Introduction
- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chapter:- 3
Atoms and Molecules
Introduction
We shall discuss about the various laws which indicates how atoms combine to form molecule, symbols and formula of atoms and compounds and various ways of expressing their masses.
Laws of Chemical Combination
Whenever reactants react together to form the products or the elements combine together to form a compound, they do this according to certain laws. These laws are called the laws of chemical combination.
Law of Conservation of Mass
It states, "Mass can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction."
Law of Constant Proportions/ Law of Definite Proportions
French chemist, joseph Proust analysed the chemical composition of a large number of compounds and came to the conclusion that the proportion of each element in a compound I constant. On this basis he proposed the law of constant proportions.
"A pure chemical compound always consists of the same elements that are combined together in a fixed (or definite) proportion by mass."
For Example:- carbon dioxide (CO2) always contains carbon and oxygen in the ratio of 3 : 8. If a sample of CO , contains 36 g of carbon then it is compulsory that it has 96g Oxygen.
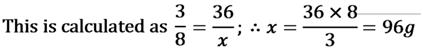
Dalton's Atomic Theory 1
- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Dalton's Atomic Theory
Dalton's Atomic Theory
Dalton's atomic theory provided an explanation for the law of conservation of mass and the law of definite proportions. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter (whether an element, a compound or a mixture), is compounds of small particles, called atoms.
The Main Postulates of Dalton's Atomic Theory are
- Every matter is made up of very small particles, called the atoms.
- Atoms are indivisible particles which can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass as well as in chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
- The relative numbers as well as kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Merits of Dalton's Atomic Theory
Dalton's atomic theory has proved to be very useful in various ways
- This theory has enabled us to explain the laws of chemical combination.
- Dalton was the first to recognize a workable distinction between the ultimate particle of an element (atom) and that of a compound (molecule).
Demerits of Dalton's Atomic Theory
- Atom is no longer considered as the smallest indivisible particle. It has been established that it is made up of electrons, protons and neutrons.
- Atoms of the same element may have slightly different masses (Isotopes).
- Atoms of different elements may have the same masses (Isobars).
- Substance made up of the same kind of atoms may have different properties.
- The ratio in which the different atoms combine to form compound may be fixed and integral but may not be simple.
Illustration
Dalton atomic theory postulated that "Atoms combine in simple whole number ratio". How has this postulate been modified?
Solution
According to the modified postulate, 'Atoms combine in whole number ratio but this ratio may not be simple." For example. in C12H22O11 (sucrose) ratio of C : H : O is 12 : 22 : 11, which is a whole number ratio but not the simple.
Illustration
Carbon and oxygen combine to form carbon dioxide gas. They do so in the same ratio 3 : 8. What mass of oxygen would be required to react completely with 6.0 g of carbon? Also calculate the mass of carbon dioxide gas so formed.
Solution
Carbon and oxygen combine as per law of constant proportions, i.e. 3 g of carbon will always combine with 8 g of oxygen or
∵ 3g carbon combines with oxygen = 8g
∴ 6g carbon will combine with oxygen = 8/3 x 6 = 16g
Total amount of carbon dioxide = 6 ± 16= 22 g
Atoms
Atoms are the smallest particles of an element which may or may not have independent existence but take part in a chemical reaction. These are the building blocks of all natter.
For Example:- atoms of hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc, are not capable in independent existence whereas atoms of helium, noon, etc are capable of independent existence.
Size of Atoms
Atoms are very small and their radius is measured in nanometres.
1/109 M =1 nm or lm = 109 nm
Radius of hydrogen atom is 0.1 nm.
Modern Symbols of Atoms of Different Elements
Although Dalton was the scientist who introduced symbols for representing elements for the first time but modern symbols for the elements were introduced by JJ Berzilius. These are defined as a short hand representation of the name of an element.
