- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Characteristics of Particles of Matter
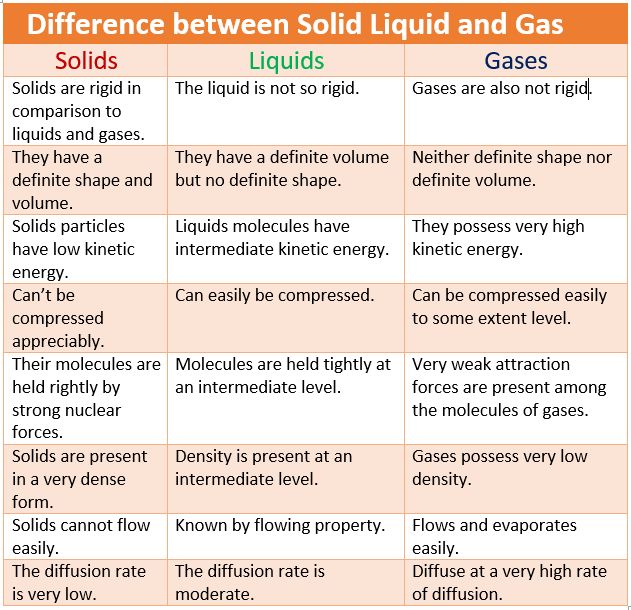
• Particles of matter have space between them
→ Gas can be compressed a lot because of the space between their particles.
Activity:- take some water in a beaker and note its level. Dissolve some salt or sugar in it with the help of a glass rod. The salt dissolves in the water but the level of water dose not change. This is because the particles of salt get the space between the particles of water.
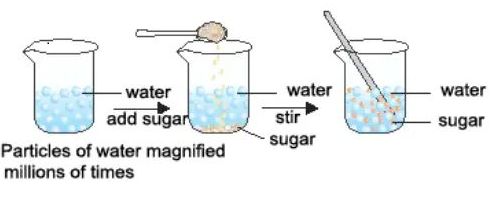
→ Additionally you would notice that there is no rise of water level takes place when one or two teaspoon of sugar/salt is added into a glass of water, this is because sugar/salt particles get adjusted in the space between the particles of water and no rise in the water level comes in result.
• Particles of matter attract each other because of force of attraction.
Activity:- Take an iron nail, a piece of chalk and rubber band. Try breaking them hummering, cutting or stretching. It is more easier to break the chalk, less easier to break the rubber band and difficult to break the iron nail. this is because the particles in the iron nail are held together with greater force than in the rubber band or challk.
→ Force of attraction between particles of matter keeps the particles bonded together. Therefore attraction between particles of solid is greatest, between particles of liquid is moderate and between particles of gas is lowest.
→ Because of the lowest force of attraction between the particles of gas we can move our hand through
air easily. To move our hand in liquid, such as water, we have to apply some force, but a solid such as wood, we cannot move our hand.
→This is because the force of attraction between particles of gas is almost negligible, in liquid the forces of attraction is moderate but it is greatest in solid.
→ The force of attraction between particles of solid, liquid and gas can be arranged in decreases in order as follows:
Solid > Liquid > Gas
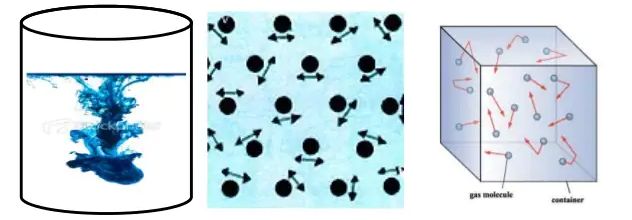
• Particles of matter are continuously moving –
Activity :- Take some water in a beaker and put a drop of blue or red ink slowly along the sides of the beaker. Leave it undisturbed for a few hours. The ink spreads evenly throughout the water due to the movement of the particles of water and ink.
The intermixing of two or more different types of matter on their own is called diffusion.
