staffing as part of Human Resource Management
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
STAFFING AS A PART OF HRM
Staffing as a part of Human Resource Management
There is a conflict on the subject of whether staffing is part of human resource management or is a separate managerial function. Many modern thinkers stress that staffing is a part of human resource management. Staffing includes only
- Training employees to improve their performance, developing their abilities,
- Introducing new employees to the organization,
- Placing the right person on the right job,
Human resource management is a wider term and includes in itself the following:
- Handling grievances and complaints.
- Analyzing jobs, collecting information about jobs to prepare job descriptions.
- Recruitment i.e., search for people
- Defending the company in lawsuits and avoiding legal complications
- Training and development of employees for efficient performance and career growth.
- Improving and Maintaining labor relations and union-management relations
- Make incentive plans and develop compensation
- Employee's welfare and Providing for social security
Conclusion: -So above discussion makes it clear that staffing is one of the parts of human resource management.
EVOLUTION OF HRM
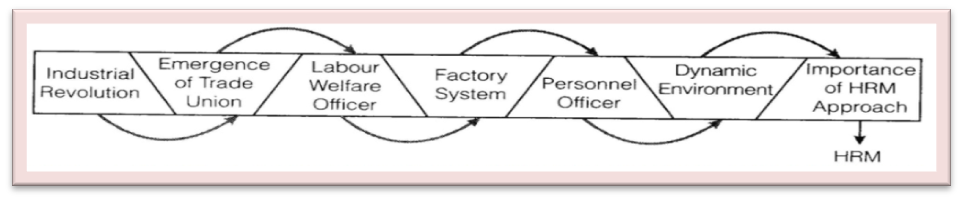
- With the emergence of the industrial revolution, trade union activities became very active.
- The trade union activities forced management to appoint a person who could act as a link between owner and persons.
- This resulted in the appointment of a labor welfare officer. His role was limited to the welfare of employees only.
- With the introduction of the factory system, a large number of laborers were employed under one roof.
- This resulted in the appointment of one more person who was given the responsibility of recruitment, selection and placement of persons. This person was known as a personnel officer.
- Due to the importance of human relation approach and the dynamic environment and changes taking place there arose the need for training and developing the employees to update their knowledge as human relation approach recognizes human factor as most important.
- This requirement for human relations approach led to the replacement of the personnel manager to human resource manager.
Introduction and Feature & Importance of Staffing
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
CONCEPT & MEANING
Staffing: - Managerial function of filling and keeping filled the positions in the organization structure.
FEATURE & IMPORTANCE:
Importance for staffing
- Structure filling
- Needed to fill the job positions created by organizational structure by putting right person on the right job.
- Improve the morale of the employees.
- Improves job satisfaction and morale of employees through appraisal and fair remuneration for their contribution.
- Key to the effectiveness of other functions.
- As all the functions are performed by human beings and human being joins the organization by staffing function only.
- Specialization.
- Today the staffing function is not a routine job but a specialized department in the organization. includes manpower planning, recruitment, training, remuneration, etc
- Human importance.
- Gives more importance to human elements by selecting, appraising and training the employees. Helps in obtaining competent personnel for various jobs.
- Assist in competing.
- Two organizations can easily acquire some type of physical and financial resources but the organization with efficient staff can easily win over its competitor
Staffing process
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
STAFFING PROCESS:
Process
- Manpower Requirement analysis
- Estimate manpower requirements according to demand to get the right number of qualified people at the right time.
- through
- Workload analysis estimation of the number and types of human resources necessary for the performance of various jobs.
- Workforce analysis to know whether a firm is understaffed, overstaffed or optimally staffed.
- Recruitment:
- Process of searching for prospective employees and motivating them to apply for jobs in an organization by using internal and external sources.
- Positive Step
- Selection:
- Choosing from among the applications the most suitable candidates to fill up the vacancies in the organization by comparing and evaluating candidates’ qualifications required to perform the job.
- Negative step
- Placement
- Asking the candidates to occupy the position in the organization for which they have been selected.
- Orientation
- Taking the new employees in the office/plant and introducing them to all employees to adjust themselves to the work environment
- Telling the rules and policies of the organization.
- Training
- Providing the required knowledge and skills relating to their jobs.
- Every new employee needs training in different departments to have sufficient knowledge of the work
- Increases workers’ knowledge, ability, and competence & make them more useful.
- Performance Appraisal
- Systematic evaluation of the employee’s performance on their job in order to determine their contribution
- Promotion of employees
- Employees should be given promotions to higher positions according to both ability and seniority.
9. Compensation
-
- Which employee receives in exchange for their contribution to the organization
- Compensation includes monetary and non-monetary incentives.