Now a days, it is the IUPAC who approves the names of the letters of the element’s name in English. The first letter of a symbol is always written in capital letter and the second letter as small letter.
e.g., chlorine – Cl, zinc – Zn and aluminium – Al.
Symbols of some elements have been taken from their names in different languages such as Latin, German, Greek, etc.
For Example:-
- Iron – Fe from Ferrum (Latin Name)
- Gold – Au from Aurum (Latin Name)
- Potassium – K from Kalium (Latin Name)
- Chlorine – Cl from Chloros (Greek Name)
- Cobalt – Co from Kobold (German Name)
- Sodium– Na from Natrium (Latin Name)
Atomic Mass
According to Dalton, each element has a characteristic atomic mass. But determining the mass of an individual atom was a relatively difficult task due to its very small size.
Hence, their relative atomic masses were determined using the laws of chemical combination and the compounds formed. For this purpose, initially oxygen was taken as standard because of the following two reasons:
(i):- Oxygen reacted with a large number of elements and formed compounds.
(ii):- This unit gave masses of most of the elements as whole numbers.
Relative Atomic Mass
It is defined as the number of times a given atom is heavier than 1/12th of mass of 1 atom of carbon-12 (C-12) or it is the average mass of the atom as compared to 1/12th the mass of one carbon-12 atom.
Atomic Mass Unit
It is defined as the mass unit equal to exactly 1/12th of the mass of one atom of C-12 isotope. Earlier, it was abbreviated as amu but according to latest recommendations of IUPAC, it is now written as `u'— unified mass.
Molecules
- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Molecules
The smallest particle of a substance which is capable of independent existence is called a molecule. In general, molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together. It shows all the properties of the substance. Molecules can be divided into two categories.
Molecules of Elements
The molecules of an element are constituted by the same type of atoms. Molecules of many elements are made up of one atom of that element. e.g. noble gases like argon (Ar), helium (He), etc.
The molecules of most of more than one atoms of the non-metals are made up of more than one atoms.
For Example:- A molecule of oxygen consists of two atoms of oxygen. Ozone (O3) consists of three atoms of oxygen.
Atomicity
It is defined as the number of atoms present in a molecule.
On the basis of atomicity, molecules can be classified as
(i):- Monatomic Molecules They consist of only one atom. e.g. He, Ne, Ar, Xe, Fe, Al, etc.
(ii):- Diatomic Molecules They consist of two atoms. e.g. H2,O2, N2,I2, Br2, C12, etc.
(iii):- Triatomic Molecules They consist of three atoms. e.g. O3.
(iv):- Tetraatomic Molecules They consist of four atoms. e.g. P4.
(v):- Polyatomic Molecules They consist of more than four atoms. e.g. S8.
Molecules of Compounds
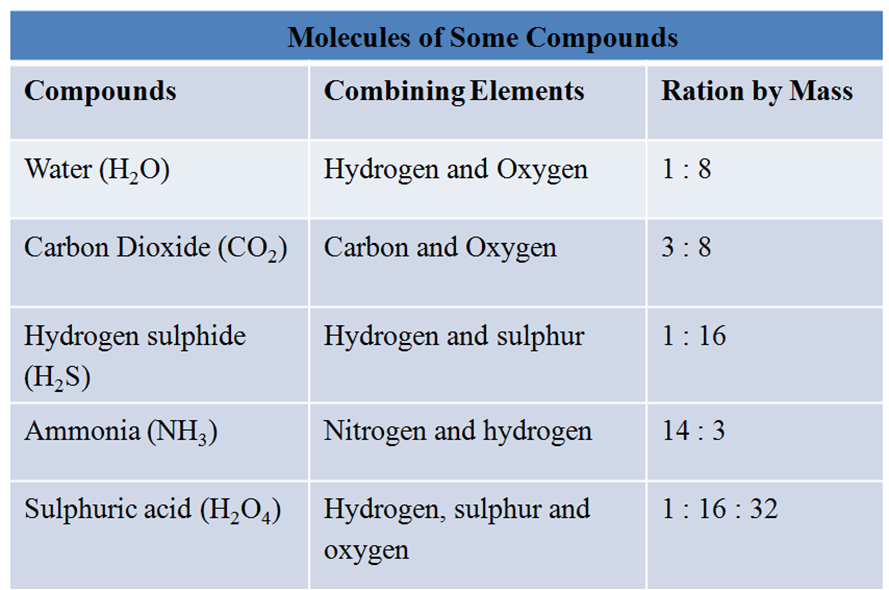
Atoms of different elements join together in definite proportions forming molecules of compounds.
