- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Types of Chemical Reactions
The chemical reactions are classified into different classes depending upon the types of chemical changes taking place. These reactions are as follows:-
- Combination Reaction
- Decombination Reaction
- Displacement Reaction
- Neutralisation Reaction
- Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
- Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
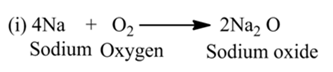
Combination Reaction
A reaction in which two or more reactants react together to form a single product is called a combination reaction.
For example,
(i):- When calcium oxide (quick lime) is dissolved in water, it forms calcium hydroxide (slaked lime).
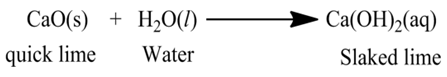
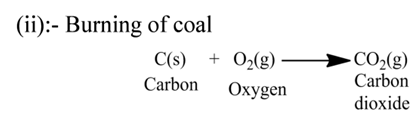
(iii):- Reaction between hydrogen gas and oxygen gas to form water.
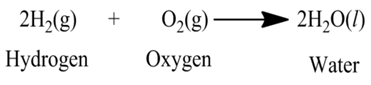
(iv):- Sulphur burns in air to form sulphur dioxide gas.
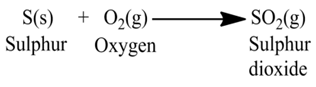
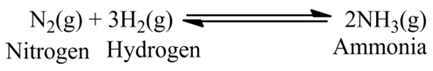
(v):- Nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen gas to form ammonia gas.
Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
(a) Exothermic Reactions:-
The reactions which are accompanied by the evolution of heat, are called exothermic reactions or the reactions in which heat is released alongwith the formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions.
For example,
![]()
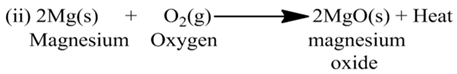
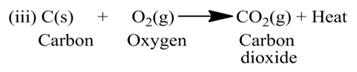
![]()
(b) Endothermic Reactions:-
The reaction, which occur by absorption of heat/energy are called endothermic reactions. It is also called hypothermic reaction. In other words, the energy needed for reaction to occur is less than the total energy released. As a result of this, the extra energy is absorbed in the form of heat.
For example,

Decomposition Reaction
A reaction, in which a single reactant breaks down to form two or more products, is known as decomposition reaction. On the basis of the form of energy required for the reaction, these reactions are of three types:-
- Thermal Decomposition
- Electroylysis
- Photolysis or Photochemical Decomposition
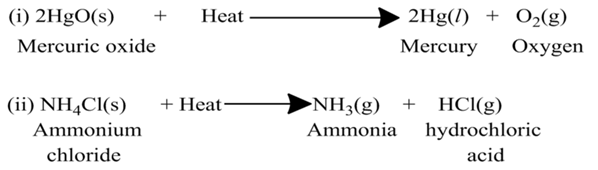
(a)Thermal Decomposition
These reactions use the energy in the form of heat for decomposition of the Reactant. For example,
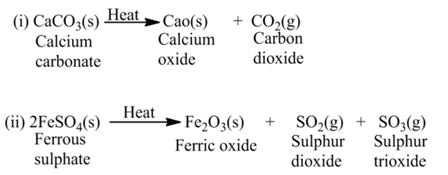
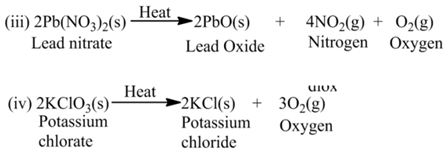
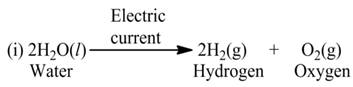
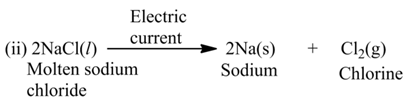
(b) Electrolysis
These reactions involve the use of electrical energy required for the decomposition of the reactant molecules. For example,
(c) Photolysis or Photochemical Decomposition
These reactions involve the use of light energy for the purpose of decomposition. For example,
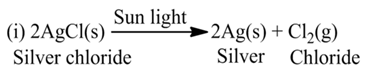
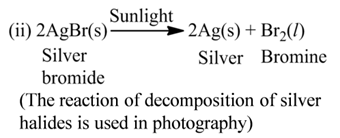
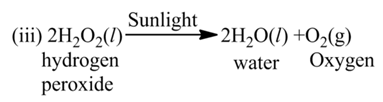
Displacement Reaction