Elements of Staffing
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
ELEMENTS OF STAFFING
Recruitment
- Process of searching for future employees and motivating them to apply for jobs in an organization by using internal and external sources.
- Positive Step
Internal and External Recruitmnet
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
SOURCES OF RECRUITMENT
INTERNAL SOURCES:
- Transfers:
- Horizontal shifting of an employee from one job to another, one department to another without a change in the responsibilities and status of the employee.
- Shortage of personnel in one branch may be filled.
- Useful in the training of employees for learning different jobs
- Promotions:
- Vertical shifting an employee to a higher position, carrying higher responsibilities, status and pay
- Improve the motivation, loyalty and satisfaction level of employees.
Merits of Internal Sources
- Simplifies the process of selecting existing candidates working in the enterprise can be evaluated more accurately because they are known to the working environment of the organization
- avoids orientation:- Employee people recruited from within the organization do not need induction training
- Facilitates Motivation A promotion at a higher level may lead to a chain of promotion at lower levels in the organization. This motivates the employees to improve their performance
- Economical there is no cost on advertisement and selection process
- Reduces imbalance Transfer helps in shifting the workforce from the surplus departments to those where there is a shortage of staff
Limitations of Internal Sources
- Promote laziness employees may become lazy if they are sure of time-bound promotions.
- Less chance to fresh talent Scope for the introduction of fresh talent is reduced.
- Avoid Competition – there is no competition from outsiders because all the vacancy is filled internally
- Narrow scope: - A new enterprise cannot use internal sources of recruitment. No organization can fill all its vacancies from internal sources.
- Trim down productivity regular transfers of employees may often reduce the productivity of the organization.
EXTERNAL SOURCES:
- Direct Recruitment:
- Notice is placed on the notice board of the firm
- Unemployed people gather outside on the specified date and are selected on the spot
- Generally for casual vacancies of unskilled or semi-skilled jobs.
- Economical method
- Casual Callers:
- Many organizations keep a database of unwanted applicants with them
- A list of such candidates can be prepared and can be screened to fill the vacancies as they arise.
- Economical method
- Advertisement:
- Used when a wider choice is required by using electronic and print media
- More information about the organization and job can be given in the advertisement.
- Employment Exchange:
- Run by the Government for unskilled and skilled jobs.
- Compulsory notification of vacancies to employment exchange is required by law.
- Economical method
- Placement Agencies and Management Consultants:
- Placement agencies provide a nationwide service.
- Collect the bio-data of a large number of candidates and recommend suitable names to their clients.
- Charge fee for their service.
- Campus Recruitment:
- Colleges and institutes of management and technology have become a popular source of recruitment for technical, professional and managerial jobs.
- Organizations maintain close contact with the universities and management institutes to recruit qualified personnel.
- Recommendations of Employees:
- Applicants are introduced by present employees, or their friends and relatives.
- Such applicants are expected to be good employees because their background is sufficiently known.
- Labor Contractors.
- Labor contractors maintain close contact with a large number of laborers
- They Provide the required number of unskilled workers at short notice.
- Web Publishing:
- Internet is now the fastest source of recruitment.
- Certain websites like naukri.com and .jobstreet.com provide information about both candidates and recruiters.
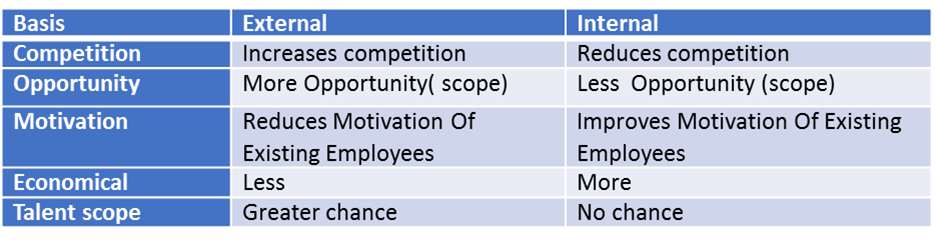
Merits of External Sources
- Wider Choice: When vacancies are advertised a large number of applicants from outside the organization apply.
- Attract Experienced Personnel: Management can attract more qualified and trained people to apply for vacant jobs in the organization.
- New Talent: External recruitment provides wider choice and brings new talent to the organization.
- Top performance Existing staff has to compete with the outsiders. They will work harder to show better performance.
Limitations of External Sources
- Lengthy process: The selection process and orientation process is time-consuming.
- Expensive process: A lot of money is spent on the advertisement and processing of applications.
- Dissatisfaction among existing staff: May gives dissatisfaction and frustration among existing employees as their chances of promotion are reduced.
Selection
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
SELECTION
Selection: Choosing from the applications the most suitable candidates to fill up the vacancies in the organization by comparing and evaluating candidates’ qualifications required to perform the job.
