is called
wavelength.
→ The distance between the centres of two consecutive compressions or two consecutive
rarefactions is also called its wavelength.
→ It is denoted by the Greek letter lamda (λ). Its SI unit is metre.
Frequency
→ No. of complete waves produced in one second or number of vibrations per second is called
frequency.
→ Number of compressions or rarefactions passed in one second is also frequency.
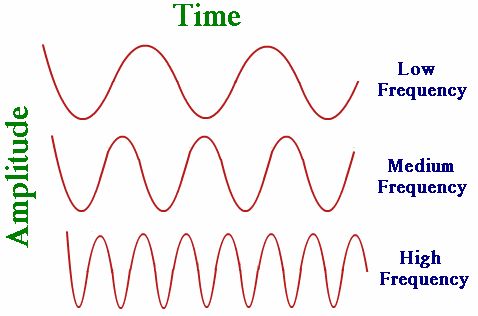
→ Frequency of wave is same as the frequency of the vibrating body which produces the wave
• The SI unit of frequency is hertz (Hz). The symbol of frequency is v (nu).
• 1 Hertz: One Hz is equal to 1 vibration per second.
• Bigger unit of frequency is kilohertz kHz = 1000 Hz.
Time Period
→ Time taken to complete one vibration is called time period.
→ Time required to pass two consecutive compressions or rarefactions through a point is called
time period.
• SI unit of time period is second (s). Time period is denoted by T.
• The frequency of a wave is the reciprocal of the time period.
• v = 1/T
Amplitude
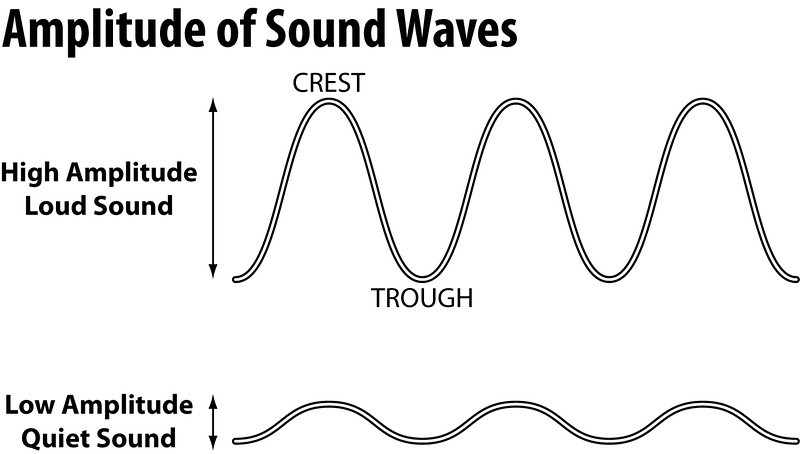
→ The maximum displacement of the particle of the medium from their original undisturbed
position is called amplitude of the wave.
• Amplitude is denoted by A and its SI unit is metre (m).
→ Sound have characteristics like pitch and loudness and timbre.
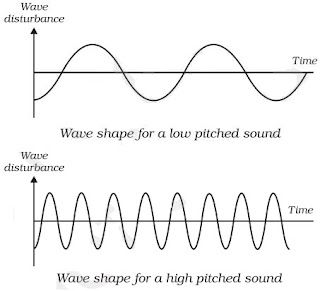
• Pitch: The pitch of sound depends on the frequency of sound (vibration).
→ It is directly proportional to its frequency. Greater the frequency, higher is the pitch and lesser the
frequency, lower is the pitch.
→ A woman’s voice is shrill having a high pitch while a man’s voice is flat having low pitch.
• Loudness: The loudness depends on the amplitude of the sound wave.
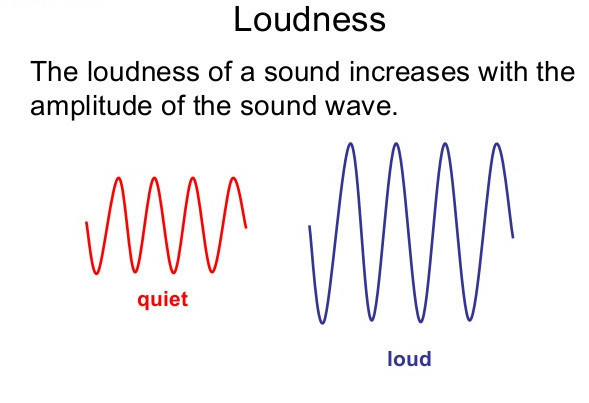
→ Loudness is the measure of the sound energy reaching the ear per sec.
→ Greater the amplitude of sound wave, greater is the energy, louder the sound; short is the
amplitude, less is the energy, soft is the sound.
→ Loudness is measured in decibel ‘dB’.
• Quality or Timbre: The timbre of a sound depends on the shape of sound wave produced by
the characteristic of musical sound.
→ It helps us to distinguish between two sounds of same pitch & loudness.
