- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Combustion And Oxidation
Combustion
All the carbon compounds burn in oxygen and yield carbon dioxide and water vapours. Heat and light are also released during this process. This reaction is called combustion.
For Example
C + O2 → CO2 + Heat + Light
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + Heat + Light
2CH3CH2OH + 6O2 → 4CO2 + 6H2O + Heat + Light
Saturated hydrocarbons give a clean flame due to their complete combustion whereas, unsaturated hydrocarbons give a yellow flame with lots of black smoke as they do not undergo complete combustion.
Oxidation
It is the process of intake of oxygen and removal of hydrogen. Reagents used for this purpose are alkaline KMnO4 + heat or acidified K2Cr2O7 + heat.
For Example
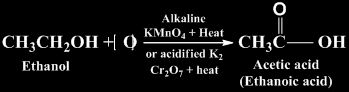
Substances that are capable of providing oxygen to other substances are called oxidising agents.
![]()
Addition Reactions
Addition of hydrogen (hydrogenation) in the presence of catalysts like palladium or nickel, to unsaturated hydrocarbons yields saturated hydrocarbons.
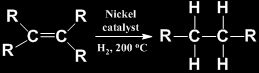
Hydrogenation of vegetable oil in the presence of nickel catalyst gives ghee. This process is called hardening of oils.
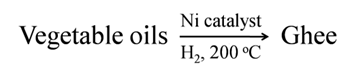
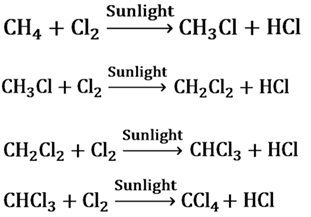
Substitution Reactions
The reactions in which a reagent substitutes an atom or a group of atoms from the reactant are called substitution reaction.
When chlorine is added to hydrocarbons at a rapid rate in the presence of sunlight, Cl replaces H atom one by one.
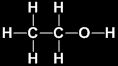
Some Important Carbon Compounds Ethanol
Its common name is ethyl alcohol and formula is C2H5OH or CH3CH2OH
Preparation
Alcohol (ethanol) is obtained by the fermentation of molasses which are obtained from sugarcane juice.
![]()
Physical Properties
Physical properties of ethanol are
- It is a liquid at room temperature. Its melting point is 156 K and boiling point is 351 K.
- It is Soluble in water due to its ability to form H- bonds with water molecules.
Chemical Properties
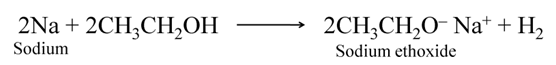
Reaction with Sodium
Ethyl alcohol reacts with sodium metal leading to the evolution of hydrogen gas along with the formation of sodium ethoxide.
Dehydration
Removal of water molecules from a compound is known as dehydration reaction.
For example
When ethanol is heated at 443K with excess conc. H2SO4, the water molecules get removed from it and ethane is obtained.

Uses
Uses of ethanol are
- It is used as an active ingredient in all alcoholic drinks.
- It is useful in medicines like tincture of iodine, cough syrups and may other tonics.
- Alcohol is used as an additive in petrol, since it is a clear fuel and gives rise to only CO2 and H2O when burnt in sufficient air.
- It is used as hypnotic (induces sleep).
- It is used for the preparation of chloroform, iodoform, ethanoic acid, ethanal, etc.
Denatured Alcohol
In order to stop the misuse of ethanol, it is made unfit for drinking by adding poisonous substances like methanol, coppet sulphate, pyridine, etc and coloured substances like dyes. Such alcohol is called. Denatured alcohol.

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