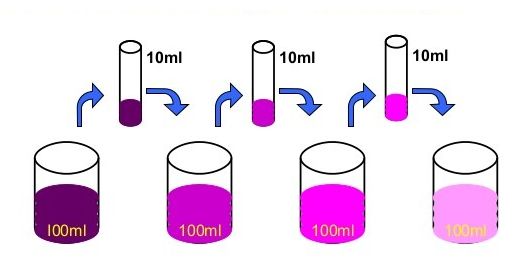
• Matter is made up of small particles –
Activity :- Dissolve 2 —3 crystals of potassium permanganate in I OOml of water in a beaker. Take lOmI of this solution and dissolve in lOOmI of water. Take lOmI of this solution and dissolve In lOOmI of water. Repeat this process 5— 6 times. This shows that a few crystals of potassium permanganate can colour a large volume of water because there are millions of tiny particles in each crystal
Classification of states of matter
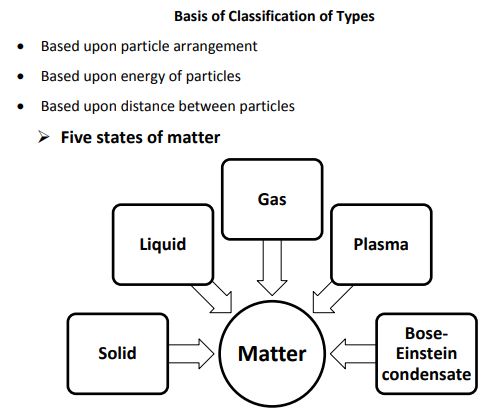
States of Matter
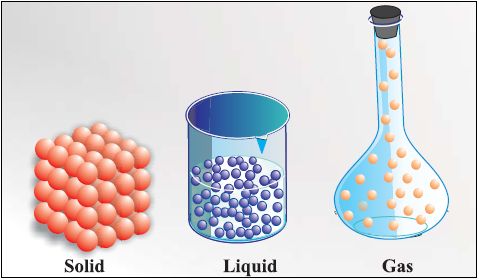
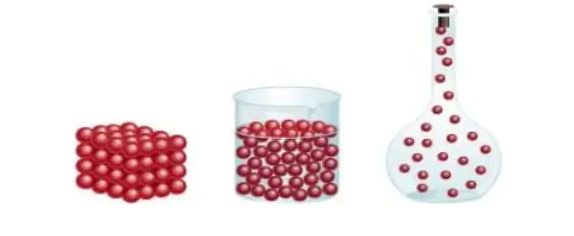
• Solid State
→ The space between the particles is very less.
→ The force of attraction between the particles is strong. Thus, particles in a solid are closely packed.
→ Solids maintain their shape even when they are subjected to external force i.e. they are rigid
→ Solids cannot be compressed.
→ The kinetic energy of the particles is very less and so solids have an orderly arrangement of particles. Therefore, solids have a fixed shape and volume.
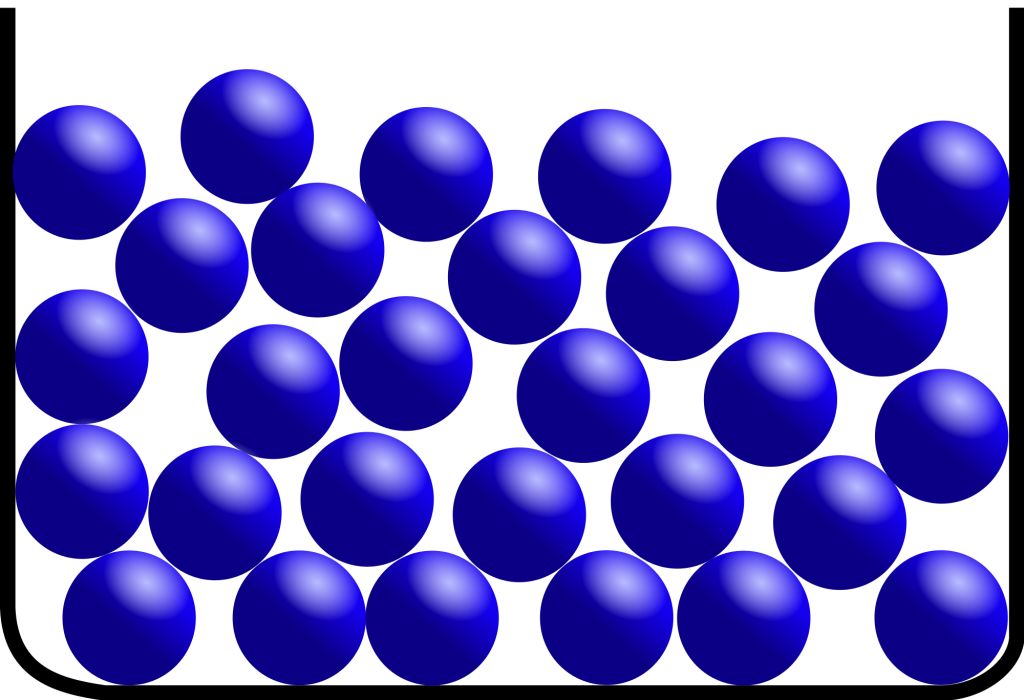
• Liquid State
→ The space between the particles is slightly more as compared to solids, but still very less as compared to gases. The particles of a liquid can slip and slide over each other.
