Introduction and Concept of Management
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
Meaning of management:- Process of getting things done with the aim of achieving goals effectively and efficiently.
Effectiveness:
- Effectiveness in management is concerned with doing the right task, completing activities and achieving goals.
- In other words, it is concerned with the end result.
Efficiency:
- Means doing the task correctly and with minimum cost.
- If by using less input resources (money, materials, equipment and persons) more benefits are derived (i.e., the outputs) then efficiency has increased.
- Efficiency is also increased when for the same benefit or outputs with fewer resources are used and fewer costs are incurred.
Effective but not efficient:
Suppose, a company’s target production is 5000 units in a year. To achieve this target the manager has to operate on double shifts due to power failure most of the time. The manager is able to produce 5000 units but at a higher production cost. In this case, the manager was effective but not so efficient, since for the same output more inputs (labor cost, electricity costs) were used.
Efficient but not effective:
Businesses may concentrate more on producing goods with fewer resources i.e., cutting down costs but not achieving the target production. Due to which the goods do not reach the market and hence the demand for them declines and competitors enter the market this is a case of being efficient but not effective since the goods did not reach the market.
Characteristics & Importance of Management
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
Nature and Significance of Management
- Multidimensional:
- Management of work:Management translates the work in terms of goals to be achieved and assigns the means to achieve it.(by planning and organizing)
- Management of people: make people work towards achieving the organization’s goals, by making their strengths effective and weakness irrelevant. (by staffing, directing, controlling)
- Management of operations: provides a process that involves the flow of input material and transforming this input into the preferred output for consumption. (purchase, production, sales, finance, advertisement)
- Continuous process:
- The management process is a series of continuous but separate functions (planning, organizing, directing, staffing and controlling which are together performed by all managers all the time.
- Group activity:
- Inorganizationdifferent individuals have different needs.
- Higher salary, promotion, learning
- A common goal can be met through teamwork and coordination
- Dynamic function:
- Adapt itself to the changing environment which is consists of various social, economic and political factors.
- In order to be successful, an organization must change itself and its goals according to the needs of the environment.
- Goal-oriented process:
- The different organizations have different goals
- School to provide quality education, mobile company to increase the customer base
- efforts of different individuals in the organization towards achieving these goals
- Intangible force:
- It does not have a physical shape that can be seen and touched,
- Its presence can be felt when organization achieve goals, targets are met according to plans and employees are happy and satisfied.
- All pervasive:
- Management is common to all organizations whether economic, social or political.
- This difference is due to the differences in culture, tradition and history
Importance of Management
- Group goals:
- Management gives a common direction to the individual departments (like finance, production, purchase) for achieving the overall goal of the organization.
- It unites physical (material-machine-money) resources and human resources in one direction of profit –survival and growth.
- Useful in a dynamic organization:
- All organizations have to function in an environment that is constantly changing(SLEPT)
- Management helps people adapt to these changes to survive and grow and able to maintain its competitive edge
- Increases efficiency:
- Managers try to reduce costs and increase productivity through better planning, organizing, directing, staffing and controlling the activities of the organization.
- As a result per unit cost of production is reduced.
- Development of society:
- Helps to provide good quality products and services, creates employment opportunities, adopts new technology for the benefit of the people and leads the path towards growth and development.
- Enhance personal objectives:
- Through motivation and leadership, the management helps individuals to develop team spirit, cooperation and commitment to group success.
- A manager motivates and leads his team in such a manner that individual members can achieve personal goals while contributing to the overall organizational objective.
Nature of Management
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
Management as a profession
Profession: -An economic activity, which is conducted by a person, having specialized knowledge, acquired by a course of study and training for serving society.
- Service motive:
- The motive of the legal and medical profession is to serve their client’s interests by rendering dedicated and committed service.
- The basic purpose of management to help the organization achieve its goals by providing good quality products at reasonable prices, thereby serving society is increasing.
- So, presently this feature of the profession is not fully present in management.
- Well-defined body of knowledge:
- All professions are based on a well-defined body of knowledge that can be acquired through instruction.
- Management too is based on a systematic body of knowledge comprising well-defined principles. This feature of the profession is present in management.
- Ethical code of conduct:
- Legal and medical professions are bound by a code of conduct that guides the behavior of its members. AIMA has devised a code of conduct.
