Lipids
Lipids are organic molecules containing hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen atoms that provide the structural and functional foundation for living cells. Because water is a polar molecule, these organic compounds are nonpolar molecules that are only soluble in nonpolar solvents and insoluble in water. These molecules are produced in the human liver and can be found in the oil, butter, whole milk, cheese, fried foods, and some red meats.
Structure of Lipids
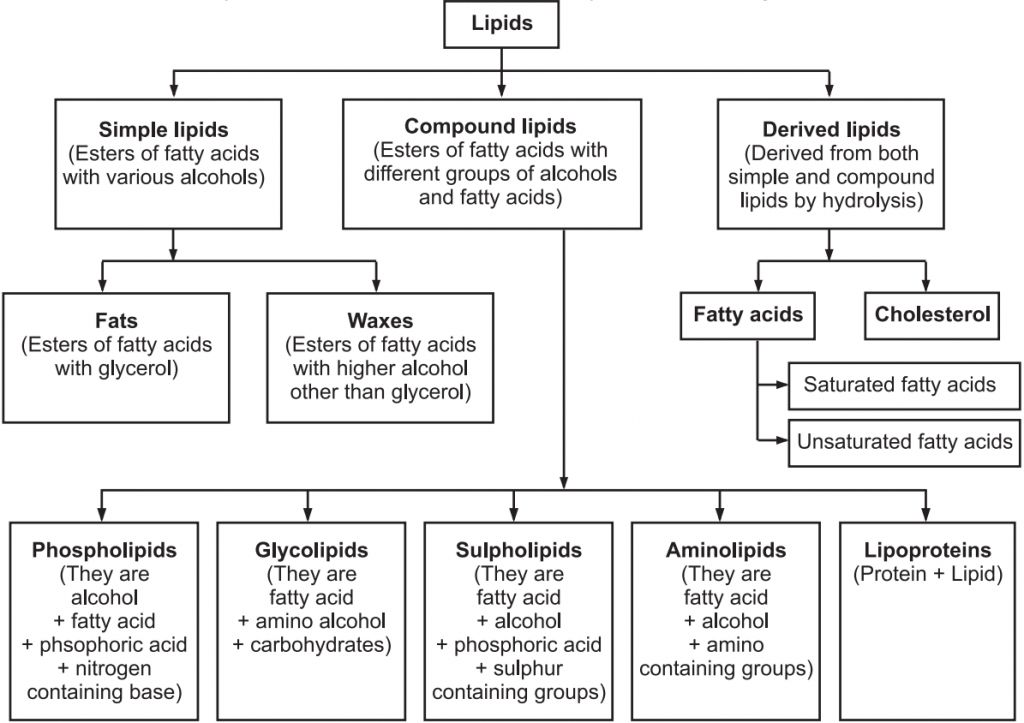
Lipids are fatty acid polymers with a long, non-polar hydrocarbon chain and a short polar area that contains oxygen.Lipids are often insoluble in water. It's possible that they're just simple fatty acids. A carboxyl group is connected to the R group in a fatty acid. The R group could be methyl (–CH3), ethyl (–C2H5), or a combination of the two (1 carbon to 19 carbons). Palmitic acid, for example, comprises 16 carbons, including the carboxyl carbon. Arachidonic acid, including carboxyl carbon, has 20 carbon atoms.Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds, while unsaturated fatty acids have one or more C=C double bonds. Glycerol, which is trihydroxy propane, is another simple lipid. Glycerol and fatty acids are found in many lipids. The fatty acids are esterified with glycerol. Monoglycerides, diglycerides, and triglycerides are the three types of lipids. Based on their melting point, these are also known as fats and oils. Oils (e.g., gingely oil) have a lower melting point and hence remain as oil in the winter. Phosphorus and a phosphorylated organic molecule are found in some lipids. Phospholipids are what they're called. They're located in the membranes of cells. One example is lecithin. Lipids with more complicated structures are found in some tissues, particularly brain tissues.
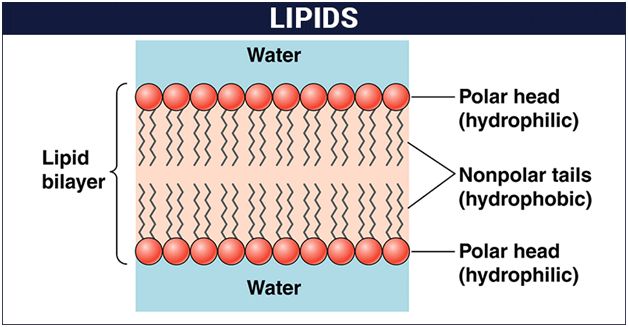
Listed below are some important characteristics of Lipids.
1. Lipids are oily or greasy nonpolar molecules, stored in the adipose tissue of the body.
2. Lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds, mainly composed of hydrocarbon chains.
3. Lipids are energy-rich organic molecules, which provide energy for different life processes.
4. Lipids are a class of compounds characterized by their solubility in nonpolar solvents and insolubility in water.
5. Lipids are significant in biological systems as they form a mechanical barrier dividing a cell from the external environment known as the cell membrane.
Classification of Lipids:
Lipids serve a critical role in our bodies. They are a component of the cell membrane's structure. They aid in the production of hormones and provide energy to our bodies. They aid in appropriate meal digestion and absorption. If we eat them in the right amounts, they constitute a nutritious element of our diet. They play a vital function in signaling as well.

 ACME SMART PUBLICATION
ACME SMART PUBLICATION
