- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
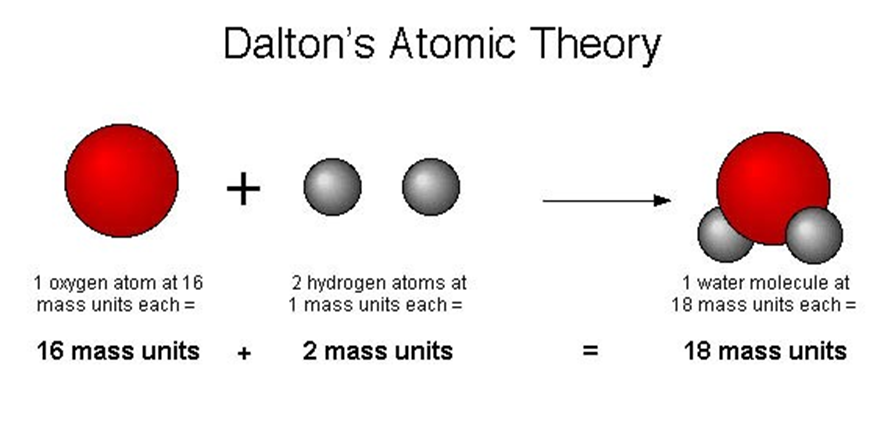
Dalton's Atomic Theory
→ According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter, whether an element, a compound or a mixture is
composed of small particles called atoms.
→ Six Postulates of Dalton's atomic theory:
(i) All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms.
(ii) Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
(iii) Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties. (Law of conservation of mass)
(iv) Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
(v) Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds. (Law of constant proportion)
(vi) The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Atom
Atoms are the smallest particles of an element which can take part in a chemical reaction.
Size of an atom: atomic radius is measured in nanometres.
The atomic symbol has three parts: -
The symbol X: the usual element symbol
The atomic number A: equal to the number of protons
The mass number Z: equal to the total number of protons and neutrons in an element.
Atomic Mass
Atomic mass and atomic mass unit
Atomic mass is the total of the masses of the electrons, neutrons, and protons in an atom, or in a group of atoms, the average mass.
Mass of an atomic particle is called the atomic mass.
This is commonly expressed as per the international agreement in terms of a unified atomic mass unit (AMU).
It can be best defined as 1/12 of the mass of a carbon -12 atom in its ground state.
Molecule
It is the smallest particle of an element or a compound which can exist independently.
• Molecules of an element constitute the same type of atoms.
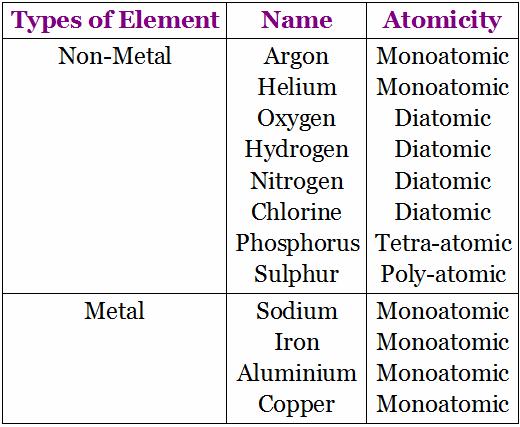
• Molecules may be monoatomic, diatomic or polyatomic.
• Molecules of compounds join together in definite proportions and constitute a different type of atoms.
- Books Name
- Yash Tyagi Coaching Science Book
- Publication
- ACERISE INDIA
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
IUPAC and atomic Symbols
IUPAC and Atomic symbols
IUPAC – International Union Of Pure & Applied Chemistry
The IUPAC approves the names of elements. According to it,
1. Symbol if an element is either the first letter of the name of the element or the first two letters of the name of an element.
