- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Occurrence and Extraction of Metals
The earth's crust is the major source of metals. Sea water is also a source for some metals. It contains soluble salts like sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, etc.
Minerals The naturally occurring elements or compounds of metal present in the earth’s crust are called minerals.
Ores Those minerals from which a particular metal be extracted profitably are called ores. Each ore is a mineral but each mineral is not an ore.
Gangue the undesirable impurities like soil, sand, etc found in ore are called gangue.
Enrichment of Ores Removal of unwanted material (gangue)
Extraction of Metals
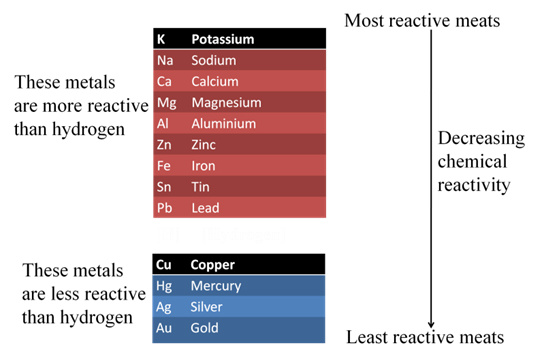
Attainment of pure metal from its compound is called extraction of metals. Some metals are found in earth’s crust in Free State while some are found in the form of their compounds. The metals present at the bottom of the reactivity series are least reactive so they are found in Free State. e.g., Gold, Silver, Platinum, Copper.
The metals at the top of the reactivity series are highly reactive so they are found as free elements. The metals in the middle of the reactivity series (zinc, iron, lead) are moderately reactive, found as oxides, sulphides or carbonates.Copper and silver are found in the combined state in their sulphide or oxide ores.
Extracting Metals Low in the Activity Series (Low in activity series)
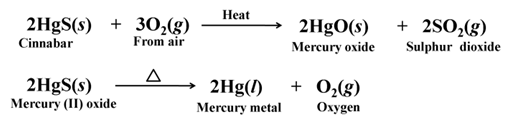
Cinnabar (HgS) is an ore of mercury, when heated in air, it first changes into its oxide and then into mercury metal.
For example,
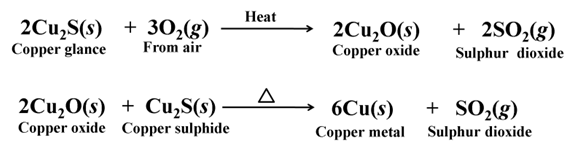
Copper glance (Cu2S) when heated in air, partially oxidised and the oxidised product reacts with the remaining copper glance to give copper metal.
For example,
Extraction of Metals in the Middle of the Activity Series
The metals in the middle of the activity series are usually present as sulphides or carbonates in nature. Sulphides are converted into oxides by roasting and carbonates are converted into oxides by calcination
Roasting

Calcination

Reducation
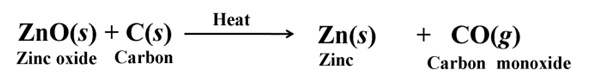
Thermit Reaction
The reaction of iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3) with aluminium is used to join railway tracks or cracked machine parts of heavy machines.
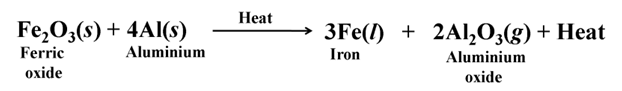
This reaction is known as thermit reaction its highly exothermic.
Extraction of Metals Towards the Top in Activity Series
These metallic compounds cannot be reduced by carbon or any other reducing agent due to their high affinity with oxygen. Therefore, electrolytic reduction is employed for these metals e.g., Na, Mg, Ca, etc.
Electrolytic reduction the salts of these metals as chlorides in molten form are electrolysed. Metal is deposited at the cathode and chlorine is liberated at the anode.
The reactions are (At cathode)
![]()
The reactions are (At anode)
![]()
Refining of Metals
It is the process of purification of the metal obtained after reduction. Various methods for refining are employed, but the most common one is the electrolytic refining.
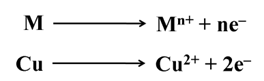
Electrolytic Refining
Many metals like Cu, Sn, Ni, Ag, Au, etc are refined electrolytically.
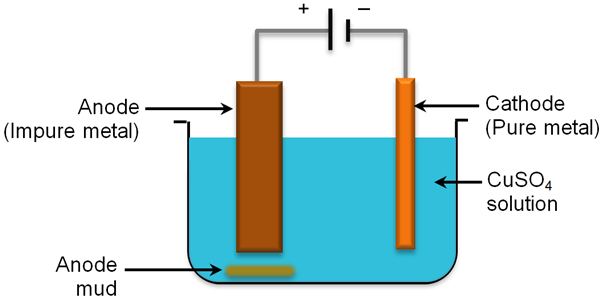
The reactions are (At cathode)

