- Books Name
- AMARENDRA PATTANAYAK Mathmatics Book
- Publication
- KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Algebra of real functions
Examples:
Q.1: Write the range of a Signum function.
Solution:
The real function f: R → R defined by
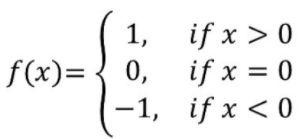
is called the signum function. Domain of f = R, Range of f = {1, 0, – 1}
Q.2: Express the function f: A—R. f(x) = x2 – 1. where A = { -4, 0, 1, 4) as a set of ordered pairs.
Solution:
Given,
A = {-4, 0, 1, 4}
f(x) = x2 – 1
f(-4) = (-4)2 – 1 = 16 – 1=15
f(0) = (0)2 – 1 = -1
f(1) = (1)2 – 1 = 0
f(4) = (4)2 – 1 = 16 – 1 =15
Therefore, the set of ordered pairs = {(-4, 15), (0, -1), (1, 0), (4, 15)}
Q.3: Let f(x) = x2 and g(x) = 2x + 1 be two real functions. Find
(f + g) (x), (f –g) (x), (fg) (x), (f/g ) (x)
Solution:
Given,
f(x) = x2 and g(x) = 2x + 1
(f + g) (x) = x2 + 2x + 1
(f – g) (x) = x2 -(2x + 1) = x2 – 2x – 1
(fg) (x) = x2(2x + 1) = 2x3 + x2
(f/g) (x) = x2/(2x + 1), x ≠ -1/2
Q.4: Redefine the function: f(x) = |x – 1| – |x + 6|. Write its domain also.
Solution:
Given function is f(x) = |x – 1| – |x + 6|
Redefine of the function is:
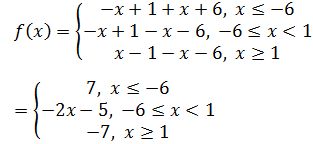
The domain of this function is R.
Q.5: The function f is defined by
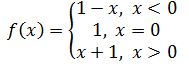
Draw the graph of f(x).
Solution:
f(x) = 1 – x, x < 0, this gives
f(– 4) = 1 – (– 4)= 5;
f(– 3) =1 – (– 3) = 4,
f(– 2) = 1 – (– 2)= 3
f(–1) = 1 – (–1) = 2; etc,
Also, f(1) = 2, f (2) = 3, f (3) = 4, f(4) = 5 and so on for f(x) = x + 1, x > 0.
Thus, the graph of f is as shown in the below figure.
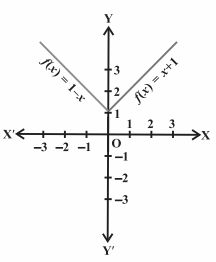
Q.6: Find the domain and range of the real function f(x) = x/1+x2.
Solution:
Given real function is f(x) = x/1+x2.
1 + x2 ≠ 0
x2 ≠ -1
Domain : x ∈ R
Let f(x) = y
y = x/1+x2
⇒ x = y(1 + x2)
⇒ yx2 – x + y = 0
This is quadratic equation with real roots.
(-1)2 – 4(y)(y) ≥ 0
1 – 4y2 ≥ 0
⇒ 4y2 ≤ 1
⇒ y2 ≤1/4
⇒ -½ ≤ y ≤ ½
⇒ -1/2 ≤ f(x) ≤ ½
Range = [-½, ½]

 KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