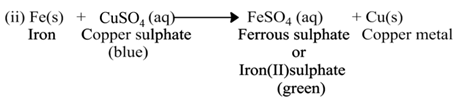
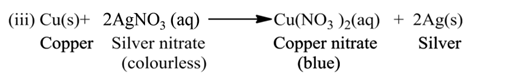
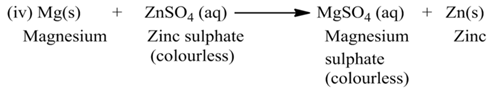
(a) Single Displacement Reaction
A reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from the solution of its compound, is called single displacement or displacement reaction.
For Example:-
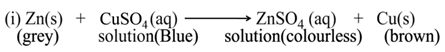
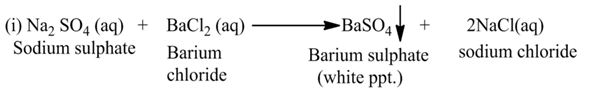
(b) Double Displacement Reaction
The reaction, in which two different ions in the reactant molecules are displaced by each other, is called double displacement reaction. For Example

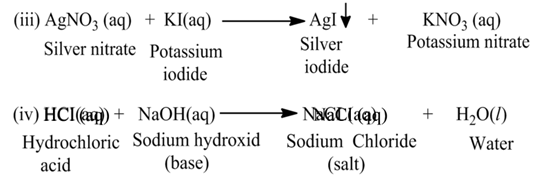
Neutralization Reaction
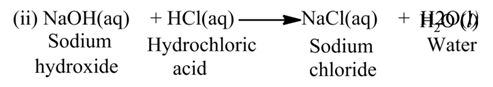
The reaction, in which an acid reacts with a base, is called neutralization reaction.
For Example:-
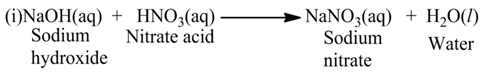
Oxidation and Reduction Reaction
OxidationThe process in which oxygen is added to a substances. OR The process in which hydrogen is removed from a substance.
For Example:-
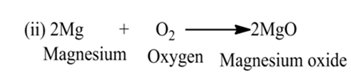
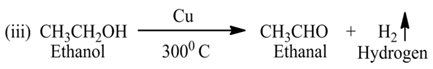
Here, ethanol is oxidized due to the removal of hydrogen.
Reduction
The process in which oxygen is removed from a substance. OR The process in which hydrogen is added to a substance.
For Example:-
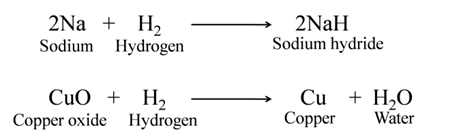
Redox Reactions
Those reactions in which oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously are called redox reactions.
(i):- In this reaction, the copper (II) oxide is losing oxygen and is being reduced. The hydrogen is gaining oxygen and is being oxidized.
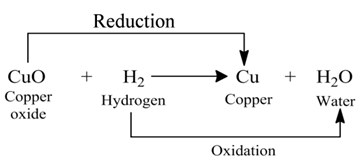
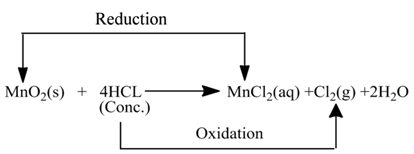
(ii):- In this reaction HCl is oxidised toCl2, whereas MnO2 is reduced to MnCl2.
Oxidising Agent
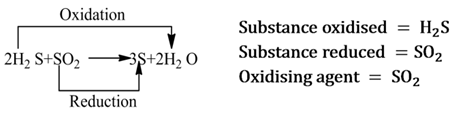
A substance which helps in the oxidation of another substance, is called oxidising agent. It either gives oxygen, removes hydrogen or accepts electrons from the substance to be oxidized.
Note:- It is always to be remembered that oxidising agent itself gets reduced.
Reducing Agent
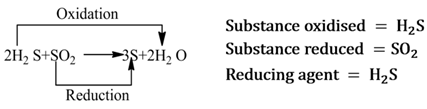
A substance that helps in the reduction of another substance, is called reducing agent. It either removes oxygen, gives hydrogen or donates electrons to the substance, that is reduced.
Note:- It is always to be remembered that reducing agent itself gets oxidised.

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