2. In case there are two letters, then the first letter is in a capital case and the second letter is in small case.
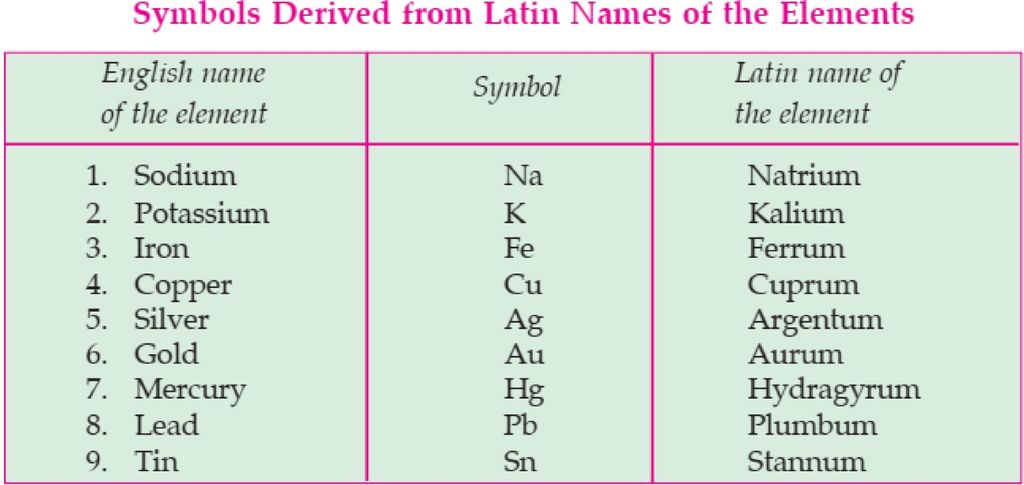
For example- lead is written as “Pb” and not as “pb”. Sometimes, the symbol is derived from the Latin name of an element. For example, if we look at the symbol of Sodium- “Na” and not .So, because it is derived from its Latin name that is, “Natrium”. Similarly, for Potassium, Copper, Iron, Mercury, etc. Latin names and symbols of a few elements are given below:
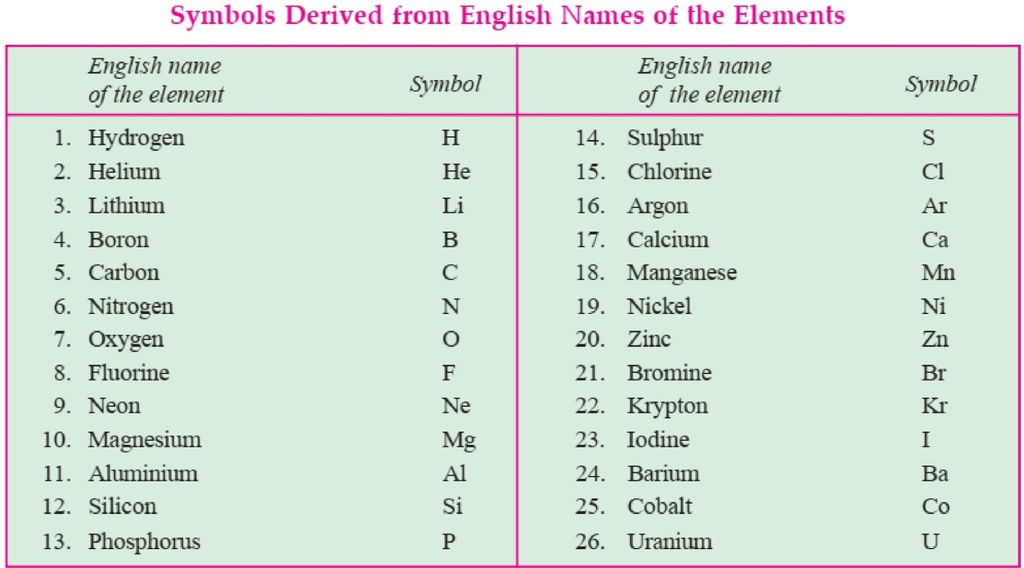
The atomic mass of the element
If we try to find the exact mass of an atom, we can’t find it. The reason being that an atom is too small in size that it is difficult to measure its size and moreover, the size of an atom changes, depending upon its neighbouring- atoms. Therefore, instead of finding its absolute mass, we try to find the relative mass of an atom. The standard element chosen for finding relative mass is carbon-6.
The relative atomic mass of an atom of an element is defined as the average relative mass of an atom as compared to an atom of 612c taken as 12u.
Atomic mass: In simple language, atomic mass is the number of times an atom of an element is heavier than 1/12th of a Carbon atom. For example: If we say that the atomic mass of Sodium is 23, it means that sodium is 23 times heavier than 1/12th of a carbon atom.
Molecule
The particle next to an atom is a molecule, but it has an independent existence and is formed when atoms combine with each other. Let us study about it. A Molecule is the smallest particle of an element or compound which is able to exist independently. For example, carbon dioxide molecule, hydrogen gas molecule, etc . But it has been seen that some molecules are formed by the combination of two atoms of the same kind like H2 and some may have two or more atoms of different kinds like H2O. This shows that in a molecule any number of atoms can be present and they may be of the same or different kinds.

Atomicity: It is the number or the kinds of atoms present in a molecule of an element. Some more examples: Phosphorous exists as P4 (tetra atomic), Sulphur exists as S8 (polyatomic), Nitrogen exists as N2 (diatomic).

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
