- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Atoms
• Atoms are building blocks of all matter.
• According to modern atomic theory, an atom is the smallest particle of an element which taking
part in chemical reaction.
• Atoms are very small and which can’t be seen even through very powerful microscope.
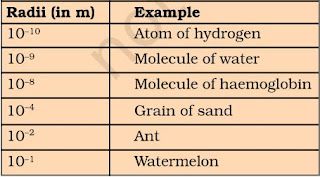
• Atomic radius is measured in nanometres. Nanometres = 10-9 m.
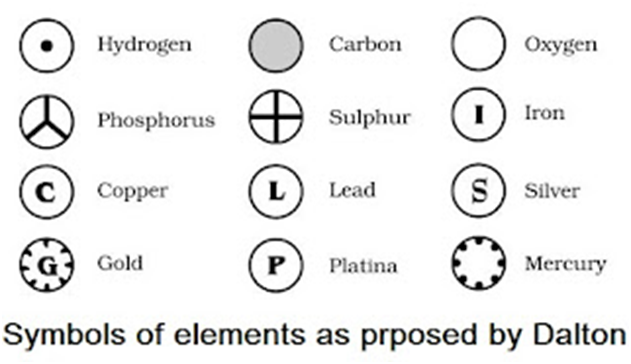
• Modern day symbols of Elements
→ Dalton was the first scientist to use the symbols for elements.
→ Berzilius suggested that the symbols of elements should be made from one or two letters of
name of the element.
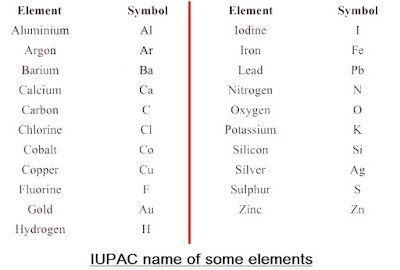
→ The name copper was taken from Cyprus, a place from where it was found for first time.
→ Now, IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) approves names of element
→ The first letter of a symbol is always written as a capital letter (uppercase) and the second letter.
as a small letter (lowercase). For example: hydrogen (H), aluminium (Al), cobalt (Co).
→ Some other symbols have been taken from the names of elements in Latin, German or Greek.For
example: Fe from its Latin name ferrum, sodium is Na from natrium, potassium is K from kalium.
• Atomic Mass
→ Dalton’s atomic theory proposed the idea of atomic mass which explained the law of constant
proportions so well.
→ The mass of an atom of an element is called its atomic mass.
→ In 1961, IUPAC have accepted ‘atomic mass unit’ (u) to express atomic and molecular mass of
elements and compounds.
→ The atomic mass unit is defined as the quantity of mass equal to 1/12 of mass of an atom of
carbon-12.
1 amu or u = 1/12 × Mass of an atom of C -12
1 u = 1.66 × 10-27 kg

• Atom existence
→ Atoms of most of the elements are very reactive and does not exist in free state.
→ Only the atoms of noble gases (such as He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe and Rn) are chemically unreactive and
can exist in the free state as single atom.
→ Atoms of all other elements combine together to form molecules or ions.
Atomicity
The number of atoms constituting a Molecule is known as its atomicity.
Compounds
A pure substance made up of two or more elements chemically combine together in a fixed ratio under fixed condition is called compound. Example: Calcium carbonate, Common salt, Sugar.
Properties of compound
1.Compounds can be separated into the constituent only by chemical methods.
2. Properties of compound differ from the properties of their constituents.
3. During the formation of a compound energy is absorbed or released.
4. The compound are homogeneous.
Valency
The combining capacity of an element is known as its valency. Valency is used to find out how the atom of an element will combine with the atom of another element to form a chemical compound.
(Every atom wants to become stable, to do so it may lose, gain or share electrons.)
• If an atom consists of 1, 2 or 3 electrons in its valence shell then its valency is 1, 2 or 3 respectively,
• If an atom consists of 5, 6 or 7 electrons in the outermost shell, then it will gain 3, 2 or 1 electron respectively and its valency will be 3, 2 or 1 respectively.
