- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Suspension and Evaporation
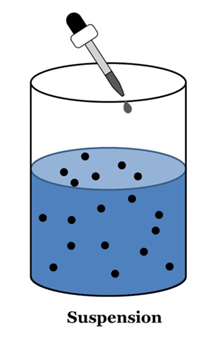
Suspension
A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which the solute particles do not dissolve but remain suspended throughout the bulk of the medium.
Properties of a Suspension
- Suspension is a heterogeneous mixture.
- Its particles can be seen by naked eyes.
- Its particles scatter a beam of light passing and make its path visible (Tyndall effect).
- It is unstable. The soluble particles settle suspension is left undisturbed or they can by the process of filtration.
Colloidal Solution

A colloid (or colloidal solution) is a mixture that is heterogeneous but appears to be homogeneous as the articles are uniformly spread
throughout the solution. e.g., milk, shaving cream, cheese etc.
Properties of a Colloid
- A colloid appears to be homogeneous but actually it is heterogeneous.
- A colloid appears to be homogeneous but actually it is heterogeneous.
- The size of particles of colloid is very small. They can not be seen even with a microscope.
- Its particles can pass through filter paper, therefore, a colloid cannot be separated by filtration. However, they get separated by a special technique, called centrifugation.
Some Common Examples of Colloids
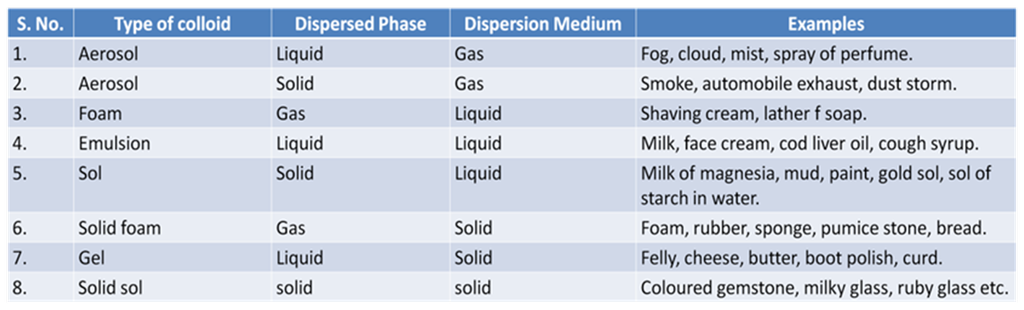
Components of a Colloid
The solute like component form the dispersed phase and the component in which the dispersed phase is suspended is known as the dispersion medium.
Evaporation
This method can be used to separate a volatile component (solvent) from a non-volatile component of a mixture.
Centrifugation
(Separation of Cream from Milk)
Two components having difference in densities can be separated by centrifugation.
Decantation
This method is also applied where a difference between densities of components lies. A less soluble solid from a liquid can be separated by first keeping the mixture undisturbed and then decanting the liquid slowly leaving the solid in the first container.
Separating Funnel
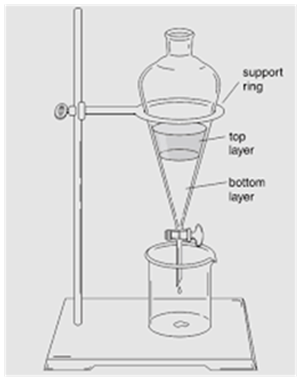
(Separation of Mixture of Two Immiscible Liquids)
This method is used for separating two immiscible liquids and is also based on the difference in densities.

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
