- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Effects of Oxidation Reaction in Everyday Life
Corrosion
The phenomenon due to which metals are slowly eaten away by the reaction of air, water and chemicals present in atmosphere, is called corrosion. Some examples of corrosion are:-
(i) Rusting of Iron Corrosion of iron is called rusting. Iron forms hydrated iron oxide (rust) when kept open in moist air.

(ii) Formation of a Green Layer Over Copper New copper (brown) vessel forms a green layer of basic copper carbonate after some time due to the reaction of air and moisture.
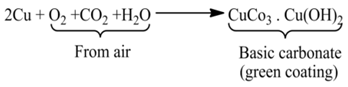
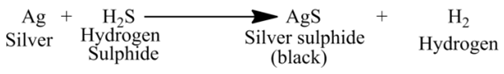
(iii) Tarnishing of Silver although silver is considered a noble metal, yet it reacts with some sulphur compounds as hydrogen sulphide to form black layer of silver sulphide.
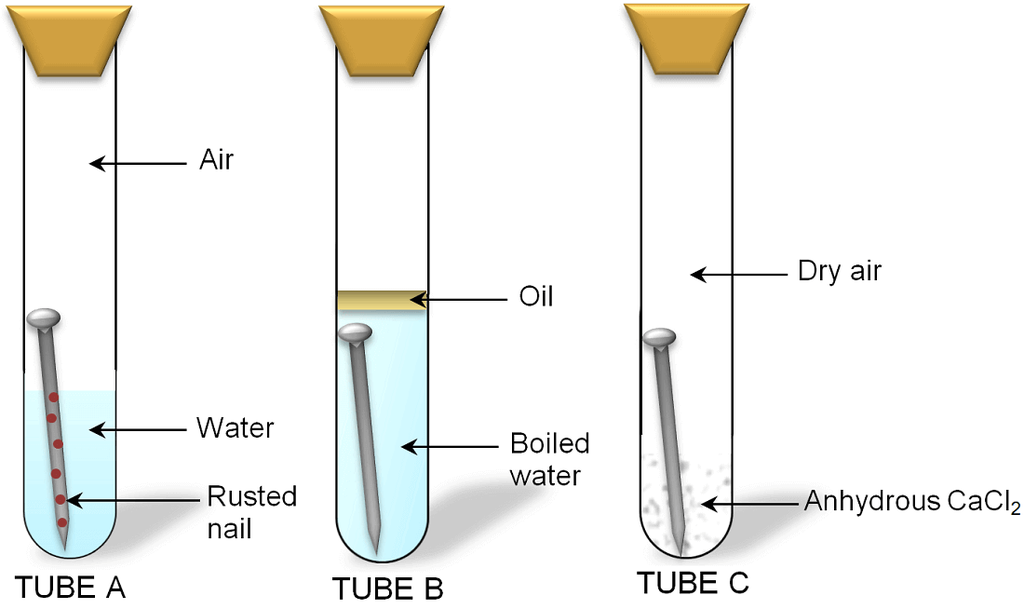
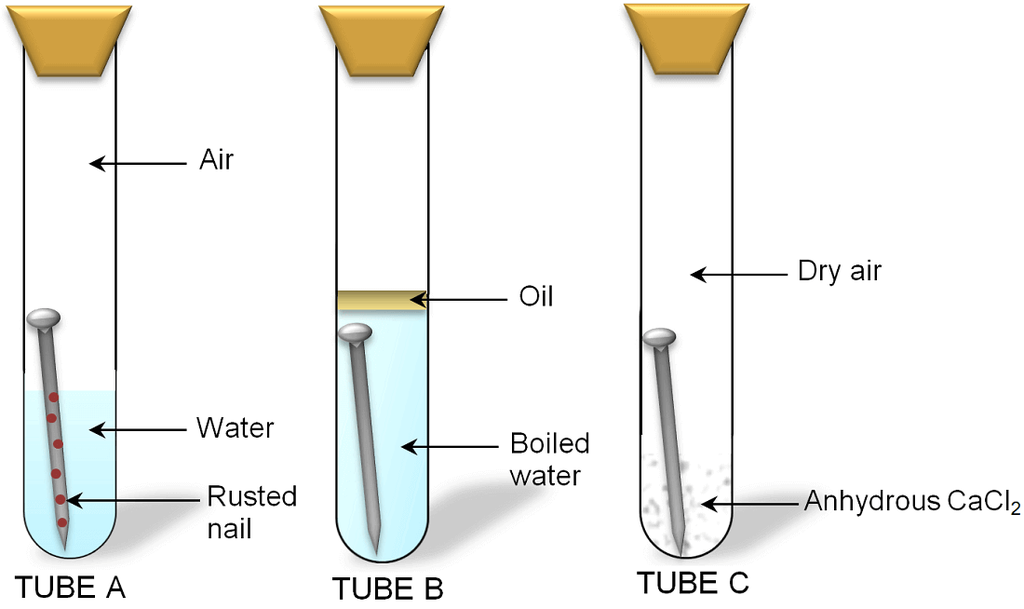
Conditions Necessary For Corrosion
The following two conditions are necessary for corrosion
- Presence of Air
- Presence of Water
Effects of Corrosion
Corrosion causes to damage to car bodies, bridges, iron railing, ships and all objects made of metals, specially those which are made of iron. Corrosion is a wasteful process in most of cases. Every year, a of tones of various metals especially iron get wasted in the country. Hence, it is quite necessary to prevent corrosion.
Exception In case of aluminium, corrosion is not proved to be wasteful. As aluminium is quite reactive metal, the top layer of it forms a thin layer of aluminium oxide which further prevents the corrosion of the metal. It is known as auto-protection mechanism.
Methods to Prevent Corrosion Iron
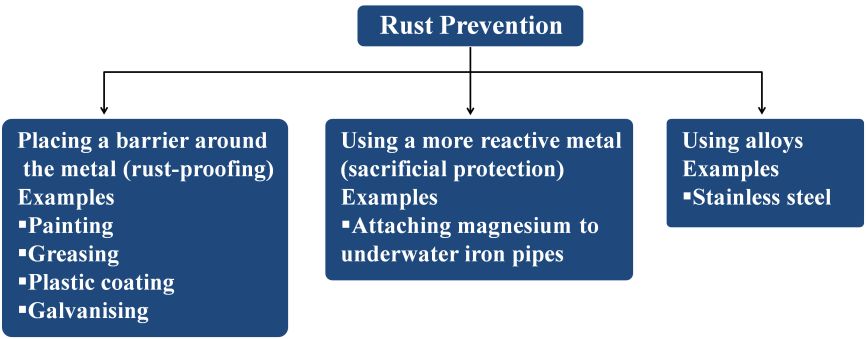
There are three genral methods to prevent corrosion of iron as shown below
Rancitidy
It is the process of slow oxidation of oil and fat present in the food materials resulting in the production of foul odour and taste in them. Conditions under which rancidity take places is when cooked food items are placed for a long time, they become rancid and unsuitable for consumption.
Methods to Prevent Rancidity
The methods to prevent rancidity are:-
- Packing of food materials in air tight containers.
- Refrigeration of cooked food at low temperatures.
- Packing of food items like potato wafers, etc in packets containing nitrogen gas instead of air.
- Avoiding the food materials and cooked food keeping in direct sunlight.
- By adding antioxidants. e.g., BHA (Butylated Hydroxy Anisole) and BHT (Butylated Hydroxy Toluene).

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