For Example, H2O molecule is made up of hydrogen and oxygen elements in the ratio of 1:8 by mass.
Ions
When atoms, groups of atoms or molecules lose or gain electron(s) they become charged. These charged species are known as ions. These can be negatively or positively charged.
Cations
The positively charged ions which are attracted towards cathode in an electric field are known as cations. e.g. Na+, K+, Ca2+, A13+ , etc.
Anions
The negatively charged ions which are attracted towards anode in an electric field are known as anions. e.g. Cl–, Br–, O, N3-, etc.
Ionic Compounds
The compound which consists of ions as its constituent particles is known as ionic compound. It contains ionic bonds. e.g. sodium chloride, consists of a positively charged) sodium ion (Na+ cation) and negatively charged chloride ion (C1- anion). Calcium oxide or quicklime (CaO) consist of calcium cation (Ca2+) and oxide anion (O2-).
Polyatomic Ion
The compound which consists of ions as its constituent particles is known as ionic compound. It contains ionic bonds. e.g. sodium chloride, consists of a positively charged) sodium ion (Na+ cation) and negatively charged chloride ion (C1- anion). Calcium oxide or quicklime (CaO) consist of calcium cation (Ca2+) and oxide anion (O2-).
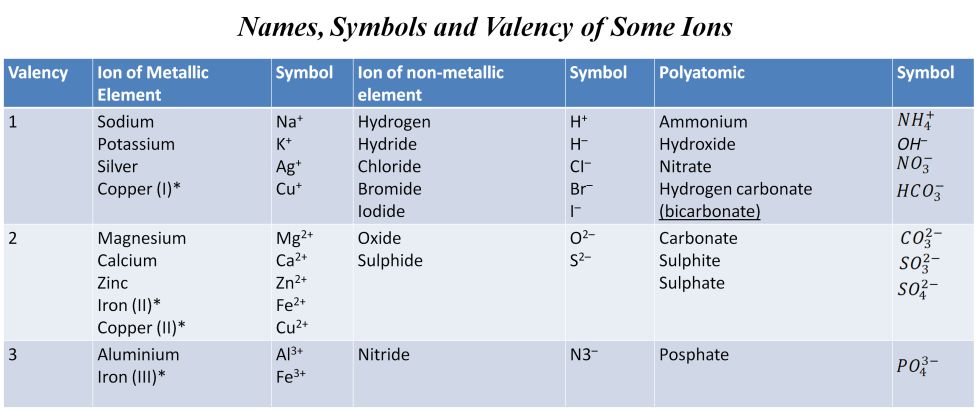
Valency
The combining power (or capacity) of an element is called its valency. Valency can be used to find out how the atoms of an element will combine with the atom(s) of another element to form a chemical compound.
Writing Chemical Formulae 1
- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Writing Chemical Formulae
The shortest way to represent a compound with the help of symbols and valency of elements is known as chemical formula. Chemical formula of a compounds shows of each combining element.
In ionic compounds, the charge on each ion is used to determine the chemical formula of a compound.
There are some rules for writing the chemical formula
(i):- The valencies or charges on the ion must be balanced.
(ii):- When a compound consists of a metal and a non-metal, the symbol of the metal is written first and on the left whereas of non-metal on its right.