- But there is no statutory backing for this code. So, presently this feature of the profession is not present in management.
- Associations of Professionals:
- Legal and medical professions are affiliated with a professional association like the bar council and medical council which regulates entry, and grants certificates of practice.
- There is, however, no compulsion for managers to be members of such an association. So, presently this feature of the profession is not present in management.
- Restricted entry:
- The entry to the above-stated profession is restricted through a prescribed qualification. But there is no restriction on anyone being appointed as a manager in any business enterprise.
- So, presently this feature of the profession is not present in management.
Conclusion: -The above discussion shows that management does not satisfy all the criteria of a profession. Management is a profession but not a fully-fledged or a true profession.
Management as an Art
The skillful and personal application of existing knowledge to achieve desired results is called art’. In the light of this statement, describe whether management is an art or not.
Ans. “The skillful and personal application of existing knowledge to achieve desired results is called art”. Management is an art because of the following reasons:
- Personalized application:
- Two managers use theoretical knowledge of management in totally different ways, like two singers or two painters.
- In management too, a manager applies his acquired knowledge in a personalized and unique manner.
- Students of management also apply these principles differently depending on how creative they are after long practice
- Existence of theoretical knowledge:
- For example, literature on dancing, public speaking, acting, or music is widely recognized
- As in art, in management too, there is a lot of literature available in various areas of management which the manager has to specialize in like finance, marketing, etc.
- Based on continuous practice and Creativity:
- Like any other art, a manager after studying various situations formulates his theories for use in a given situation. This gives rise to different styles of management
- Management satisfies these criteria as a manager gains experience through regular practice and becomes more effective.
Management is an art because it has various features of art
Management as a Science
Science: - Systematized body of knowledge that explains certain general truths or the operation of general laws
Ans. Yes, Management is a science but not an exact science. Because of the following reasons:
- Based on observation and experimentation:
- Like science, management principles are derived through observation and repeated experimentation.
- However, management deals with a human whose behavior is difficult to understand and is not capable of being accurately predicted.
- Therefore, management can be called an inexact science or a social science
- Universal validity:
- Principles of management like principles of pure science provide managers with certain standardized techniques that can be used in different situations.
- However, since the principles of management have to be modified according to a given situation, their application and use are not universal. So, this feature of science is not fully present in management
- Systematized body of knowledge:
- Like science, management is a systematic body of knowledge with theories and principles that have developed over a while.
- So, this feature of science is present in management.
Objectives & Levels of Management
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
Levels of Management
Meaning:- Every individual in the hierarchy is responsible for the successful completion of a particular task. Authority-responsibility relationship binds individuals as superiors and subordinates Give rise to different levels in an organization.
Top-level management:- Consists of the Board of Directors, Chief Executive and departmental heads.
Functions:
- Complex and stressful, demanding long hours and commitment to the organization.
- Analyze the business environment and its implications for the survival of the firm.
- Responsible for the welfare and survival of the organization.
- Decide long-term goals of the organization and strategies for their achievement.
Middle level management:-Consists of departmental managers, divisional heads.
Functions:
- Making manpower planning to see that their department has the necessary personnel.
- Assign necessary duties and responsibilities to them.
- Co-operate with other departments for smooth functioning of the organization.
- Responsible for all the activities of first-line managers.
- Outlook the policies framed by top management.
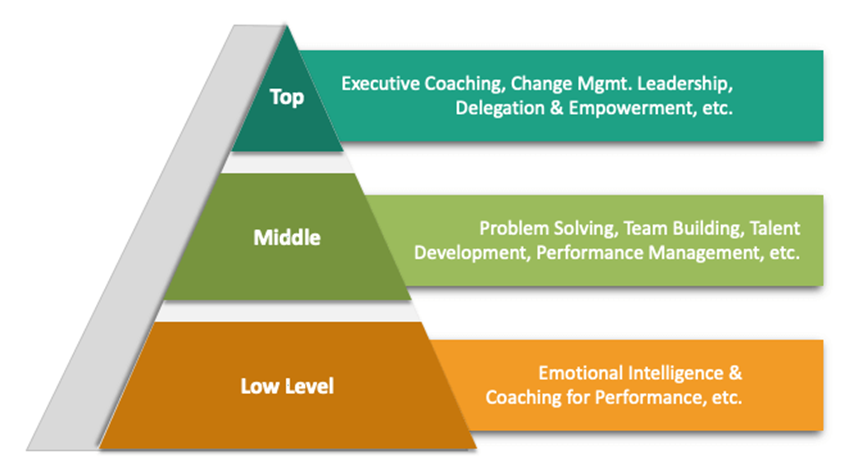
Operational management:-Consists of superintended, supervisors, section officers etc.