• If an atom has 4 electrons in the outermost shell than it will share this electron and hence its valency will be 4.
• If an atom has 8 electrons in the outermost electron and hence its valency will be 0.
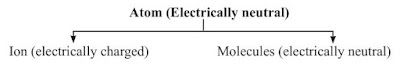
Ions
An ion is an electrically charged atom or group of atoms.
An ion is formed by the loss or gain of electrons by an atom, so it contains an unequal number of electrons and protons.
There are two types of ions:
Cation: A positively charged ion is known as cation.
For Ex: Na+, Mg2+
A cation is formed by the loss of one or more electrons by an atom.
Na – e– ——–>Na+
Z=11 Z=10
2,8,1 2,8
K, L, M K, L
Mg – e– ——–> Mg2+
Z=12 Z=10
2,8,2 2,8
K,L,M K,L
Anion: A negatively charged ion is known as anion.
For Ex: Cl–, O2-
An anion is formed by gain of one or more electron by an atom.
Cl + e– ——–> Cl–
Z=17 Z=18
2,8,7 2,8,8
K, L, M K, L, M
O + e– ———> 02-
Z=8 Z=10
2,6 2,8
K, L K, L
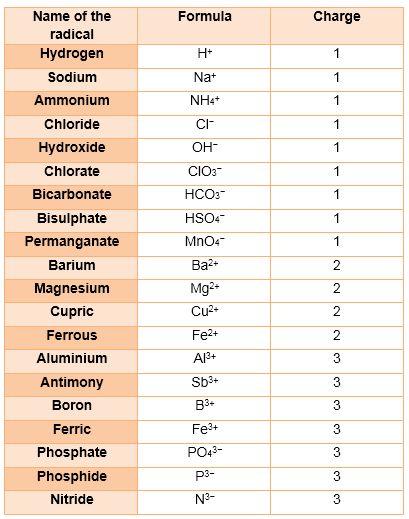
Radicals
An atom or group of atoms having a charge, i. e. either negative or positive, on it.
The radicals having positive charge are called cations.eg. Sodium ion.
The radicals having negative charge are called anions. eg. Chloride ion.
- Books Name
- Yash Tyagi Coaching Science Book
- Publication
- ACERISE INDIA
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Compound
Compound