Process of Selection
- Preliminary Screening: Candidates not fulfilling minimum requirements are not considered further based on the information supplied in the application forms and are sent a letter of regret.
- Selection Tests: An employment test is to measure certain characteristics of individuals. Various test are
- Intelligence Tests: an indicator of a person’s learning ability or the ability to make decisions and judgments.
- The aptitude test: is a measure of an individual’s potential for learning new skills.
- Personality Tests: provide clues to a person’s emotions, reactions, maturity and value system, etc.
- Trade Test: Measure the existing skills of the individual. They measure the level of knowledge and proficiency in the area of professions or technical training.
- Interest Tests: Know the interests or involvement of a person in a job
- Employment Interview:
- Interview is a formal, in-depth conversation to evaluate the applicant’s suitability for the job.
- The role of the interviewer is to ask job-related and other general questions.
- Reference and Background Checks:
- Employers may ask for names, addresses, and telephone numbers of references to verify and get additional information about an applicant.
- Previous employers, known persons, teachers and university professors can act as references.
- Selection Decision:
- The final decision has to be made from among the candidates who pass the tests, interviews and reference checks.
- Medical Examination:
- In certain jobs, candidates are required to get compulsory physical and mentally fitness certificates. Like defense services, astronauts.
Job Offer:
-
- Applicant who has passed all the barriers is given a letter of appointment.
- Contains a date to report on the job.
- Contract of Employment: Contains two important Documents
-
- Attestation form:- Contains certain essential details about the candidate for future reference
- Contract of employment:-includes basic information like Job Title Duties, Responsibilities, allowances, hours of work, termination of employment, etc.
-
Training & Development
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
TRAINING & DEVELOPMENT
Training: - refers to the process designed to maintain and improve current job positions.
Development: - refers to the process designed to develop necessary skills for future work activities.
Difference between Training and Development

Benefits to the organization
- Reduces wastage: -Systematic learning is always better than hit and trial methods and reduces wastage of efforts and money.
- Orientation:-Induction Training helps the employee to know the working conditions in the organization
- Adaptation:-Helps adjust to fast-changing technological and Economic environment by learning the latest technique
- Motivation:- Increases employee morale and reduces absenteeism and employee turnover
- Employee productivity: -improves employee productivity both in terms of quantity and quality, leading to higher profits.
- Realistic application Employees apply theoretical knowledge to practical use, especially in the case of new employees
Benefits to the Employee
- Skills and knowledge Improved led to a better career for the individual when learning a new skill
- Accident Reduced makes the employee more efficient to handle machines which reduce the chances of accidents.
- More earning training Increases the performance of the employees which helps them to earn more.
- Employee Morale Increases the satisfaction and morale of employees the employee and makes them independent and happy.
Methods of Training
- Books Name
- BUSINESS STUDIES-XII
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Business Studies
METHODS OF TRAINING
Methods.
- On-the-job method of training: -Where employees work in the actual work environment. Means learning while doing. Simple and economical method. Methods
- Apprenticeship Programmers
- Internship Training
- Induction training
- Off-the-job method of training. Methods are used away from the workplace. Means learning before doing. Expensive method of training. Methods
- Vestibule Training
Training Methods
On the Job Methods: On-the-Job methods refer to the methods that are applied to the workplace, while the employee is working
- Apprenticeship Programmers (On job method of training)
- Meaning:-Practical form of training where the trainee is placed under an experienced supervisor for an agreed amount of time.
-
- Advantage: - Trainee learns valuable skills which are in high demand in the market. Candidate may be paid, unpaid or partially paid.
-
- Includes:-Plumbers, electricians, iron-workers.
- Internship Training: (on job method of training)
- Meaning: - Joint program in which educational institutions and business firms cooperate.
- Candidates work free to gain experience in a particular field.
- Advantage organization gets experienced candidates and needless training when they begin full-time regular employment.
- Includes Medical representatives, law, accounting and finance
- Induction training(On job method of training)
- Meaning: Provide new employees by the employer to help in adjusting to their new job by
- Introduction to the business/department and its personnel/management structure
- Outline of the factory buildings factory and offices
- Business rules and procedures
- Advantage: - Help a new employee settle down quickly into the job by becoming familiar with the people, the surroundings, the job and the business
- Includes–New employees
- Vestibule Training: (Off job method of training)
- Meaning: Training is conducted away from the actual work floor and employees use the same materials and equipment.
- Advantages: - relax from fear of mishandling sophisticated, costly machinery by untrained staff. Training is provided by experienced and expert staff
- Includes:- A highly technical job like astronauts, train pilots and cabin attendants

 ABCD CLASSES
ABCD CLASSES
