- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Chapter:- 1
CHEMICAL REACTIONS & EQUATIONS
Introduction
We come across a variety of changes around us which may be both physical and chemical. A physical change can be easily reversed, but it is not easy to reverse a chemical change. Some common examples of physical change are evaporation, melting of wax, freezing of water, etc and common examples of chemical change are changing of milk to curd, rusting of iron, digestion of food, etc.
All chemical changes are accompanied by chemical reactions and these are represented with the help of chemical equations. In this chapter, we will study about the various types of chemical reactions and the chemical equations which represent chemical changes.
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a change in which one or more substance(s) or reactant(s) react to form new substance(s) with entirely different properties. Breaking of the old bonds and formation of the new bonds is responsible for the occurrence of a chemical reaction.
Some examples where chemical reactions take place are
(i):- Digestion of food,
(ii):- Rusting of iron,
(iii):- Photosynthesis,
(iv):- Respiration,
(v):- Burning of fuels
A chemical reaction represents the change of the species taking part in the reaction into new species. The reacting species are known as reactants (The substances that undergo chemical change in the chemical reaction, are the reactants) and the new species formed as a result of the reaction are called products (The new substances formed during reaction, are the products).
A chemical reaction can be identified by either of the following observations:-
(i):- Change in state,
(ii):- Change in colour,
(iii):- Evolution of gas↑,
(iv):- Change in temperature,
(v):- Formation of a precipitate↓.
There are some chemical reactions which can show more than one characteristics.
For example, reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide solution shows two characteristics; formation of a precipitate of leads iodide and change in colour (from colourless to yellow).
Similarly, reaction between zinc granules and dilute hydrochloric acid shows two characteristics; evolution of a hydrogen gas and change in temperature (rise in temperature).
Chemical Equation
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction. Symbols and formulae of the reactants and products are used for the same.
For example, the reaction of burning of methane gas can be represented by the following equation
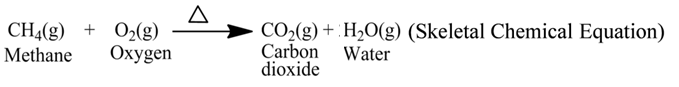
![]()
Making a Chemical Equation More Informative
A chemical equation gives idea about the various substances taking part in a reaction and also about their atoms or molecules included in the reaction. It also tells about the nature of reaction whether it is reversible or not. But following facts remain unexplained with the help of a chemical equation
(i):- Physical states of substances,
(ii):- Reaction conditions,
(iii):- Evolution / absorption of energy
(iv):- Kinetics of the reactions.
Balanced Chemical Equation
A balanced chemical equation is that in which the total number of atoms of each element are equal on both sides of the equation.
Need to Balance a Chemical Equation
According to the law of conservation of mass, 'mass can neither be created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction.'
It means that the total mass of every element present in the products (RHS) of a chemical reaction has to be equal to their total mass present in the reactants (LHS). In other words, the number of atoms of each element remains the same, before and after a chemical reaction. In order to satisfy the law of conservation of mass, a chemical equation should be balanced.
Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen (word equation)

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