(iii):- When compound is formed with polyatomic ions, the ion is enclosed in a bracket before writing the number to indicate the ratio. e.g. Ca(OH)2.
Formulae of Simple Compounds
To write the chemical formula for simple compounds.
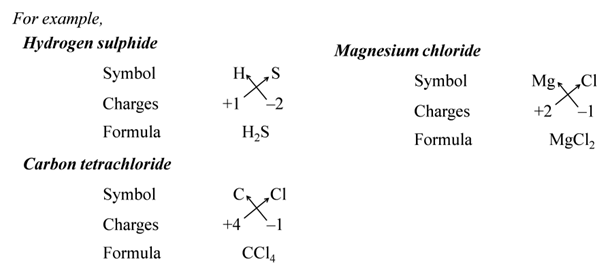
(i):- Write the symbols of constituent elements and their valencies as shown below.
(ii):- Write the symbol of cation first followed by the symbol of anion.
(iii):- Then criss-cross their charges or valencies to get the formula.
Note:- The simplest compounds made up of two different elements are also called binary compounds.
In other words, the positive and negative charges must balance each other and the overall structure must be neutral.

Note:- When the valency of both elements are numerically equal, the subscripts are also not written.
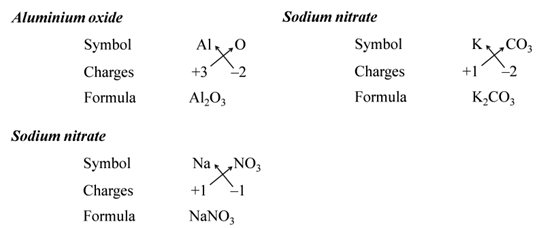
We use brackets when we have two or more of the same ions in the formulae. For Example:-
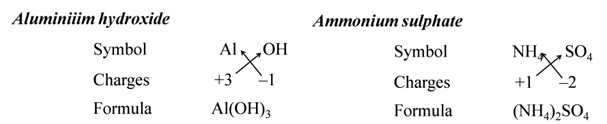
All subscripts must be reduced to lowest term (except for molecule or covalent compound). For Example:-

Illustration
Write symbols of the following elements:
Silver, Chromium, Chlorine, Mercury, Lead, Copper, Gold, Aluminium.
Solution
Silver (Ag), Chromium (Cr), Chlorine (CI), Mercury (Hg), Lead (Pb), Copper (Cu), Gold (Au), Aluminium (Al).
Illustration
Define atomic mass unit.
Solution
One atomic mass unit is the mass unit (u) equal to exactly 1/12th of the mass of one atom of C-12 isotope.
Illustration
How many kinds of atoms are present in a molecule of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)?
Solution
CaCO3 is a heteroatomic molecule which contains three types of atoms, i.e. one atom of calcium, one atom of carbon and three atoms of oxygen.
Molecular Mass
The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic Masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance. Therefore, the relative molecular mass of a molecule is its relative mass expresses in atomic mass units (u).
For example,
The relative molecular mass of water (H2O) is 18 u, which can be calculated as
Atomic mass of hydrogen =1 u
Atomic mass of oxygen = 16 u
H2O contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Therefore, molecular mass of water is
= 2x1 + 1 x 16 = 18 u
Illustration
Calculate the molar mass of the following substances:
(i):- Ammonia, (ii):- Hydrochloric acid, (iii):- Phosphorus molecule,
(iv):-Hydrogen molecule, (v):- Oxygen molecule, (vi):- Sulphur dioxide
Solution
(i):- Molar mass of ammonia (NH3)
=1 x 14 + 3 x 1 = 17 u
(ii):- Molar mass of hydrochloric acid (HCI)
=1 x 1 + 1 x 35.5 = 36.5 u
(iii):- Molar mass of phosphorus molecule (P4)
= 4 x 31 = 124 u
(iv):- Molar mass of hydrogen molecule (H2)
= 2 x 1= 2 u
(v):- Molar mass of oxygen molecule (O2)
= 2 x 16 = 32 u
(vi):- Molar mass of sulphur dioxide (SO2)
= 32 + 2 x 16 = 64 u
Formula Unit Mass
It is the sum of the atomic masses of all atoms present in a formula unit of a compound.
