- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Non-Metals
Elements that are electronegative in nature are called non-metals. It means non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions.
For Example, iodine, sulphur, hydrogen, etc.

Physical Properties of Non-Metals
- Brittleness Non-metals are neither malleable nor ductile but they are brittle in nature.
- Physical State Most of the non-metals are soft (if solid). Only diamond, a form of carbon is the hardest known substance. Other non-metals are gases except bromine which is a liquid.
- Metallic Lustre the non-metals do not have lustre. However, diamond, iodine and graphite, have lustre.
- Electrical and Thermal Conductivity Non-metals are generally poor conductors of heat and electricity except graphite.
- Melting and Boiling Points Generally, non-metals have low melting and boiling points. But non-metals that are solids have comparatively higher boiling points. (e.g., B. Si, C, etc.)
Chemical Properties of Non-Metals
- Reaction with Oxygen Non-metals react with oxygen to form oxides. These oxides are generally acidic. Only some of the non-metallic oxides are neutral.
Acidic oxides are CO2, SO2, P2O5, etc. For Example:-
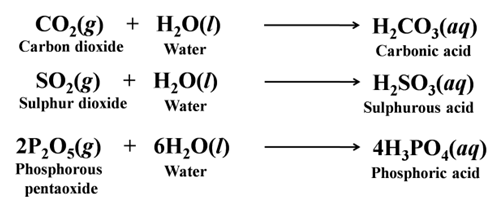
Neutral oxides are CO, H2O, N2O, etc.
Reaction with Water Non-metals do not react with water or steam to evolve hydrogen gas. This is because non-metals cannot give electrons to hydrogen in water therefore, hydrogen gas cannot be released.
Reaction with Acids Non-metals do not react with acids to release hydrogen gas. Reason is that non-metals cannot loose electrons and give it to hydrogen ions of acids so, that the gas is released.
Displacement Reaction Non-metals also show displacement reaction like metals. For Example:-
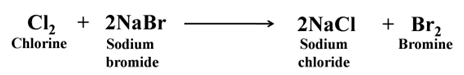
Formation of Covalent Compounds Non-metals form covalent compounds with other non-metals like hydrides, chlorides, etc.
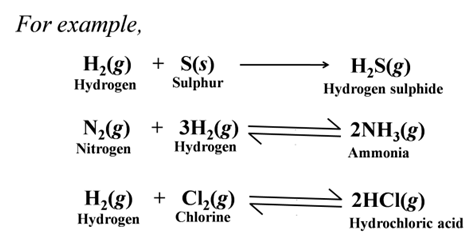
Exceptions Among Metals and Non-metals
- All metals (except mercury, a liquid metal) exist in solid state at normal room temperature.
- Gallium and cesium, (metals) have very low melting point. When kept on the palm, they start melting.
- Iodine, diamond and graphite are lustrous although they are non-metals.
- Diamond has a very high melting point and is very hard although it is a non-metal.
- Alkali metals have Low densities and low melting points. They are too soft to be cut with a knife.
- Graphite is a good conductor of electricity although it is non-metal.
Reaction of Metals and Non-Metals
Formation of Ionic Compounds
We know that noble gases are unreactive and the reason for their unreactive nature is the presence of 8 electrons in their outermost shell (octet) with an exception of helium (which has duplet i.e., two electrons in the outermost or the only shell).
The elements try to get 8 electrons in their outermost shell as it is the state of maximum stability or
minimum energy (by gaining or losing electrons).
To recall them, see the following table:-

Formation of Sodium Chloride
The two oppositely charged ions (sodium and chloride ions in the below case) bind together with the help of strong electrostatic forces of attraction which is termed as ionic bond or electrovalent bond and the compounds having it are called ionic or electrovalent compounds.
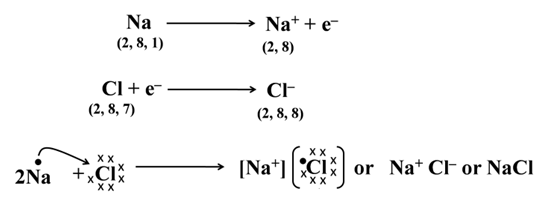
Thus, it is also clear that ionic compounds (like sodium chloride) do not exist as discrete molecules but indeed they are the aggregates of oppositely charged particles.
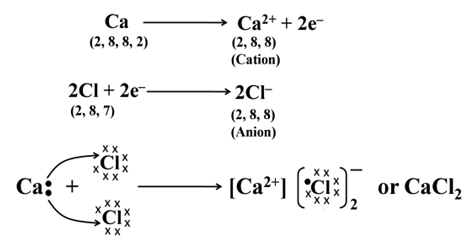
Formation of Calcium Chloride
Formation of ionic bond, can further be understood by taking an example of calcium chloride (where calcium is a metal and chlorine is a non-metal), in which calcium (Ca) with configuration K, L, M, N have a tendency to lose teo electrons and chlorine with configuration K, L, M have a tendency to gain one electron.
Thus, the two electrons lost by Ca are achieved by two Cl atoms. The Ca atom acquires two positive charges (Ca2+) and each Cl atom acquires a negative charge (Cl–). These oppositely charged ions are held together by electrostatic forces i.e., by ionic bond.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
- Physical Nature Ionic compounds are crystalline solids.
- Melting and Boiling Points These compounds have high melting and boiling points as large amount of energy is required to break strong forces of attraction.
- Solubility These compounds are soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents like kerosene, benzene, ether, petrol, etc.
- Conduction of Electricity Ionic compounds are good conductors of electricity, but they conduct electricity either in molten state or in their aqueous solution.

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