When atoms of two or more different elements combine together in a definite proportion by mass and volume, it forms a compound. for example:- H2O is formed only when the ratio of H and O is 2:1 by volume and ratio by mass is 1:8.
Ion
We know that the atom is neutral, that is, the number of positive and negative charges in it is equal but if sometimes, an atom gains or loses negative or positive charge, it no longer remains neutral. It becomes an “ion”. Let us study about it.
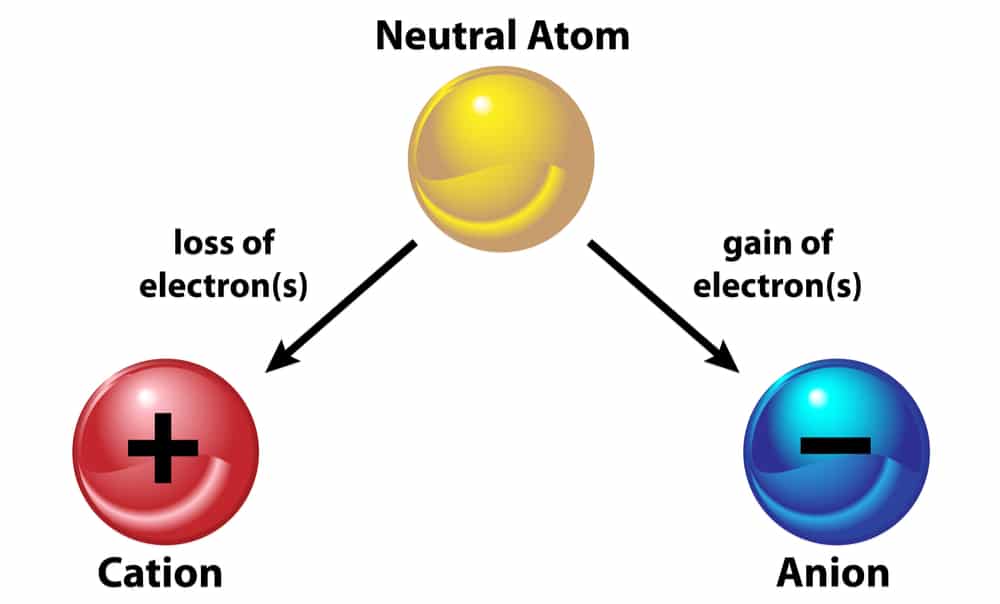
Ion:- The atom that bears a charge is called an “ion”. Ion is of two types:
1. Cation
2. Anion
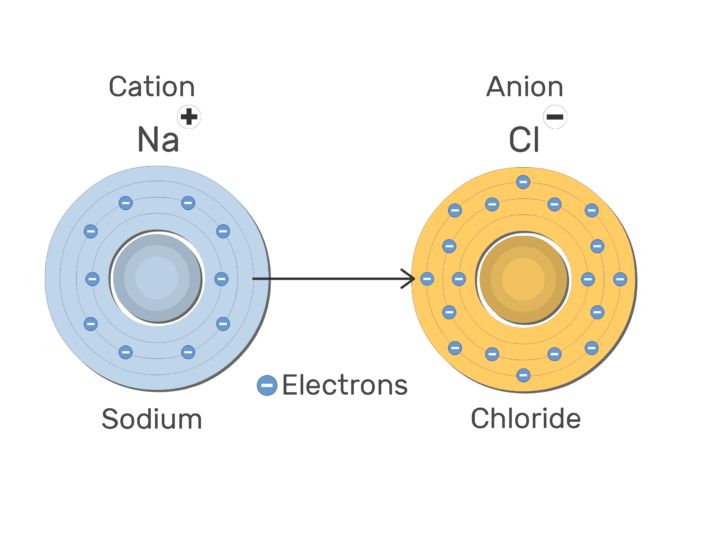
Cation: they are positively charged ions. They are formed when an atom loses a negative charge. Therefore, they always have negative charges less than normal atoms. Example: Na -1 negative charge Na+ (cation)
Anion: they are negatively charged ions and are formed when an atom gains a negative charge. Therefore, they have negative charges more than normal atoms. Example: S +2 negative charges S2- (anion)
>> 7.2. You might expect that by this time in the history of modern civilization science would have ..." style="width:389px; height:523px" data-cke-upload-id="3" data-widget="uploadimage">
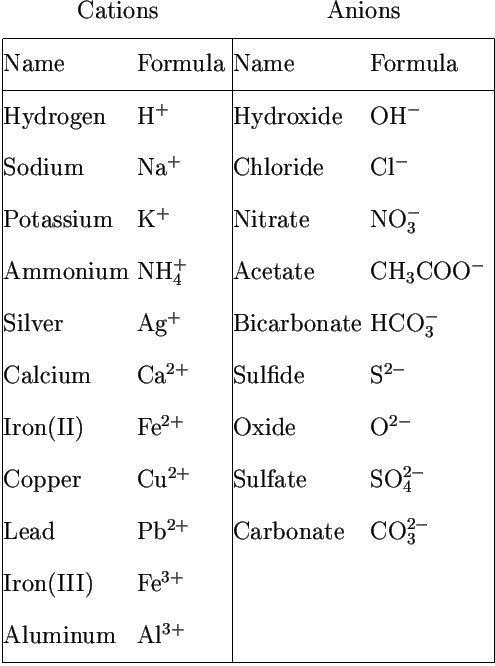
Valency and Radicals
The group of atoms that bears a charge is also called a polyatomic ion. The following radicals are given below:

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