Formula unit mass is calculated in the same manner as we calculate the molecular mass.
e.g. formula unit mass for sodium chloride (NaCI)
= 1 x 23 + 1 x 35.5 = 58.5 u
Mole Concept
One mole of any species (atoms, molecules, ions or particles) is that quantity in number having a mass equal to its atomic or molecular mass in grams.
e.g. 1 mole of carbon (atomic mass =12) is equal to 12 g.
1 mole of oxygen (O2, molecular mass = 2 x 16) is equal to 32 g.
1 mole of water (H2O, molecular mass = 2 x 1 + 1 x 16) is equal to 18 g.
Avogadro Constant
The number of particles present in 1 mole of any substance is same and fixed, which is equal to 6.022 x 1023. This is a constant, known as Avogadro constant or Avogadro number (NA).
Thus, mole is also defined as number of particles equal to the Avogadro constant, NA(6.022 x 1023).
1 mole = 6.022 x 1023 particles, in number.
Molar Mass and Moles
The mass of 1 mole of a substance is equal to its relative atomic or molecular mass in gram. Since the atomic mass or molecular mass of an element gives us the mass of one atom of that element in atomic mass units (u). Thus, to get the mass of 1 mole of an atom of that element we have to take the same numerical value but change the units from `if to 'g‘.
Illustration
Find the mass of :
(i):- 1 mole of nitrogen atoms, (ii):- 8 moles of aluminium atoms, (iii):- 0.2 mole of oxygen atoms, (iv):-2 moles of water molecules.
Solution
(i):- Mass of 1 mole of nitrogen atoms
- = molar mass in gram =14 g
(ii):- We know that,
- mass of 1 mole of Al-atoms = 27 g
- Mass of 8 moles of Al-atoms = 8 x 27 = 216 g
(iii):- Mass of 0.2 mole of oxygen atoms = 0.2 x 16 = 3.2 g
- Mass of 1 mole of oxygen atoms =16 g
(iv):- Mass of 2 moles of water molecules = 2 x 18 = 36 g
- Mass of 1 mole of water molecule =18 g
Percentage Composition
The percentage composition of an element in a compound is the percentage of the mass contributed by the element to the total mass of the compound. It is obtained by dividing mass of that element in the compound by the total mass of the compound and multiplying by 100, i.e.,.
![]()
Illustration
Calculate the percentage composition of carbon in CO2.
Solution
Molar mass of CO2 =12 + 2 x16 = 44g mol-1
Mass due to carbon (C) = 12 g
Percentage composition of C = 12/44 x100 = 27.3%
Advanced Level
Illustration
Write the molecular formulae of all the compounds that can be formed by the 3M combination of the following ions: ![]()
Solution
(a):- Compounds of Cu2+ = CuCl2, CuSO4, Cu3(PO4)2
(b):- Compounds of Na+ = NaCl, Na2SO4, Na3PO4
(c):- Compounds of Fe3+ = FeCl3, Fe2(SO4)3, FePO4
Illustration
Calculate the number of moles of magnesium present in a magnesium ribbon weighing 12 g. Molar atomic mass of magnesium is 24 g mol-1.
From the table, find
(a) A pair of ions (b) An atom of noble gas
(c) A pair of isobars (d) A pair of isotopes
Solution
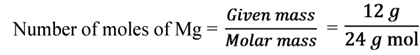
Illustration
Calculate the formula unit mass of CaCl2.
Solution
Atomic mass of Ca = 40 and Cl = 35.5
CaCl2 = 40 + 2 x 35.5 = 40 + 71 = 111u
Illustration
Give the names of any two elements present in the following compounds:
Baking powder, Common salt, Sulphuric acid
Solution
Baking powder (NaHCO3) Sodium, hydrogen, carbon and oxygen.
