- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Change of State of Matter

→ The phenomenon of change from one state of matter to another, and then back to the original state is called the interconversion of states of matter.
→ Matter Can Change its State. Water can exist in three states of matter:
• Solid as ice
• Liquid as water
• Gas as water vapour
Effect of Temperature
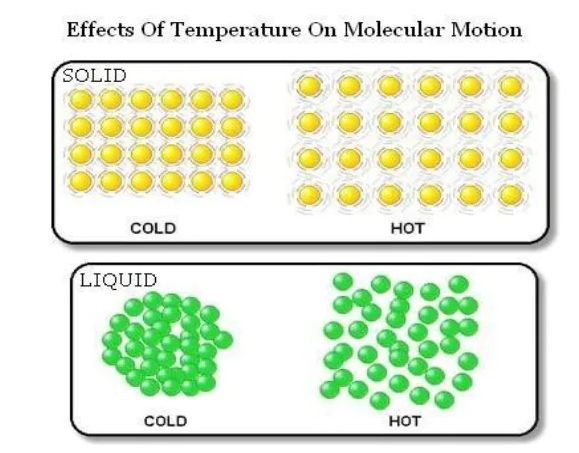
→ On increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy of the particles increases which overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles thereby solid melts and is converted into liquid.
→ The temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its
melting point.
The melting point of ice is 273.16 K.
The process of melting, that is, change of solid state into liquid state is also known as fusion.
STATES OF MATTER
Matter around us exists in three different states– solid, liquid and gas, dependent on the characteristics of the particles of matter.
1. SOLID STATE – Solids have a definite shape, distinct boundaries and fixed volumes, that is, have negligible compressibility.
- Solids may break under force but it is difficult to change their shape, so they are rigid.
Examples, a pen, a book, a needle and a piece of wooden stick, a granule of sugar.
- There are objects that are solid in state but seems do not follow the above rule but actually they do
- A rubber band changes shape under force and regains the same shape when the force is removed. If excessive force is applied, it breaks.
- A sponge has minute holes, in which air is trapped, when we press it, the air is expelled out and we are able to compress it.
2. LIQUID STATE – liquids have no fixed shape but have a fixed volume.
- They take up the shape of the container in which they are kept.
- Liquids flow and change shape, so they are not rigid but can be called fluid.
- Solids, liquids and gases can diffuse into liquids (e.g. oxygen and carbon dioxide dissolves in water, which helps the survival of aquatic animals and plants)
- The rate of diffusion of liquids is higher than that of solids.
- This is because in the liquid state, particles move freely and have greater space between each other as compared to particles in the solid state.
3. GASEOUS STATE – gases are highly compressible as compared to solids and liquids
- Due to its high compressibility, large volumes of a gas can be compressed into a small cylinder and transported easily
- Examples: liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinder, Compressed natural gas (CNG) fuel tanks
- Due to high speed of particles and large space between them, gases show the property of diffusing very fast into other gases.
- Rate of diffusion is much faster than solids and liquids
- In the gaseous state, the particles move about randomly at high speed.
- Due to this random movement, they exert pressure which is the force exerted by each gas particles per unit area on the walls of the container.
- Books Name
- Yash Tyagi Coaching Science Book
- Publication
- ACERISE INDIA
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Plasma and Bose Einstein condensate state
Two states of matter are plasma and BEC, let’s understand them:
Plasma: It consists of ionized gas, such that its particles are super energetic and super excited. In devices such as tube lights and CFL, the gases get ionized on the passage of current and glow with the color depending upon the nature of the gas. For Example: Neon gas emits red glow, argon emits green – yellow, etc.
Bose Einstein Condensate State: It is the fifth state of matter and it is obtained on super cooling the gas at almost absolute Kelvin zero temperature.
Temperature and temperature scales
You often fall sick, sometimes due to high fever. Then the first step that has to be taken is to measure temperature by using thermometer which records the temperature of the body in a given scale.
Temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness of body or We can also say that temperature measures the extent of motion of atoms. It is measured with the help of thermometer.

There are different scales on which temperature can be recorded:
Commonly used scales are Celsius and Kelvin
Celsius Scale:
- It is written as oC
- On it the lower fixed point (at which ice melts) is O oC
- The upper fixed point on it (at which water boils) is 100 oC
Kelvin Scale:
- The lower fixed point is- 273K
- The upper fixed point is 373 K
- Kelvin scale is called as absolute zero scale of temperature because on it the lowest possible temperature is zero
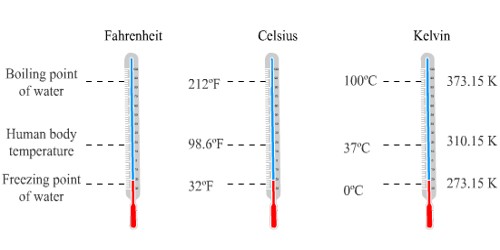
Relation between K & oC :
These scales are interconvertable by using the well defined relations like 0 oC = 273 K
So, K = oC + 273 or oC = K -273
For example, if we need to convert 25 oC to K then, we need to add 273 to it and it comes out to be 298K.

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
