- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Bohr's Model of an Atom
To overcome the objections raised against Rutherford's model of the atom, Neils Bohr put forward the following postulates about the model of an atom.
(i):- Atom consists of positively charged nucleus around which electrons revolve in discrete orbits i.e., electrons revolve in certain permissible orbits and not just in any orbit.
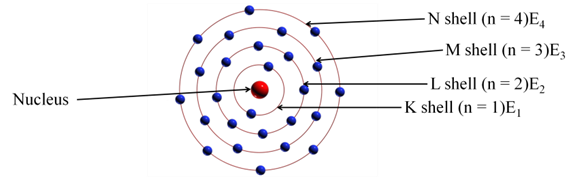
(ii):- Each of these orbits are associated with certain value of energy. Hence, these orbits are called energy shells or energy levels.
(iii):- Starting from nucleus, energy levels (orbits) are represented by numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, etc) or by alphabets (K, L, M, N, etc).
(iv):- Normally, the electrons present in first energy level (E1) have lowest energy. k Energies increase going towards outer energy levels.
(v):- Energy of an electron remains same as long as it remains in discrete orbit and it does not radiate energy while revolving.
(vi):- When energy is supplied to an electron, it can go to higher energy levels. While an electron falls to lower energy level, it radiate energy.
Neutrons (n)
Neutrons are another sub-atomic particles, discovered by J Chadwick in 1932. It is represented by n. Neutrons are electrically neutral particles and are as heavy as protons.
(i.e., their mass is 1.67493x10–27 kg). Neutrons are present in the nucleus of all atoms except hydrogen. The mass of the atom is given by the sum of the masses of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus.

Distribution of Electrons in Different Orbits (Shells)
For writing the number of electrons in different energy levels, there are some rules.
- The maximum number of electrons present in a shell is given by the formula 2n 2, where n is the orbit number or energy level, 1, 2, 3…….
Therefore, the maximum number of electrons in different shells are as follows
First orbit or K-shell = 2 x (1)2 = 2
Second orbit or L-shell = 2 x (2)2 = 8
Third orbit or M-shell = 2 x (3)2 =18
Fourth orbit or N-shell = 2 x (4)2 = 32 and so on.
- The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in the outermost orbit is 8.
- Electrons are not accommodated in a given shell, unless the inner shells are filled.
Valency
The electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom are known as the valence electrons. The combining capacity of the atom of an element with the atom(s) of other element(s) in order to complete its octet is known as valency.
Atomic Number
It is defined as the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom. It is nearly denoted by Z.
For Example:-
![]()
Mass Number
It is defined as the sum of number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number is denoted by A.
Mass number (A) = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
![]()
Number of neutrons = Mass number – Atomic number
∵ Atomic number = Number of protons
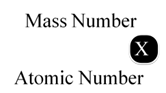 In the notation for an atom, the atomic number, mass number and symbol of the element are to be written as
In the notation for an atom, the atomic number, mass number and symbol of the element are to be written as
Atomic Weight
Mass of an individual atom is called atomic mass or atomic weight. It is nearly equal to the mass number.
For Example:-
(i):- Carbon, atomic number (Z) = 6,
Mass number (A) =12,
Atomic mass =12.01 u
(ii):- Oxygen, atomic number (Z) = 8,
mass number (A) = 16, atomic mass = 15.99
Different Atomic Species; Isotopes
These are defined as the atoms of the same element, having the same atomic number but different mass numbers. For Example:- there are 3 isotopes of hydrogen atom, namely protium ![]()
![]() and tritium
and tritium ![]()
For Example:- The two isotopic forms of chlorine atom with masses 35 u and 37 u occur in the ratio of 3 : 1.
Therefore, the average atomic mass of chlorine atom, can be calculated as
![]()
Applications of Isotopes
- An isotope of uranium (U-235) is used as a fuel for the production of electricity in nuclear reactors.
- U-238 is used to determine the age of very old rocks and even the age of the earth.
- An isotope of cobalt (Co-60) is used in the treatment of cancer.
- An isotope of carbon (C-14) is used to determine the age of old specimens of wood or old bones of living organisms.
- An isotope of iodine (I-131) is used in the treatment of goitre.
- P-32 is used in agricultural research.
- Na-24 is used to detect blood clots.
Isobars
Atoms of different elements with different atomic numbers, but same mass number, are known as isobars.
![]()
Isotones
Atoms of different elements having the same number of neutrons are called isotones.
![]()

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