Common salt (NaCl) Sodium and chlorine.
Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) Sulphur, hydrogen and oxygen.
Illustration
6 g of coke consisting 100% carbon, is burnt in air. Find the number of oxygen atoms consisted by the carbon dioxide gas thus formed.
Solution
Each carbon atom combine with two oxygen atoms up on combustion as follows: 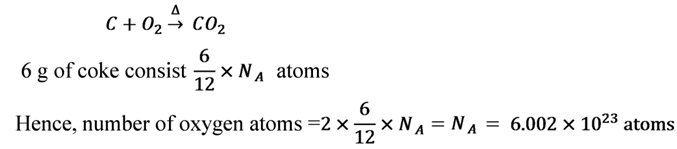
Illustration
Find the number of atoms in 120 g of calcium and 120 g of iron. Which one has more number of atoms and how much is the difference?
[Atomic mass of Ca = 40 u, Fe = 56 u]
Solution
Molar mass of Ca = 40 g
∵ 40 g of Ca contains, number of atoms = 6.022 x 1023
Then, let the size of the nucleus be x m.

Illustration
List down three different names given to the path in which electrons revolve around the nucleus. Also explain why are they called so?
Solution
The three different names are:-
Discrete orbit It is called so because electrons revolve in certain distinct path and not just in orbit.
Energy level (energy shell) The energy associated with different orbits (with which electron revolves) is distinct for each orbit, hence it is called so.
Stationary state Since, the energy associated with an orbit is fixed. Hence, the electron revolving in a particular orbit have stationary energy. That's why, orbit is also called stationary state.
Illustration
A metal (mass number = 40) having same number of protons and neutrons, combines with two chlorine atoms. Identify the element with which electronic configuration of this metal matches in combined state.
Solution
∵ Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
⇒ 40 = 2 x Number of protons
⇒ Number of protons = 20
Hence, the metal is calcium (Ca).
Since, it combines with 2 Cl atoms (total valency = 2)
Hence, it will acquire 2 positive charge, after losing 2 electrons as
K L M
Electronic configuration of Ca2+ ion = 2, 8, 8
This electronic configuration matches to that of argon (Ar).
Dalton's Atomic Theory
- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Dalton's Atomic Theory
Dalton's atomic theory provided an explanation for the law of conservation of mass and the law of definite proportions. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter (whether an element, a compound or a mixture), is compounds of small particles, called atoms.
The Main Postulates of Dalton's Atomic Theory are
- Every matter is made up of very small particles, called the atoms.
- Atoms are indivisible particles which can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass as well as in chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
- The relative numbers as well as kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Merits of Dalton's Atomic Theory
Dalton's atomic theory has proved to be very useful in various ways
- This theory has enabled us to explain the laws of chemical combination.
- Dalton was the first to recognize a workable distinction between the ultimate particle of an element (atom) and that of a compound (molecule).
Demerits of Dalton's Atomic Theory
- Atom is no longer considered as the smallest indivisible particle. It has been established that it is made up of electrons, protons and neutrons.
- Atoms of the same element may have slightly different masses (Isotopes).
- Atoms of different elements may have the same masses (Isobars).
- Substance made up of the same kind of atoms may have different properties.
- The ratio in which the different atoms combine to form compound may be fixed and integral but may not be simple.
Atoms
Atoms are the smallest particles of an element which may or may not have independent existence but take part in a chemical reaction. These are the building blocks of all natter.
For Example:- atoms of hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc, are not capable in independent existence whereas atoms of helium, noon, etc are capable of independent existence.
Size of Atoms
Atoms are very small and their radius is measured in nanometres.
1/109 M =1 nm or lm = 109 nm
Radius of hydrogen atom is 0.1 nm.