Functions:
- Solving workers’ problems and complaints, ensuring proper working environment and safety of workers, inviting.
- The link between workers and middle-level managers, creating better human relations with workers.
- Instructions of the middle management to the workers are passed.
- Maintain Quality of output, wastage of materials is minimized and safety standards are maintained.
Objectives of Management
- Social objectives:
- Using environmental friendly methods of production.
- Giving employment opportunities to the disadvantaged sections of society.
- Right quality goods should be provided to customers.
- Organizational Objectives:
- Survival: to survive, an organization must earn enough revenues to cover costs, reducing wastage.
- Profit: essential incentive for the successful operation of the enterprise and the reward for bearing the risks.
- Growth: increasing sales volume, increase in the number of employees, the number of products or the increase in capital investment, etc.
- Personal objectives:
- Management try to provide like good salary and a good working environment.
- Chances of growth, promotion to an employee.
- Good working conditions should be provided at the workplace.
- Employees should be rewarded for their good and hard work.
Functions of Management
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
Process means: - The activities that management performs to get things done with its functions like (POSDC).
- Planning: - This means setting goals in advance and developing a way of achieving them efficiently and effectively.
- Organizing:-function of assigning duties, grouping tasks, establishing authority and allocating resources required to carry out a specific plan.
- Staffing: - Aspect of management is to make sure that the right people with the right qualifications are available at the right places and times to accomplish the goals of the organization.
- Directing:- Involves leading, influencing and motivating employees to perform the tasks assigned to them. Involves leading, influencing and motivating employees to perform the tasks assigned to them.
- Controlling: - the management function of monitoring organizational performance towards the attainment of organizational goals.
Coordination-The essence of Management
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
Coordination: -The process by which a manager matches the activities of different departments is known as coordination. Coordination is the force that binds all the other functions of management.
Nature of Coordination
- Pervasive function:
- Coordination is required at all levels of management due to the interdependent nature of activities of various departments.
- Without Coordination, there will be duplicity and confusion instead of harmony and integration of activities
- Responsibility of all managers:
- Top-level managers coordinate with the middle level to ensure that the overall policies for the organization are duly carried out which in turn coordinates with both the top level and first-line managers.
- Integrates group efforts:
- Coordination unites diverse interests into purposeful work activity and gives a common focus to a group effort.
- It gives a common focus to a group effort to ensure that performance is as it was planned and scheduled
- Continuous process:
- Coordination is not a one-time function but a continuous process
- Coordination is all-time process that begins at the planning stage and continues till controlling.
- Ensures unity of action:
- The purpose of coordination is to secure unity between departments and ensures that all action is aimed at achieving the goals of the organization.
- It acts as the binding force between departments and ensures that all action is aimed at achieving the goals of the organization.
- Deliberate function:
- The manager coordinates the efforts of different people in a mindful and planned manner so that the members of departments work willingly and cooperate.
- Even where members of a department willingly cooperate and work, coordination gives direction to that willing spirit.
Importance of Coordination
- Growth in size:
- As organizations grow in size, the number of people employed by the organization also Increases.
- All individuals differ in their habits of work, background, approaches to situations and relationships with others
- It becomes necessary to ensure that all individuals work towards the common goals of the organization through coordination
- Functional differentiation:
- Functions of an organization are divided into departments, divisions and sections like finance, production, marketing, or human resources.
- All these departments may have their own objectives and policies.
- The process of linking the activities of various departments is accomplished by coordination.
- Specialization:
- Modern organizations are famous for a high degree of specialization arising out of the Complexity of modern technology and the diversity of tasks to be performed.
- This often leads to conflict amongst different specialists as well as others in the organization.
- Therefore, some coordination is required by an independent person to reconcile the differences in approach, interest or opinion of the specialists

 ABCD CLASSES
ABCD CLASSES