The reactions are (At anode)
Corrosion
It is the process of slow eating away of metals by the reaction of atmospheric air and moisture.For example, rusting of iron, tarnishing of silver, formation of green coating over copper etc.

Prevention of Corrosion
Rusting of iron is prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, galvanising, chrome plating, anodising and by making alloys.
Galvanisation
The process of coating iron and steel objects with a thin layer of zinc is called galvanisation. It is done by dipping the object in molten zinc.

Anodising
It is the process of forming a thick oxide layer on the surface of metal. At ordinary temperature the surfaces of metals like zinc, aluminium, etc are covered with a thin layer of oxide. This oxide layer is protective and prevents the metal from further oxidation. This layer can be made more thick by anodising.
In this process. Clean metal is taken as anode and dilute H2SO4 as electrolyte. When electric current is passed. O2 gas is liberated which reacts with metal to form a layer of oxide.
Alloy
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal. It is prepared by mixing the metals in molten state and then cooling the mixture. The electrical conductivity and melting point of an alloy is less than that of pure metals.
For example,
- Amalgam If an alloy contains mercury as one of its components, it is called amalgam.
- Alloying of Gold Pure gold is very soft. It is called 24 carat gold. To increase the strength and hardness of gold and to make it suitable for making jewellery, alloy of gold is made with either silver or copper.
- Alloying of Iron Pure iron is very soft and stretches easily when hot. It is mixed with a small amount of carbon (about 0.05%) and it becomes strong.
Alloying
It is the method of improving the properties of a metal by mixing two or more metals

Purpose of Making Alloy
- Alloy do not corrode or corrode to very less extent.
- Alloy is much harder and stronger than the pure metal.
- Alloy has less conductance than pure metal.
- Some alloys have, low melting point and hence used for soldering of metals.
Alloys, their Composition and Uses
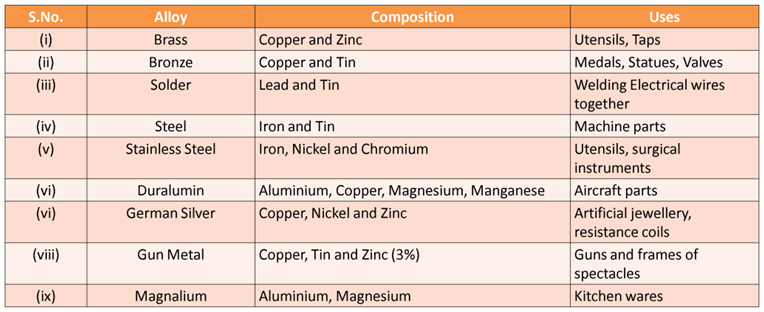
Constituents and Uses of Alloys
Brass (copper and zinc) it is used in making utensils and taps.
Bronze (copper and tin) it is used in making medals, statues, etc.
Solder (lead and tin) it is used to weld electrical wires.

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
