- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chapter:- 4
Carbon and its Compounds
Carbon and Its Compounds
Carbon is considered as the third most important element, after oxygen and hydrogen, for the existence of life on the earth.
The Covalent Bond
![]()
Thus, there are 4 electrons in its outermost shell and its octet can be completed by the following two ways
- It could lose 4 electrons and form C4+ cation. But a massive amount of energy is required to remove 4 electrons leaving behind a carbon cation with 6 protons in its nucleus holding on just two electrons together.
- It could gain 4 electrons and can form C4- anion. But for a nucleus having 6 protons, it would be difficult to hold on 10 electrons, i.e. 4 extra electrons.
In order to overcome this problem, carbon shares its valence electrons with other atoms of itself or atoms of other elements.
- This type of bonding is called covalent bonding.
- The bonds which are formed by the sharing of an electron pair between two same or different atoms are known as covalent bonds.
- The number of electrons shared show the covalency of that atom.
Formation of Hydrogen Molecule
Atomic number of H = 1
![]()
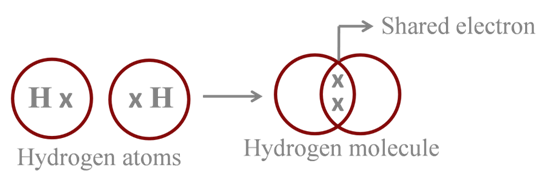
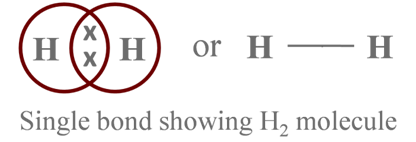
The shared pair of electrons constitutes a single bond between the two H-atoms
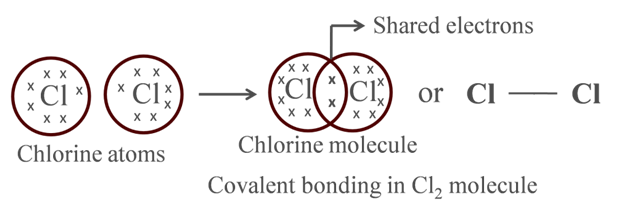
Formation of Chlorine Molecule
Atomic number of Cl = 17
![]()
It has 7 electrons in its outermost shell and thus requires 1 more electron to fulfill its outermost shell.
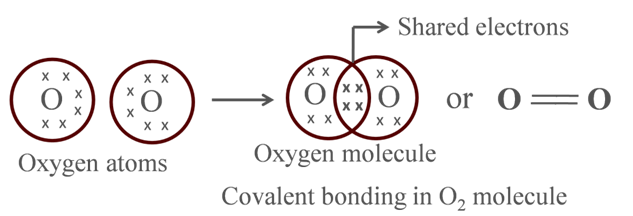
Formation of Oxygen Molecule
Atomic number of O = 8
![]()
It requires 2 electrons to fulfill its octet for attaining noble gas configuration.
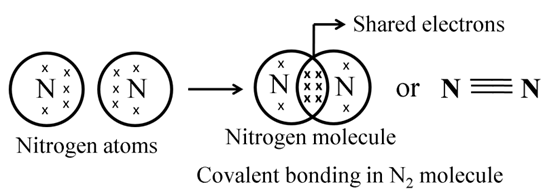
Formation of Nitrogen Molecule
Atomic number of N = 7
![]()
It needs 3 more electrons to attain noble gas configuration.
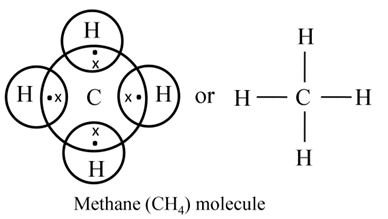
Formation of Methane (CH4)
In the formation of a methane molecule one carbon atom shares its 4 electrons with four different hydrogen atoms
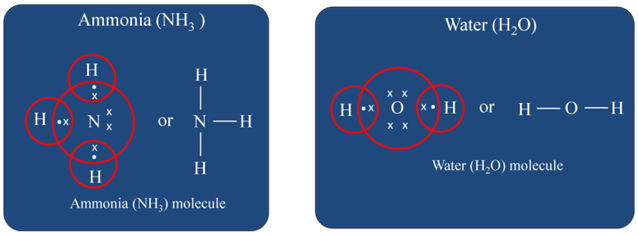
Formation of Ammonia and Water Molecule
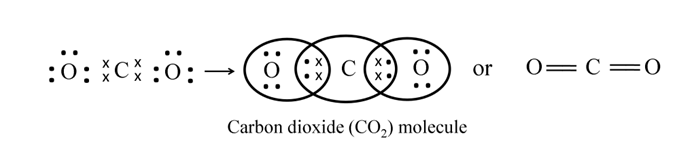
Formation of Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Atomic number of C = 6
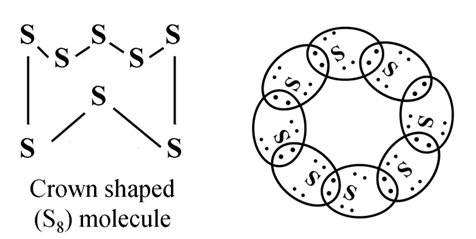
Formation of Sulphur Molecule (S8)
Atomic number of sulphur = 16
Properties of Covalent Compounds
Covalently bonded molecules are called covalent compounds.
- Their constituents are molecules, not ions.
- They have strong bonds within the molecule but intermolecular forces are weak, which is responsible for low melting and boiling points of these compounds (except graphite and diamond).
- In these compounds, electrons are only shared and no charged particle is formed. Therefore, these compounds are bad conductors of electricity due to the absence of free electrons or ions. However, graphite is an exception of it, which is a good conductor of electricity.
- These compounds are generally insoluble in water but some of them are capable to form H bond which are soluble in water.
Difference between Covalent and Ionic Compounds
- Covalent compounds have lower intermolecular force in comparison with ionic compounds.
- Covalent compounds have comparatively lower boiling and melting points than the ionic compounds.
- Covalent compounds are poor conductors of electricity while ionic compounds are good conductors of electricity in their aqueous solution or in molten state.
- Covalent compounds are formed by the sharing of electrons where as ionic compounds are formed by the lose or gain of electrons.

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