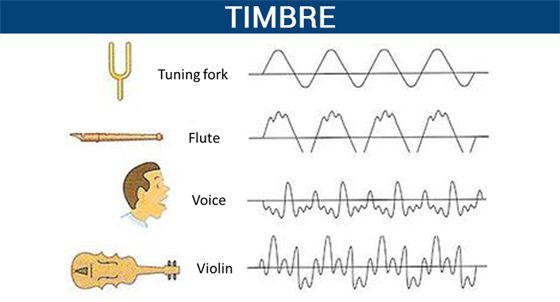
• Sound of single (same) frequency is called tone while a mixture of different frequencies is called
note.
• The distance travelled by a wave in one second is called velocity of the wave.
• Its SI unit is metre per second (m/s ).
Velocity = Distance travelled/Time taken
⇒ v = λ/T
(λ is the wavelength of the waves travelled in one time time period T)
v = λv (1/T = v)
So, Velocity = Wavelength × Frequency
This is the wave equation.
Example: What is the frequency of sound wave whose time period is 0.05 second ?
Ultra Sound
The ultrasound waves are the sound waves with high frequency. Due to this, they can travel long distances despite any obstacles between their paths.
Application of Ultra Sound
• The ultrasound waves are used in clearing parts of objects that are hard to reach such as a spiral tube or electronic components. In order to clean the objects, they are put in a solution, then the ultrasonic waves are passed through the solution. As a result, the dust particles on the object get detached and fall off them.
• Ultrasound waves can recognize tiny cracks in metallic objects that are used in the manufacture of large structures, buildings and scientific equipment. The presence of such cracks can lower the strength of these structures and machines. Hence, the ultrasound waves are passed through the metallic objects and detectors are used to detect the waves that pass through the cracks. If a crack is present the ultrasound waves would reflect back.
• Ultrasonic waves are also used in a medical process called Echocardiography. In this process, the ultrasound waves are passed through various parts of the heart in order to form the images of the organ.
• Ultrasonic waves are also used in a procedure called Ultrasonography. In this procedure, the ultrasonic waves are passed through the internal organs of the body in order to get their image. In this way, the doctors can find out the cause of a disease or any abnormalities in the organs. The ultrasound waves travel through the tissues of the body and as soon as the density of the tissue changes, they reflect back. The reflected waves are then converted into electrical signals which form the images of the internal organs.
• Ultrasound waves are also used to break the kidney stones.
SONAR – Sound Navigation and Ranging
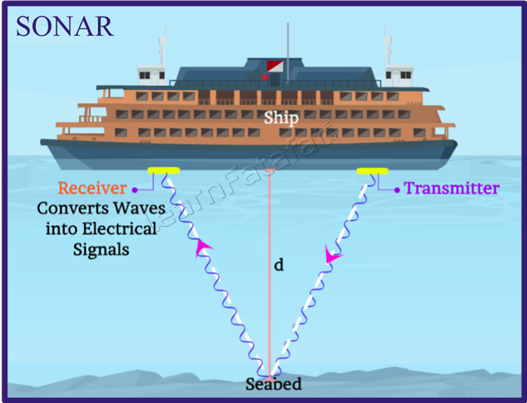
• This device is used to find the distance, direction and speed of objects that are present under the water. It uses Ultrasonic waves to do so.
• The Sonar consists of two main devices – The transmitter and the detector (or receiver). The main function of the transmitter is the production and transmission of the Ultrasonic waves in water.
• As these waves travel underwater, they, when hit by an object, reflect back to the detector. The detector then converts these sound waves into electrical signals which are then interpreted.
• The distance of the object is calculated with the help of the speed of sound in water and time taken by the way to reach the detector. This process is called Echo Ranging.
Uses of Sonar
• Finding the depth of a water body such as sea
• Detecting the presence of underwater objects like submarines, hills, icebergs and ships
The Human Ear
The ear is a sensitive organ of the human body. It is mainly involved with detecting, transmitting and transducing sound and maintaining a sense of balance is another important function of the human ear. Human ear includes:
• The outer ear or the visible part of the ear is called the pinna.
• Pinna collects sound from the surroundings.
• Sound passes through a tube called an auditory canal.
• Eardrum (tympanic membrane) vibrates in response to incident sound waves.
• Vibrations are amplified and transmitted further by three bones hammer, anvil and stirrup in the middle ear to the inner ear.
• In the inner ear, cochlea converts pressure signals into electrical signals.
• Electrical signals are transmitted by the auditory nerve to the brain for interpretation.
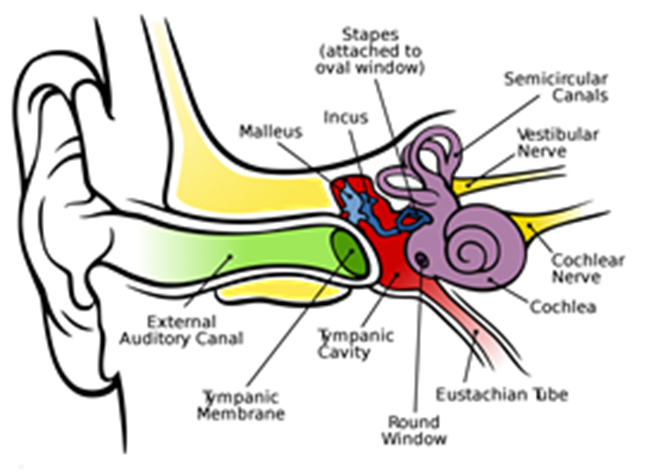
Structure of Human Ear

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