→ The force of attraction between the particles is strong enough to hold the particles together not strong enough to hold the particles in a fixed position.
→ Liquids do not have a fixed shape but have a fixed volume. Liquids take up the shape of the container in which they are poured.
→ The kinetic energy of the particles is more than that of solids. Thus, liquids have a disorderly arrangement of particles compared solids.
→ Liquids cannot be compressed much. The compressibility of liquids is almost negligible.
• Gaseous State
→ The particles are much farther apart from one another as compared to solids and liquids.They have a very disorderly arrangement of particles compared to the solids and liquids.
→ The force of attraction between the particles is negligible, hence particles of a gas move free in all the directions.Gases thus can mix or diffuse into other gases.
→ The particles of a gas have maximum kinetic energy. They move with high speed in all directions and can exert pressure on the walls of its container.
→ Gases neither have a definite shape nor a definite volume.They fill up the container completely
→ Gases can be compressed easily. Example: the LPG cylinders used at home and the CNG cylinder used in vehicles.
CHARACTERISTICS OF PARTICLES OF MATTER
1. Particles of matter have space between them
2.Particles of matter are co ntinuously moving –
- They possess kinetic energy.
- Increase in temperature also increases the kinetic energy of the particles
- Thus, Particles of matter intermix on their own with each other.
- They do so by getting into the spaces between the particles.
- This intermixing of particles of two different types of matter on their own is called diffusion
- On heating, diffusion becomes faster.
3. Particles of matter attract each other.
- The strength of this force of attraction varies from one kind of matter to another.
- Books Name
- Yash Tyagi Coaching Science Book
- Publication
- ACERISE INDIA
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Molecular Theory of Matter
Theory of molecular structure of matter
According to this theory,
- Matter is made up of small particles called molecules.
- They are in a state of continuous motion. Due to this, we can say that they possess K.E.
- K.E. Increases with ↑ se in temperature.
- K.E. Is maximum in gases and least in solids.
- The space between molecules is called intermolecular space which is found to be least in solids and maximum in gases.
- There is a force that exists between particles of matter and is called intermolecular force
- Intermolecular force ↓ ses with increase in Intermolecular space
Terminology involved
Before we start with more properties of matter let us know some terms which will be used in this chapter.
- Matter: Anything that occupies space is matter.
- Material: The term is used to describe a particular kind of matter.
Materials are of two Types:
- Homogenous
- Heterogeneous

Homogeneous Materials: Are those that have the same composition and same properties throughout the sample. For example, if you take water in a glass and add salt to it and stir it. It will result in formation of a mixture that has same properties and uniform composition (that is no distinct layers are seen). They mix thoroughly. If you take sample from any part of that mixture, it will show similar properties.
Heterogeneous Materials: are those that have different composition and different properties in different parts of the sample. For example, if we take sand in water, then we will see that inspite of stirring, it does not dissolve in water. It will settle at the bottom of the container and few particles will be seen floating in the water. If you take a sample from any part of it, it will show different properties.
Molecule: Is a term used for particular type of matter that has independent existence in nature like oxygen molecule, carbon dioxide molecule, water molecule, etc.
Molecular structures and properties of solids, liquids and gases
Now let us do Physical Classification of Matter: this classification is done on the basis of physical properties of matter, that is the properties that can be seen or felt by touching, looking etc.