Modern Symbols of Atoms of Different Elements
Although Dalton was the scientist who introduced symbols for representing elements for the first time but modern symbols for the elements were introduced by JJ Berzilius. These are defined as a short hand representation of the name of an element.
Now a days, it is the IUPAC who approves the names of the letters of the element’s name in English. The first letter of a symbol is always written in capital letter and the second letter as small letter.
e.g., chlorine – Cl, zinc – Zn and aluminium – Al.
Symbols of some elements have been taken from their names in different languages such as Latin, German, Greek, etc.
For Example:-
- Iron – Fe from Ferrum (Latin Name)
- Gold – Au from Aurum (Latin Name)
- Potassium – K from Kalium (Latin Name)
- Chlorine – Cl from Chloros (Greek Name)
- Cobalt – Co from Kobold (German Name)
- Sodium– Na from Natrium (Latin Name)
Atomic Mass
According to Dalton, each element has a characteristic atomic mass. But determining the mass of an individual atom was a relatively difficult task due to its very small size.
Hence, their relative atomic masses were determined using the laws of chemical combination and the compounds formed. For this purpose, initially oxygen was taken as standard because of the following two reasons:
(i):- Oxygen reacted with a large number of elements and formed compounds.
(ii):- This unit gave masses of most of the elements as whole numbers.
Relative Atomic Mass
It is defined as the number of times a given atom is heavier than 1/12th of mass of 1 atom of carbon-12 (C-12) or it is the average mass of the atom as compared to 1/12th the mass of one carbon-12 atom.
Atomic Mass Unit
It is defined as the mass unit equal to exactly 1/12th of the mass of one atom of C-12 isotope. Earlier, it was abbreviated as amu but according to latest recommendations of IUPAC, it is now written as `u'— unified mass
Writing Chemical Formulae
- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Writing Chemical Formulae
The shortest way to represent a compound with the help of symbols and valency of elements is known as chemical formula. Chemical formula of a compounds shows of each combining element.
In ionic compounds, the charge on each ion is used to determine the chemical formula of a compound.
There are some rules for writing the chemical formula
(i):- The valencies or charges on the ion must be balanced.
(ii):- When a compound consists of a metal and a non-metal, the symbol of the metal is written first and on the left whereas of non-metal on its right.
(iii):- When compound is formed with polyatomic ions, the ion is enclosed in a bracket before writing the number to indicate the ratio. e.g. Ca(OH)2.
Formulae of Simple Compounds
To write the chemical formula for simple compounds.
(i):- Write the symbols of constituent elements and their valencies as shown below.
(ii):- Write the symbol of cation first followed by the symbol of anion.
(iii):- Then criss-cross their charges or valencies to get the formula.
Note:- The simplest compounds made up of two different elements are also called binary compounds.
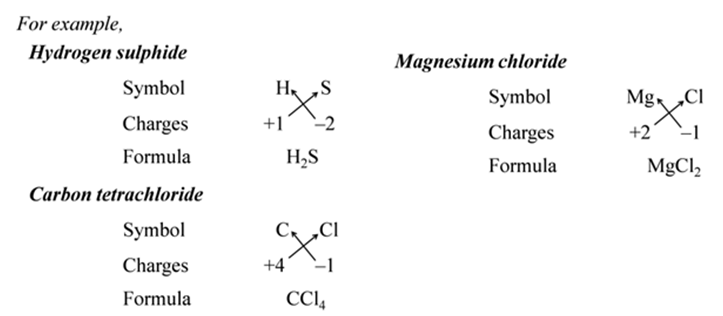
In other words, the positive and negative charges must balance each other and the overall structure must be neutral.

Note:- When the valency of both elements are numerically equal, the subscripts are also not written.
