- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Salts
Salts are produced by the neutralisation reaction between acid and base.
![]()

Here X is non – metal and M is metal i.e., we can say when metal ion takes place of H - ions, then salt is formed.
Family of Salts
Salts having the same positive or negative radicals are said to belong to a family. For Example:-
NaCl and Na2SO4 belong to the family of sodium salts. Similarly, NaCl and KCl belong to the family of chloride salts.
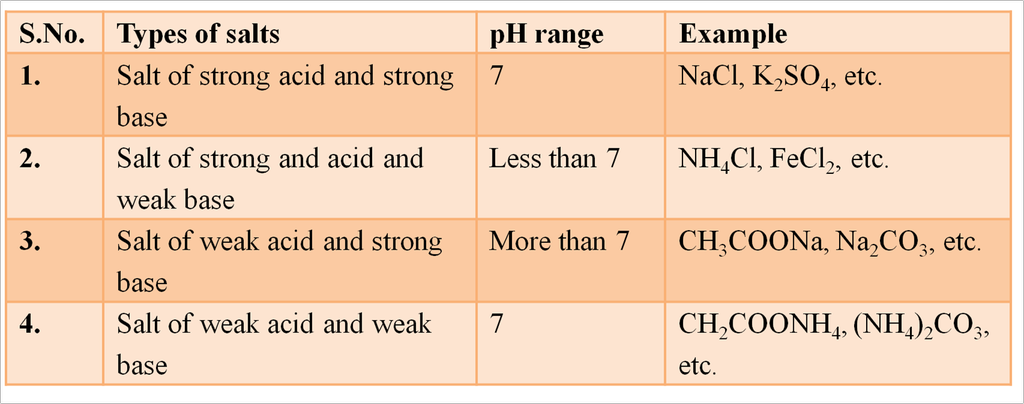
pH of Salts
- Salts of strong acid and a strong base are neutral with pH value of 7.
- Salts of a strong acid and weak base are acidic with pH value less than 7.
- Salts of strong base and weak acid are basic in nature with pH value more than7.
Common Salt: Sodium Chloride
Common salt is formed by the combination of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solution. It is the salt that we use in food.
It is obtained on large scale from sea water by separating other salts from it. It may also be obtained from rock salt.
Uses of Sodium Chloride
- Common salt, apart from cooking food, is used as a preservative.
- It is also used for manufacture of Na metal and Cl2 (g) by electrolysis in molten state.
- The common salt is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, bleaching power and many more.
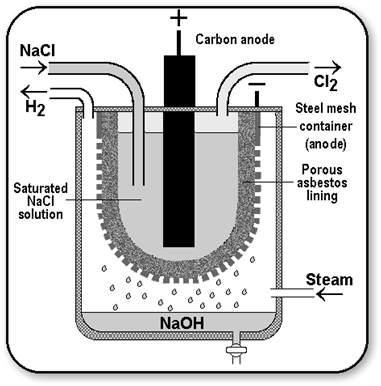
Caustic Soda (Sodium Hydroxide [NaOH])
When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (called brine), it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. The process is called the chlor-alkali process because of the products formed chlor for chlorine and alkali for sodium hydroxide.
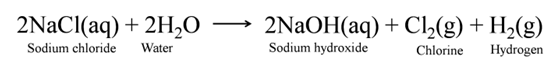
Uses of Hydrogen
- Hydrogen is used in the hydrogen of oils to obtain solid fats. (Vegetable ghee).
- It is used to make ammonia for fertilizers, methanol and production of hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid is used in the preparation of ammonium chlorides, in medicines and cosmetics.
- Liquid hydrogen is used as a fuel for rockets.
Uses of Chlorine
- Chlorine is used to sterlise drinking water supply and the water in swimming pools.
- It is used in the production of bleaching powder, Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC) pesticides, chloroform, paints and dyestuff.
Uses of Caustic Soda
- It is used for making soaps and detergents.
- It is used in the production of bleaching powder, Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC) pesticides, chloroform, paints and dyestuff.
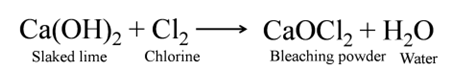
Bleaching Powder
(Calcium Oxychloride [CaOCl2])
It is produced by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime.
On standing for a longer time, it undergoes auto-oxidation due to which bleaching action decreases. Hypo or sodium bisulphite is used as antichlor during bleaching action.
Uses of Bleaching Powder
- It is used for bleaching purposes in textile and paper industry and in laundry.
- It is also used as a disinfectant for water.
- It is used as an oxidizing agent too.
- It is used in the manufacture of chloroform.
Baking Soda
(Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate or Sodium Bicarbonate [NaHCO3])
The soda commonly used in the kitchen for making tasty crispy pakoras is baking soda. It is the major constituent of baking powder. Sometimes it is added for faster cooking. Chemically it is sodium hydrogen carbonate. It is produced using sodium chloride as one of the raw materials.
Manufacture of baking soda is shown in reaction below
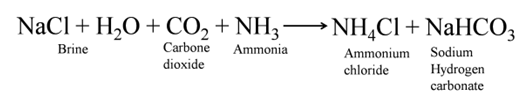
Uses of Baking Soda
For making baking powder, which is a mixture of baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) and a mild edible acid such as tartaric acid. When baking powder is heated or mixed in water, the following reaction takes place
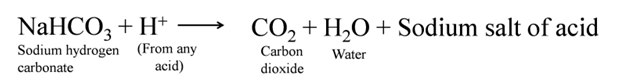
Carbon dioxide produced during the reaction causes bread or cake to rise making them soft and spongy.
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is also an ingredient in antacids. Being alkaline, it neutralises excess acid in the stomach and provides relief.

It is also used in soda-acid fire extinguishers
Washing Soda
(Sodium Carbonate [Na2CO3.10H2O])
Sodium Carbonate can be obtained by heating baking soda; recrystallisation of sodium carbonate gives washing soda. It is also a basic salt.
![]()
Uses of Washing Soda
- It is used in glass, soap and paper industry.
- It is used for the manufacture of sodium compounds like borax.
- It also removes permanent hardness of water.
- It is used as cleansing agent (detergent) in houses and laundries.
Plaster of Paris
(Calcium Sulphate Hemihydrate [CaSO4.1/2H2O])
It is obtained by heating gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) at 373 K. At this temperature, gypsum loses water molecules and forms plaster of paris.
![]()
When gypsum is heated above 400K, dead burnt plaster (anhydrous CaSO4) is obtained which does not have the property of hardening.
Uses of Plaster Paris
- It is used by doctors for joining the fractured bones in right position i.e., for making plaster to support fractured bones.
- POP made by it is also used for making decorative pieces and for making designs on ceilings.
Water of Crystallization
Crystals of some compounds seem to be dry (or anhydrous), but actually contain some water molecules attached to them. This water is called water of crystallization and such salts are called hydrated salts. Water of crystallization is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt. For Example:-
- Hydrated copper sulphate (blue vitriol) CaSO4.5H2O
- Hydrated ferrous sulphate (green vitriol) FeSO4.7H2O
- Washing soda crystals Na2CO3.10H2O
This water is removed by heating the crystal of the hydrated salt.

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