According to it, matter is divided into 3 types:
- Solids
- Liquids
- Gases
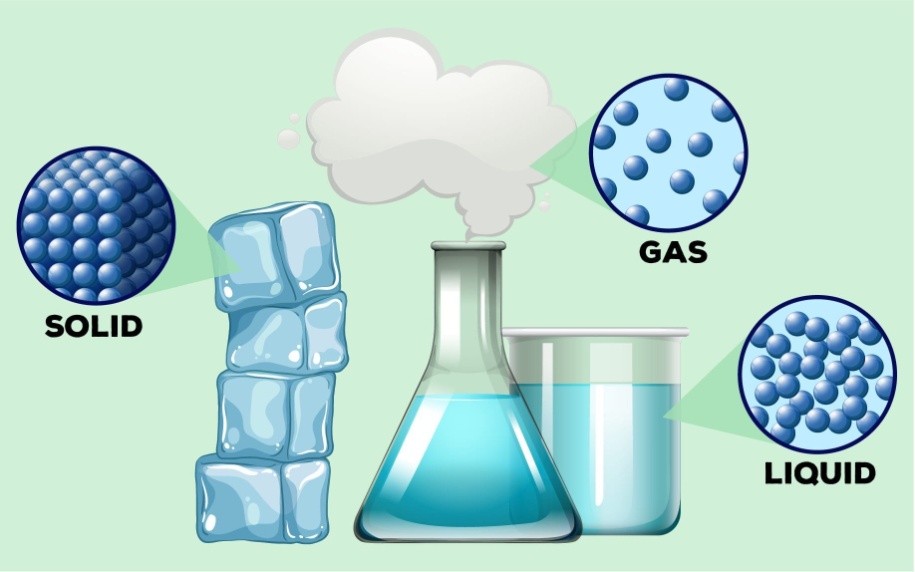
Solids
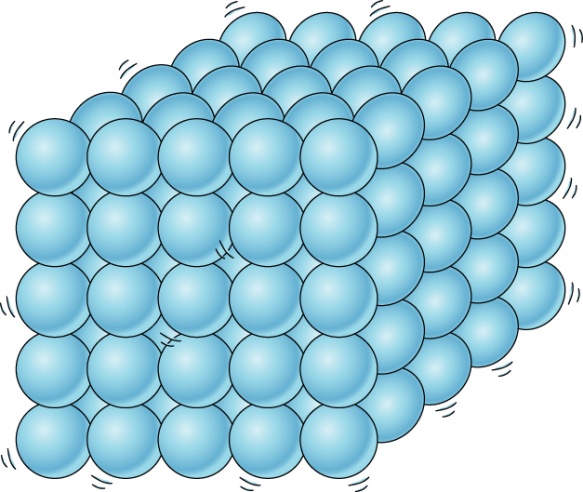
if you take any solid let’s say we consider wood, what properties can you find in it by looking at it.
- First property that we can make out is: That it has fixed shape and volume: we realize this because when wood is kept on the floor or any surface, it occupies definite space.
- Another property that we notice is: It is not compressible: if we it try to squeeze it or change its shape, we cannot do so. This is probably due to the reason that there is no space between solid particles and in order to compress it, there should be space between particles. This is because when we apply force, the particles fill those empty spaces and come closer.
- Another property: They don’t need container to hold them: we don’t have to put an almirah or any other solid in a container. it can be kept as such on the surface.
- They do not flow: This is because when wood is kept at a place, it remains at the same place. It doesn’t flow or move on its own.
- Their diffusion tendency is nil: it is seen that wood doesn’t move from one side of room to another side of room on its own as the particles do not have that much energy that they keep on moving.
Let us try to understand solids on the basis of theory of molecular structure:
Explanation of Solids on the basis of Molecular Structure
If we see any solid we observe that in solids, particles are tightly packed. They are very closely packed due to which there is hardly any space between particles or we can say that intermolecular spaces are very less and when particles are closer, that means the intermolecular forces of attraction are stronger. As a result, solids have fixed shape, volume and can’t be compressed.
Now do you understand that why wood or any other solid doesn’t flow or compress or diffuse and why they possess high density.
Liquids
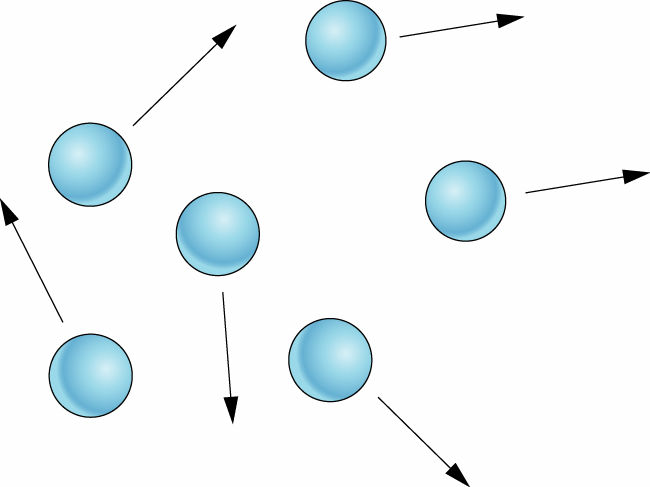
Let’s sum up the properties of gases in comparison to solids and liquids
- They have neither fixed shape nor fixed volume
- They are highly compressible
- They can flow, diffuse to great extent
- They have very very low density
- They can fill the entire space
Explanation of gases on the basis of molecular structure
In gases the particles are very far apart. Due to this, they have high kinetic energy and keep on moving randomly. As a result, the intermolecular spaces are very large and intermolecular forces are almost nil.

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