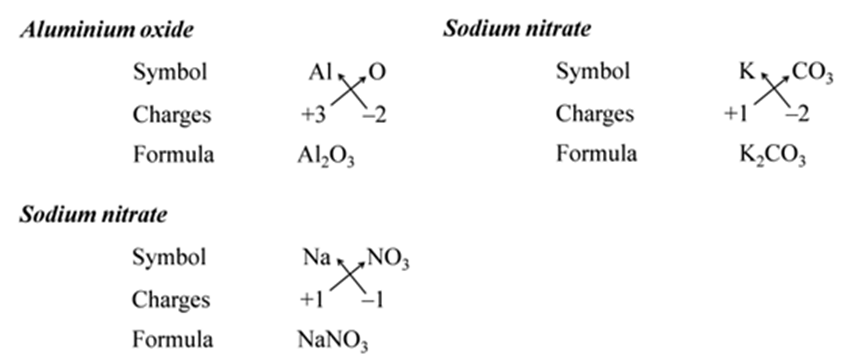
We use brackets when we have two or more of the same ions in the formulae. For Example:-
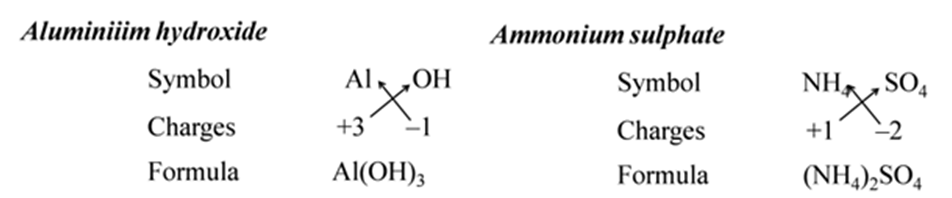
All subscripts must be reduced to lowest term (except for molecule or covalent compound). For Example:-

Molecular Mass
The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic Masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance. Therefore, the relative molecular mass of a molecule is its relative mass expresses in atomic mass units (u).
For example,
The relative molecular mass of water (H2O) is 18 u, which can be calculated as
Atomic mass of hydrogen =1 u
Atomic mass of oxygen = 16 u
H2O contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Therefore, molecular mass of water is
= 2x1 + 1 x 16 = 18 u
Formula Unit Mass
It is the sum of the atomic masses of all atoms present in a formula unit of a compound.
Formula unit mass is calculated in the same manner as we calculate the molecular mass.
e.g. formula unit mass for sodium chloride (NaCI)
= 1 x 23 + 1 x 35.5 = 58.5 u
Mole Concept
One mole of any species (atoms, molecules, ions or particles) is that quantity in number having a mass equal to its atomic or molecular mass in grams.
e.g. 1 mole of carbon (atomic mass =12) is equal to 12 g.
1 mole of oxygen (O2, molecular mass = 2 x 16) is equal to 32 g.
1 mole of water (H2O, molecular mass = 2 x 1 + 1 x 16) is equal to 18 g.
Avogadro Constant
The number of particles present in 1 mole of any substance is same and fixed, which is equal to 6.022 x 1023. This is a constant, known as Avogadro constant or Avogadro number (NA).
Thus, mole is also defined as number of particles equal to the Avogadro constant, NA(6.022 x 1023).
1 mole = 6.022 x 1023 particles, in number.
Molar Mass and Moles
The mass of 1 mole of a substance is equal to its relative atomic or molecular mass in gram. Since the atomic mass or molecular mass of an element gives us the mass of one atom of that element in atomic mass units (u). Thus, to get the mass of 1 mole of an atom of that element we have to take the same numerical value but change the units from `if to 'g‘.
Percentage Composition
The percentage composition of an element in a compound is the percentage of the mass contributed by the element to the total mass of the compound. It is obtained by dividing mass of that element in the compound by the total mass of the compound and multiplying by 100, i.e.,.
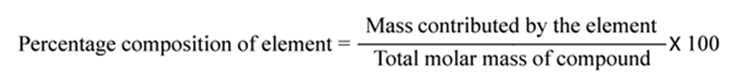

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
